Hormonal acne is common in Malaysia and often caused by hormonal changes, menstrual cycles, or PCOS. Breakouts on the jawline and chin affect confidence. Treatments include prescription topicals, oral medications, and in-clinic procedures. Expert guidance ensures safe, personalized care for clearer, healthier skin with lasting results.
What Is Hormonal Acne?
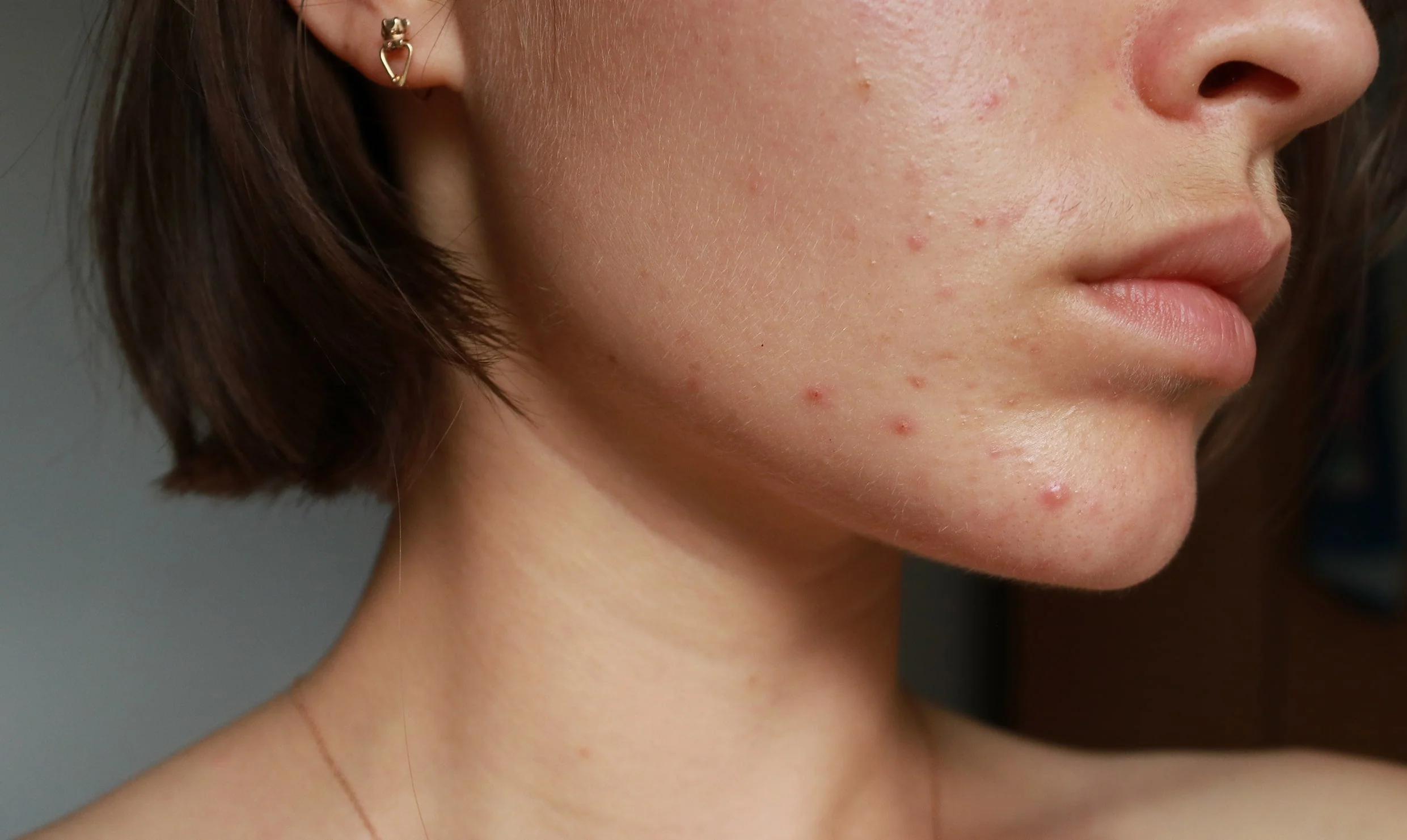
Hormonal acne occurs when hormones affect oil production in the skin. It is most common in adults, especially women aged 20–40.
Unlike regular pimples, hormonal acne:
Appears along the jawline, chin, and lower cheeks.
Can form painful cysts or inflamed nodules.
Often recurs in cycles, linked to hormones.
Main causes include:
Androgen fluctuations: Increase oil and clog pores.
Menstrual cycles: Flare-ups before periods are common.
PCOS or endocrine disorders: Lead to persistent hormonal imbalances.
Lifestyle factors: Stress, poor sleep, and diet can worsen acne.
Tip: Early consultation with a certified aesthetic doctor prevents scarring and long-term skin damage.
Signs You Have Hormonal Acne
Hormonal acne often differs from regular breakouts. Recognizing the signs helps guide effective, targeted treatment. Key indicators include:
Location of Breakouts: Persistent pimples along the jawline, chin, and lower cheeks.
Timing: Flare-ups often worsen before menstruation in women.
Type of Lesions: Deep, painful cysts or nodules rather than surface-level whiteheads or blackheads.
Recurrence: Acne that persists despite over-the-counter treatments.
Associated Symptoms: Conditions like PCOS, irregular periods, or excessive hair growth may indicate underlying hormonal imbalance.
Early recognition and consultation with a certified aesthetic physician are crucial to prevent scarring and achieve long-lasting, clear skin.
Why Self-Treatment Often Fails
Over-the-counter creams may help temporarily, but they cannot fix hormonal imbalances.
Helpful topical support:
Retinoids: Clear clogged pores and improve skin turnover.
Benzoyl peroxide: Reduces acne-causing bacteria.
Non-comedogenic moisturizers: Keep skin hydrated and barrier strong.
Clinical insight: Topicals are supportive but rarely enough for persistent hormonal acne.
Evidence-Based Treatments You Can Find In Malaysia
1. Prescription Topical Treatments
How they work: Retinoids and azelaic acid reduce inflammation and unclog pores.
Timeline: Results in 8–12 weeks.
Side effects: Mild dryness or irritation.
Best for: Mild to moderate acne.
2. Oral Medications
Anti-androgens (Spironolactone): Reduce oil production in women.
Oral contraceptives: Regulate hormonal fluctuations.
Isotretinoin: For severe, cystic, or resistant acne.
Monitoring: Needed to track side effects.
3. In-Clinic Procedures
Chemical Peels: Remove dead skin and reduce inflammation.
Laser/Light Therapy: Targets bacteria and redness.
Microneedling: Reduces scarring and promotes healing.
Pro tip: Combining in-clinic procedures with topical or oral treatments gives the best results.
Lifestyle & Skincare Support
Even with medical treatment, lifestyle matters:
Diet: Low-glycemic and anti-inflammatory foods help.
Stress management: Sleep, exercise, and meditation regulate hormones.
Daily skincare: Gentle cleanser, non-comedogenic moisturizer, and sunscreen.
Hydration: Keeps skin barrier strong and supports healing.
A holistic approach ensures long-lasting skin health.
Tips for Patients in Malaysia
See a certified aesthetic physician: Personalized plans are safer and more effective.
Set realistic expectations: Results take weeks to months; instant fixes don’t exist.
Avoid overuse of OTC products: Harsh scrubs or chemicals can worsen acne.
Track flare patterns: Helps doctors adjust treatments for best results.
FAQ – Hormonal Acne
Q: What is hormonal acne?
A: Acne caused by hormonal changes, usually on the jawline and chin.
Q: Can lifestyle changes alone cure hormonal acne?
A: No, they help but must be combined with medical treatments.
Q: Are oral medications safe?
A: Yes, under supervision from a certified aesthetic physician.
Q: How long until I see results?
A: Topicals: 8–12 weeks; combined therapies: 3–6 months.
Q: Can hormonal acne come back?
A: Yes, due to ongoing hormonal fluctuations. Maintenance therapy helps prevent relapses.
How to Choose the Right Hormonal Acne Clinic in Malaysia
Choosing the right clinic ensures safe, effective, and lasting results. Look for:
Certified doctors: Board-certified or LCP-certified aesthetic physicians experienced in hormonal acne.
Evidence-based treatments: Prescription topicals, oral medications, and in-clinic procedures like chemical peels or lasers.
Personalized care: Tailored plans based on hormonal profile, acne severity, and lifestyle.
Safety & transparency: Clear explanation of benefits, risks, and monitoring for medications or procedures.
Proven track record: Verified patient results and testimonials demonstrating reliable outcomes.
Tip: Avoid clinics promising instant cures. Hormonal acne requires professional, medically supervised care.
GLOJAS Specialist Clinic – Trusted Hormonal Acne Experts
At GLOJAS Specialist Clinic, hormonal acne treatment malaysia combines:
Prescription topicals
Oral medications
Advanced in-clinic procedures
All treatments are tailored by certified aesthetic physicians. Care is safe, personalized, and evidence-based, helping patients achieve clearer, healthier skin with lasting results.
Conclusion
Hormonal acne can affect both appearance and confidence. The most effective approach combines medical treatments, in-clinic procedures, and lifestyle support. Working with a certified aesthetic physician ensures a safe, tailored plan that addresses root causes and promotes long-term skin health.
