Tanam Rambut Malaysia: Panduan Lengkap untuk Rambut Lebat & Sihat
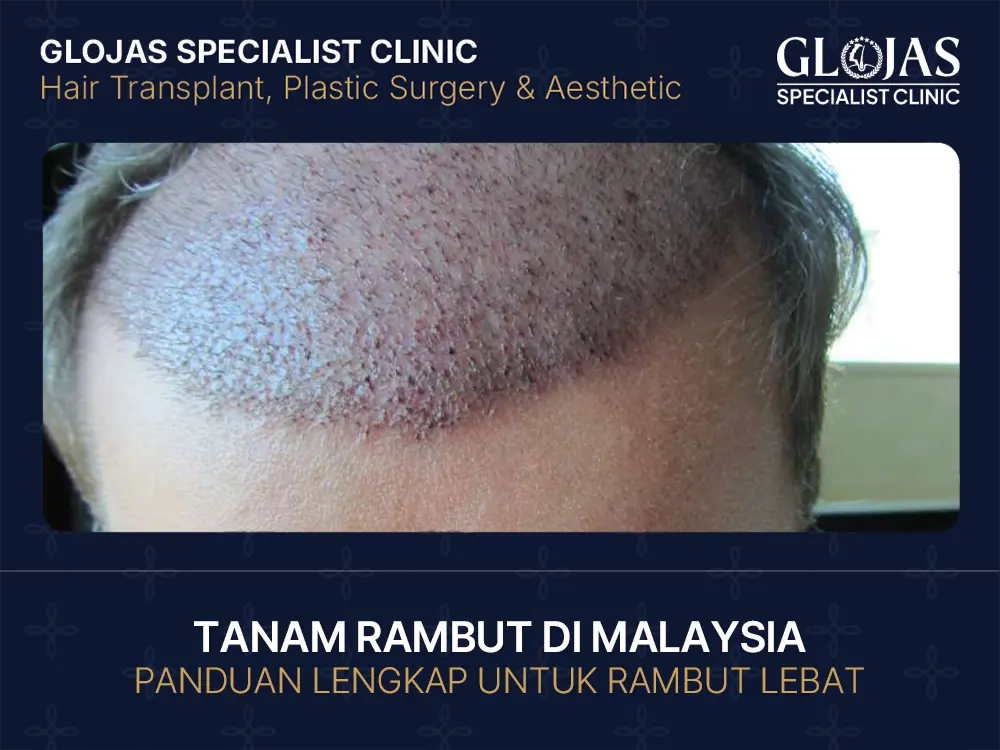
Pernah tak korang rasa kurang yakin bila tengok cermin, nampak dahi makin luas atau rambut makin jarang? Jangan risau, korang tak keseorangan. Isu keguguran rambut adalah perkara biasa, dan berita baiknya, teknologi perubatan sekarang dah makin canggih. Jom kita sembang habis-habisan pasal tanam rambut Malaysia dan macam mana ia boleh ubah penampilan korang! GLOJAS Specialist Clinic merupakan peneraju tanam rambut di Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia dengan teknik SMART™ FUE yang memberikan hasil natural, tanpa parut, dan kadar kemandirian graf setinggi 99.9% oleh pakar bertauliah ABHRS. Apa Itu Tanam Rambut? Definisi dan Konsep Tanam Rambut Tanam rambut, atau dari segi medikalnya dipanggil transplantasi rambut, adalah prosedur memindahkan folikel rambut dari kawasan yang masih lebat (biasanya belakang kepala) ke kawasan yang botak atau nipis. Ia bukan pakai rambut palsu ya, tapi rambut asli korang sendiri! Jenis-jenis Tanam Rambut yang Popular di Malaysia Di Malaysia, terdapat dua teknik utama yang selalu menjadi pilihan iaitu FUE dan FUT. Selain itu, ada juga kaedah DHI (Direct Hair Implantation) yang semakin naik daun kerana hasilnya yang sangat natural dan pemulihan yang pantas. Siapa Calon Sesuai untuk Tanam Rambut? Punca Rambut Gugur dan Kesan pada Lelaki & Wanita Banyak faktor yang buat rambut gugur—genetik, stres, perubahan hormon, atau kekurangan nutrisi. Bagi lelaki, selalunya berpunca daripada Male Pattern Baldness. Wanita pula biasanya mengalami penipisan di bahagian tengah. Masalah ini bukan sahaja menjejaskan rupa, tapi juga kesihatan mental dan keyakinan diri. Penilaian Klinikal sebelum Prosedur Bukan semua orang boleh terus buat transplant. Korang perlu ada “kawasan penderma” yang cukup sihat. Doktor akan periksa tahap keguguran mengikut skala Norwood (untuk lelaki) atau Ludwig (untuk wanita) sebelum memberi lampu hijau. Teknik & Kaedah Tanam Rambut FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) Ini teknik paling favourite di Malaysia. Folikel rambut diambil satu demi satu menggunakan alat khas. Kesannya? Tiada parut panjang, kurang sakit, dan korang boleh balik kerja dalam masa singkat. FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation) FUT melibatkan pengambilan jalur kulit dari belakang kepala. Walaupun kedengaran agak ngeri, teknik ini sangat berkesan untuk mereka yang memerlukan jumlah graf rambut yang banyak dalam satu sesi. Teknologi Terkini dan Robotik dalam Tanam Rambut Zaman sekarang dah ada bantuan robotik seperti sistem ARTAS. Teknologi ini membantu doktor memilih folikel terbaik dengan ketepatan tinggi, meminimumkan kesilapan manusia. Untuk memahami lebih lanjut mengenai piawaian keselamatan, korang boleh rujuk garis panduan dari Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia (KKM) bagi memastikan pusat perubatan adalah berdaftar. Proses & Langkah Tanam Rambut di Klinik Malaysia Konsultasi Awal dan Pemeriksaan Kulit Kepala Langkah pertama mestilah jumpa pakar. Doktor akan guna alat trichoscope untuk tengok kesihatan kulit kepala korang. Penting untuk pilih doktor yang berdaftar dengan Majlis Perubatan Malaysia (MMC) supaya prosedur korang selamat dan sah dari segi undang-undang. Persediaan Sebelum Prosedur Biasanya, korang kena berhenti ambil ubat cair darah, berhenti merokok, dan jangan ambil kafein sehari sebelum prosedur. Rambut juga mungkin perlu dipotong pendek mengikut keperluan teknik yang dipilih. Prosedur Tanam Rambut: Apa yang Perlu Dijangka Prosedur ini mengambil masa antara 4 hingga 8 jam bergantung kepada jumlah graf. Korang akan diberi bius setempat (local anesthesia), jadi korang akan sedar tapi tak rasa sakit. Boleh layan Netflix atau dengar lagu sambil doktor buat kerja! Pemulihan dan Penjagaan Selepas Tanam Rambut Selepas prosedur, kawasan tanam akan nampak berkerak sedikit. Jangan gatal tangan nak kopek! Gunakan syampu khas dan elakkan aktiviti berat selama seminggu. Korang boleh baca tips penjagaan rambut dan kulit kepala untuk pastikan folikel baru tu “pegang” dengan kuat. Kos Tanam Rambut di Malaysia Faktor Menentukan Harga Harga biasanya dikira mengikut jumlah graf (per graft). Lagi luas kawasan botak, lagi banyak graf diperlukan, maka lagi tinggilah kosnya. Pengalaman doktor dan teknologi yang digunakan juga memainkan peranan. Perbandingan Kos di Klinik Tempatan Di Malaysia, kos purata adalah sekitar RM5 ke RM12 per graft. Secara kasar, bajet yang perlu ada adalah antara RM8,000 hingga RM20,000. Walaupun nampak mahal, ia adalah pelaburan seumur hidup berbanding rawatan bulanan yang belum tentu berkesan. Risiko, Kesan Sampingan & Keselamatan Kesan Sampingan yang Biasa Antara kesan biasa termasuklah bengkak di dahi, gatal-gatal, dan “shock loss” (rambut asal luruh sekejap sebelum tumbuh baru). Jangan panik, ini semua normal dan bersifat sementara. Bagaimana Memastikan Prosedur Selamat Pastikan klinik mempunyai sijil LCP (Letter of Credentialing and Privileging) bagi tujuan estetik. Korang juga boleh menyemak senarai pakar kulit di laman Persatuan Dermatologi Malaysia (PDM) untuk mendapatkan pendapat kedua yang lebih pakar. Kejayaan & Testimoni Pesakit Keputusan Sebelum dan Selepas Hasil penuh biasanya nampak selepas 9 hingga 12 bulan. Rambut baru akan tumbuh secara berperingkat dan kelihatan sangat natural sehingga orang tak perasan korang pernah buat transplant! Kisah Pesakit dari Malaysia Ramai rakyat Malaysia, termasuk selebriti dan influencer, dah mula terbuka berkongsi perjalanan mereka. Majoritinya berpuas hati kerana bukan saja rupa berubah, tapi rasa lebih yakin bila berhadapan dengan orang ramai. Soalan Lazim Tentang Tanam Rambut Tempoh Pertumbuhan Rambut Selepas Prosedur Rambut baru biasanya mula keluar pada bulan ke-3. Pada bulan ke-6, korang akan nampak perubahan ketara, dan hasil vavavoom akan muncul selepas setahun. Kekerapan Rawatan Susulan Biasanya hanya perlu 1 atau 2 kali susulan untuk doktor pantau pertumbuhan. Selepas itu, korang bebas nak potong atau gaya rambut macam biasa. Pilihan Alternatif Tanpa Pembedahan Kalau belum sedia nak bedah, ada pilihan lain seperti ubat Minoxidil atau rawatan Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) yang menggunakan darah sendiri untuk kuatkan akar rambut.
Hair Transplant Procedure Step-by-Step in Malaysia: What to Expect
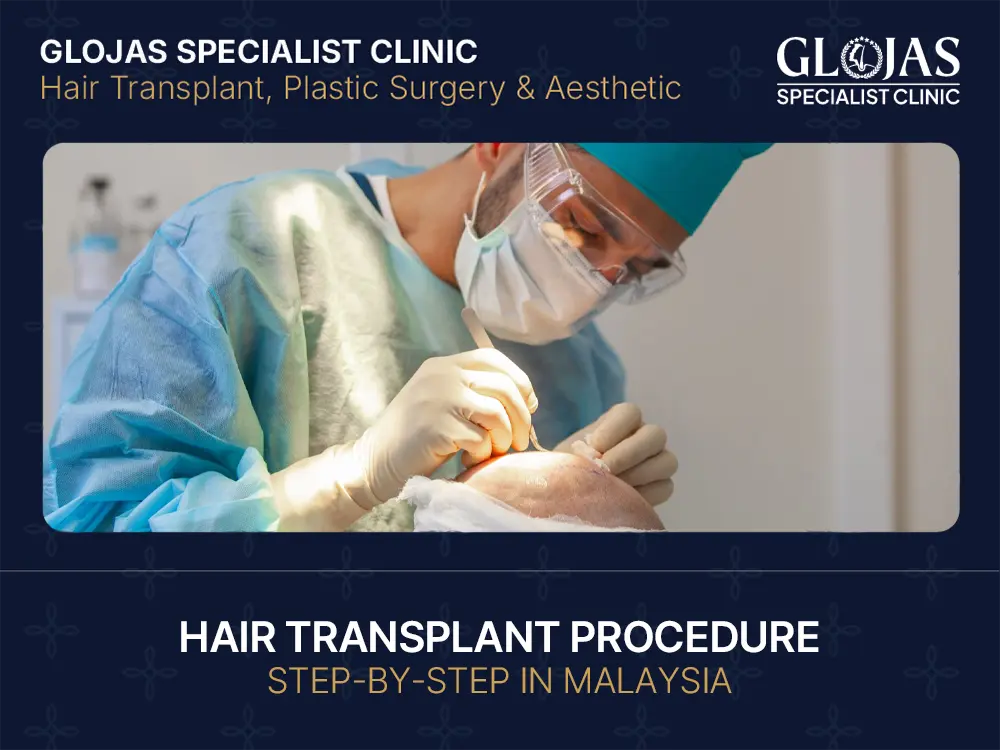
How Does a Hair Transplant Procedure Actually Works? If you’ve been spending more time staring at your receding hairline in the mirror than you’d like to admit, you aren’t alone. Hair loss is a common journey for many Malaysians, but thanks to modern technology, it doesn’t have to be a permanent one. Malaysia has become a hub for high-quality, affordable hair restoration. In this guide, we’re breaking down exactly what happens during a hair transplant so you can walk into the clinic feeling like a pro. Summary of Hair Transplant Procedure Think of a hair transplant as “relocating” your assets. We take healthy, permanent hair follicles from the back or sides of your head (the donor area) and move them to the thinning spots (the recipient area). It’s a meticulous process, but the results are designed to last a lifetime. Quick Overview of Hair Transplant Procedure’s Step Preparation: Prepping the donor site. Harvesting: Extracting the “seeds” (follicles). Design: Mapping out your new look. Implantation: Planting the follicles into the thinning areas. Aftercare: Ensuring everything heals perfectly. Typical Duration and What to Expect Most procedures take between 4 to 8 hours, depending on how many grafts you need. You’ll be awake the whole time—usually catching up on Netflix or chatting with the medical team. While it is a surgery, the local anesthesia ensures you won’t feel a thing during the actual process. Step 1: Donor Area Preparation The journey begins at the back of your head. This area is genetically resistant to balding, making it the perfect “nursery” for new hair. Cleaning and Numbing the Donor Area First, the medical team thoroughly cleans the scalp to prevent infection. Then, they apply a local anesthetic. You might feel a tiny pinch from the needle, but within minutes, the area will be completely numb. According to the International Society of Hair Restoration Surgery, patient comfort is a top priority in modern clinics. Marking the Donor Sites The surgeon will then mark the specific zone where they’ll be taking the hair. This ensures they don’t over-harvest, keeping your donor area looking thick and natural even after the hair is moved. Step 2: Harvesting Hair Follicles This is where the magic (and the science) happens. There are two main ways to get those follicles out. Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) Method FUE is the most popular choice in Malaysia. The surgeon uses a tiny “punch” tool to pluck individual hair follicles one by one. The best part? There’s no linear scarring, making it ideal if you like to keep your hair short. Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) Method Also known as the “strip method,” this involves removing a small strip of skin from the donor area. The follicles are then dissected under a microscope. While it leaves a thin scar, it’s often more efficient for patients needing a massive number of grafts in one session. You can learn more about the technical differences from the American Academy of Dermatology. Step 3: Recipient Area Preparation Now that we have the “seeds,” we need to prepare the “soil.” Designing Hairline and Implant Sites This is the artistic part. Your surgeon will draw your new hairline, taking into account your face shape and age. A good surgeon knows that a “straight line” looks fake; they aim for a slightly irregular, natural-looking hairline that blends seamlessly with your existing hair. Local Anesthesia Application Just like with the donor area, the recipient site gets numbed up. Once the “freeze” kicks in, you’re ready for the final stage. Step 4: Implanting Hair Follicles This step requires the precision of a jeweler. Creating Recipient Site Channels The surgeon creates tiny incisions (channels) in the thinning areas. The angle and depth of these channels are crucial because they determine the direction your new hair will grow. If they aren’t angled correctly, the hair won’t look natural. Placing Hair Follicles with Precision The extracted follicles are then carefully placed into these channels. The team ensures the density is consistent so you don’t end up with patchy spots. This stage often takes the longest because of the sheer level of detail involved. Step 5: Immediate Post-Procedure Care You’re done! But the next 48 hours are vital for the survival of those new grafts. Cleaning and Dressing the Scalp The staff will gently clean your scalp and apply a light dressing or ointment. Some clinics provide a specialized headband to help reduce forehead swelling, a common and temporary side effect mentioned by WebMD. Instructions for First 24–48 Hours You’ll receive a “survival kit” with saline sprays and specific washing instructions. The golden rule? Don’t touch or scratch the grafts. They need time to firmly anchor themselves into their new home. Most patients are back to light work within 2 to 3 days, though you’ll want to avoid heavy gym sessions for a couple of weeks, as recommended by the Mayo Clinic. Conclusion Getting a hair transplant in Malaysia is a straightforward, safe, and life-changing decision for many. By understanding the step-by-step process—from the initial numbing to the final placement—you can approach your procedure with confidence.
Sapphire Hair Transplant In Malaysia: Benefits, Cost, Results
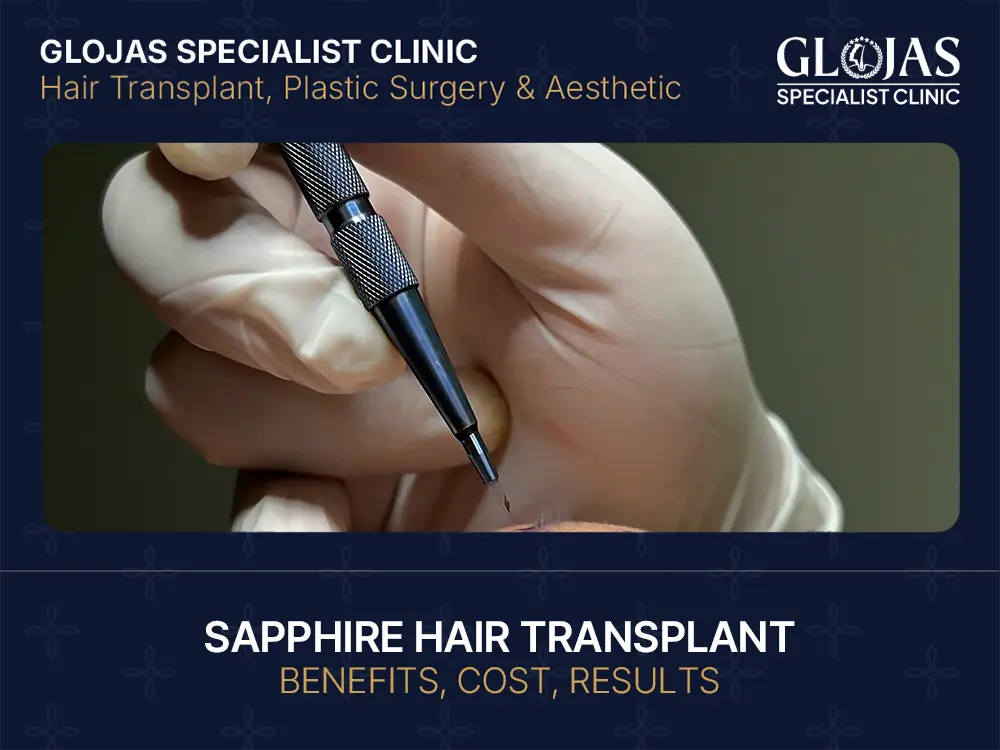
Dealing with a receding hairline or thinning crown can be a total confidence killer. If you’ve been scrolling through social media looking at hair restoration “glow-ups,” you’ve likely bumped into the term Sapphire FUE. It’s currently the gold standard in Malaysia for those wanting a natural look with faster healing. Let’s break down why this tech is changing the game for hair loss in KL and beyond. What Is Sapphire Hair Transplant? At its core, a Sapphire hair transplant is a refined version of the Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) method. The “secret sauce” isn’t in the hair itself, but in the tools used. Instead of standard steel blades, surgeons use blades made from sapphire gemstone. This might sound fancy, but it’s actually about precision and skin health. How Saphhire Hair Transplant Differs from Traditional FUE In a traditional FUE, steel blades are used to create the tiny slits (channels) where the hair follicles go. Sapphire blades are much sharper, smoother, and more durable. Because sapphire is a gemstone, it allows for V-shaped incisions rather than the U-shaped ones made by steel. This means the incisions are smaller, leading to less trauma to your scalp. Benefits of Sapphire Blades in Hair Transplant Higher Density: Because the incisions are tiny, surgeons can place grafts closer together for a thicker look. Less Scabbing: Smaller wounds mean your head won’t look like a construction zone for as long. Natural Direction: The precision of the blade allows the doctor to mimic your natural hair growth angle perfectly. Antibacterial Properties: Sapphire is non-reactive, which reduces the risk of infection during the healing process. Who Is an Ideal Candidate for Sapphire Hair Transplant In Malaysia? While it’s a brilliant tech, it isn’t a “magic wand” for everyone. You need a healthy donor area—usually the back or sides of your head—to provide the hair. Men vs. Women: Hair Loss Patterns Men usually deal with androgenetic alopecia, which creates that classic “M” shape or a bald spot on top. Women often see thinning along the part line. Sapphire FUE works for both, though women often prefer it because it allows for high-density filling without a “pluggy” look. Age and Hair Density Considerations Most experts suggest waiting until your hair loss pattern has stabilized (usually mid-20s or older). If you go too early, you might lose more natural hair behind the transplant, leaving you with a weird “island” of hair. The Sapphire Hair Transplant Procedure Step by Step Ready to take the plunge? Here’s what a typical day at a Malaysian clinic looks like. Initial Consultation and Assessment Your surgeon will use a high-powered camera to check your scalp. They’ll measure your graft count—basically, how many “hairs” they need to move from the back to the front. Donor Hair Extraction Techniques Under local anesthesia, individual hair follicles are removed one by one. This is the “extraction” phase. The goal is to leave the back of your head looking totally normal even after taking a few thousand hairs. Hair Graft Implantation with Sapphire Blades This is where the magic happens. The surgeon uses the sapphire blade to create the channels. Then, the extracted follicles are meticulously placed into these tiny slots. Expected Procedure Duration Expect to spend a full day at the clinic. Most sessions take between 6 to 8 hours. You can usually watch Netflix or listen to a podcast while the team works. Recovery and Aftercare Tips The first week is crucial. You’ll be given a special headband to prevent swelling and a specific way to wash your hair. Post-Transplant Care Guidelines You’ll need to sleep with your head elevated for a few nights and avoid heavy exercise. According to the International Society of Hair Restoration Surgery (ISHRS), following post-op instructions is just as important as the surgery itself for long-term graft survival. Timeline for Hair Growth and Results Weeks 2-4: The “Shock Loss” phase. The transplanted hair falls out. Don’t panic! The roots are still safe inside. Months 3-4: New sprouts begin to appear. Months 12-18: Full, thick results. Managing Side Effects and Complications Minor swelling or itching is common. Some people get “folliculitis” (little pimples) as the hair breaks through the skin. A quick check-in with your clinic usually clears this up with a simple cream. Results and Long-Term Effectiveness Once those hairs take root, they are yours for life. These follicles are genetically resistant to the hormones that cause balding. Comparing Sapphire Hair Transplant vs. Standard FUE Feature Standard FUE Sapphire FUE Blade Material Surgical Steel Sapphire Gemstone Incision Shape U-Shaped (slighter wider) V-Shaped (ultra-fine) Graft Density Moderate Very High Healing Time 10–14 days 5–7 days Risk of Infection Standard Reduced (gemstone is non-reactive) Maintaining Healthy Hair After Transplant Even though the new hair is permanent, your old hair can still fall out. Many doctors recommend FDA-approved hair loss treatments like Minoxidil or Finasteride to keep your native hair strong. Cost of Sapphire Hair Transplant in Malaysia Malaysia is a massive hub for medical tourism because you get world-class quality at a fraction of the price found in the US or UK. Factors Affecting Price Graft Count: More baldness = more grafts = higher price. Typical costs in Malaysia range from RM 6,000 to RM 25,000. Surgeon’s Experience: High-end clinics in Bangsar or Mont Kiara might charge a premium for their expertise. Technology: Sapphire blades are more expensive than steel, so expect a slightly higher price tag than basic FUE. Financing and Packages Available Many clinics offer 0% interest installment plans or “all-in” packages that include your meds, post-op washes, and even hotel stays if you’re flying in from overseas. Choosing the Right Hair Transplant Clinic in Malaysia Don’t just go for the cheapest option. Your hair is an investment in your face! Credentials of a Certified Hair Surgeon In Malaysia, look for doctors who are LCP (Letter of Credentialing and Privileging) certified by the Ministry of Health. Membership in the American Board of Hair Restoration Surgery (ABHRS) is a huge plus for credibility. Patient
Is Hair Transplant in Malaysia Worth It? Complete Guide (2026)

Dealing with a receding hairline or a thinning crown can be a hit to your confidence. If you’ve spent hours in front of the mirror wondering where your hair went, you aren’t alone. Fortunately, Malaysia has become a global hub for high-quality, affordable hair restoration. In this guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about getting a hair transplant Malaysia, from costs to the latest tech. What Is a Hair Transplant? At its core, a hair transplant is a surgical technique that moves hair follicles from a part of the body with plenty of hair (the donor site) to a bald or thinning part (the recipient site). It’s not “new” hair; it’s just your existing hair being redistributed to where you need it most. How Hair Transplant Works (Donor to Recipient Process) The process relies on “donor dominance.” Hair follicles at the back and sides of your head are genetically resistant to DHT (dihydrotestosterone), the hormone responsible for male pattern baldness. When these follicles are moved to the front or crown, they keep that resistance and continue to grow naturally. Is Hair Transplant Permanent? Yes! Because the transplanted follicles are taken from DHT-resistant zones, they are intended to grow for a lifetime. While your non-transplanted hair might continue to thin over time, the “new” hair is there to stay. Types of Hair Transplant Procedures in Malaysia Malaysia offers some of the most advanced techniques in the world. Choosing the right one depends on your budget and how much downtime you can afford. FUE Hair Transplant (Follicular Unit Extraction) This is the most popular method. Doctors extract individual hair follicles one by one using a micro-punch tool. It leaves tiny, dot-like scars that are virtually invisible, even with short hair. DHI Hair Transplant (Direct Hair Implantation) DHI is a modified version of FUE. Instead of creating channels first and then placing grafts, a specialized tool called a “Choi Implanter Pen” does both at once. This often results in higher graft survival rates and a more natural-looking density. FUT Hair Transplant (Strip Method) FUT involves removing a small strip of scalp from the back of the head. The strip is then divided into individual grafts under a microscope. While it leaves a linear scar, it’s often cheaper and better for patients needing a massive number of grafts in one session. Sapphire FUE vs Standard FUE In Sapphire FUE, the blades used to create incisions are made from sapphire (a gemstone) rather than steel. This allows for smaller, more precise incisions, leading to faster healing and less scabbing. Robotic Hair Transplant – Is It Available in Malaysia? Yes, some high-end clinics in Kuala Lumpur utilize the ARTAS Robotic System. It uses AI to identify and extract the best donor hairs, reducing human error and fatigue during long procedures. Who Is a Suitable Candidate for Hair Transplant? Not everyone is a candidate. You need a stable supply of donor hair and realistic expectations. Male Pattern Baldness: Most men with clear “Norwood Scale” recession are great candidates. Female Hair Loss: Women often experience diffuse thinning, so a doctor must ensure the donor area is stable. Receding Hairline: Perfect for those looking to “lower” their forehead. Crown & Vertex: Requires a high number of grafts to achieve dense coverage. Beard, Eyebrow & Body Hair: You can actually move hair from your chest or beard to your head (or vice versa)! Hair Transplant Procedure Step-by-Step 1. Consultation & Assessment The doctor uses a trichoscope to check your hair density. According to the International Society of Hair Restoration Surgery (ISHRS), a proper diagnosis is the most critical step to ensure you aren’t suffering from an underlying medical condition. 2. Donor Area Preparation The back of your head is usually shaved (though “no-shave” FUE is an option) and numbed with local anesthesia. 3. Graft Extraction & Implantation Grafts are carefully pulled and kept in a specialized cooling solution. The doctor then designs your hairline—this is where the “artistry” comes in—and implants the grafts at the correct angle and depth. 4. Duration Expect to spend 4 to 8 hours in the clinic. Most places provide lunch and let you watch Netflix during the process! Hair Transplant Before and After Results Hair Growth Timeline (1–12 Months) Month 1: The “Ugly Duckling” phase. Most transplanted hair falls out (this is normal!). Months 3-4: New, fine hairs start to poke through. Months 6-9: Significant thickening and length. 1 Year: Full, final results. Note: Don’t panic when you see shedding. The follicle is still alive under the skin; it’s just hitting the “reset” button. Hair Transplant Recovery & Aftercare Recovery is surprisingly quick. Most people return to office jobs within 3 to 5 days. Washing: You’ll be given a special shampoo and taught how to gently “tap” your head rather than rub it. Exercise: Avoid heavy lifting for at least 2 weeks to prevent blood pressure spikes that could “pop” the grafts. Sleep: Use a travel pillow to keep your head elevated for the first few nights to reduce swelling. Risks, Side Effects & Complications While safe, it is still a surgical procedure. Common side effects include: Swelling: Usually around the forehead and eyes. Shock Loss: Temporary thinning of original hair due to the “trauma” of surgery. Infection: Rare, but possible if aftercare isn’t followed. Always check the Ministry of Health Malaysia (MOH) website to ensure your clinic is licensed. Hair Transplant Cost in Malaysia Malaysia is significantly cheaper than the US or UK but offers similar (or better) medical standards. Factor Estimated Cost (MYR) Average Price RM 8,000 – RM 25,000 Cost Per Graft RM 5 – RM 12 Malaysia vs. The World: While Turkey is famous for “hair mills” at rock-bottom prices, Malaysia offers a safer middle ground with board-certified doctors and highly regulated private hospitals. Choosing the Best Hair Transplant Clinic in Malaysia Don’t just go for the cheapest price. Look for: LCP Certification: In Malaysia, aesthetic doctors must have a Letter of Credentialing and Privileging. Case Studies:
Understanding the Shedding Phase: What to Expect Post-Transplant

It is the moment every hair transplant patient dreads: a few weeks after your procedure, the hair you just paid for starts falling out. Before you panic, take a deep breath. This is a normal, healthy part of the recovery process. What Is the Shedding Phase (Shock Loss)? Definition and Overview The “Shedding Phase,” medically known as telogen effluvium (or shock loss), is the temporary loss of newly transplanted hair or existing hair near the recipient site. It is a transitional phase and does not mean the transplant has failed. Why It Happens After a Hair Transplant In Malaysia Hair follicles are highly sensitive. The process of moving them from one part of the scalp to another—along with the local anesthesia and tiny incisions—shocks the follicles. In response, they enter a “resting state” and shed the hair shaft to prepare for new growth. Timeline of the Shedding Phase When Shedding Typically Starts Most patients notice shedding between 2 to 8 weeks post-surgery. You might see hairs on your pillow, in the shower, or in your hands when you apply topical treatments. Duration of the Shedding Phase This phase usually lasts for about 2 to 4 weeks. By the end of the third month, the shedding should stop entirely as the follicles begin their new growth cycle. What Happens to Hair Follicles During This Time The hair shaft falls out, but the follicle bulb remains safely tucked under the skin. Think of it like a plant losing its leaves in winter; the roots are still alive and healthy beneath the surface. Causes of Shock Loss Trauma to Hair Follicles During Transplant Even with the most advanced DHI or FUE techniques, the follicle experiences “intubation” trauma and a temporary lack of oxygen while outside the body. For more on how follicles react to surgery, the International Society of Hair Restoration Surgery (ISHRS) provides detailed clinical breakdowns. Stress or Scalp Inflammation The physical stress of surgery and the natural inflammatory response of the scalp can trigger nearby non-transplanted hairs to shed as well. This is why some patients notice thinning in areas that weren’t even touched. Temporary Hair Cycle Disruption Hair grows in cycles: Anagen (growth), Catagen (transition), and Telogen (resting). The surgery forces a large number of follicles into the Telogen phase simultaneously, resulting in a synchronized shed. Who Is Most Likely to Experience Shock Loss? Factors Like Age and Hair Type Patients with very fine hair or those undergoing a transplant while their hair loss is still actively progressing are slightly more prone to shock loss. Extent of Hair Transplant and Technique Used Large sessions (over 3,000 grafts) create more “trauma” to the scalp, which may increase the likelihood of temporary shedding compared to smaller, targeted sessions. How to Manage the Shedding Phase Proper Post-Transplant Care The key is to avoid “mechanical” trauma. Do not scratch the itchy areas or pick at scabs, as this can dislodge the graft before it has fully anchored (which takes about 10 days). Products and Medications That Help Doctors often recommend Minoxidil or Finasteride to maintain existing hair and speed up the regrowth of transplanted follicles. Always consult your surgeon before starting these. You can check the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) for safety guidelines on hair loss medications. Lifestyle Tips to Support Hair Regrowth Nutrition: Eat a diet rich in Biotin, Zinc, and Iron. Hydration: Keep your scalp hydrated from the inside out. Rest: Avoid strenuous exercise for at least 14 days to keep blood pressure stable. When to Be Concerned About Hair Shedding Signs of Abnormal or Excessive Hair Loss If you see redness that doesn’t go away, pus-filled bumps (folliculitis), or if the shedding is accompanied by severe pain, these could be signs of an infection rather than standard shock loss. When to Contact Your Surgeon If you are still shedding heavily past the 4-month mark, or if the scalp appears “patchy” in the donor area, schedule a follow-up. Reputable clinics, like those registered with the Malaysian Medical Council (MMC), will offer free post-op reviews. Expected Hair Regrowth After Shock Loss Initial New Hair Growth Timeline Months 3–4: Fine, “peach fuzz” hairs begin to emerge. Months 6–9: Hair becomes thicker, darker, and more visible. Full Results and Patience Tips Full results take 12 to 18 months. The best tip? Stop checking the mirror every hour! Take one photo a month to track your progress accurately. Tips to Minimize Shedding After a Hair Transplant Choosing the Right Technique (FUE, DHI, FUT) DHI (Direct Hair Implantation) is often associated with less shock loss because the follicles spend less time outside the body. To learn more about technique safety, visit the American Board of Hair Restoration Surgery (ABHRS). Gentle Hair Care Practices Use a sulfate-free, pH-balanced shampoo. When drying, pat your hair gently with a microfiber towel—never rub. Supporting Scalp Health Some clinics in Malaysia offer PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) therapy alongside the transplant to nourish the scalp and minimize the severity of shock loss. You can find accredited providers via the Malaysian Society of Aesthetic Medicine (MSAM).
DHI Hair Transplant Explained: Everything You Need to Know
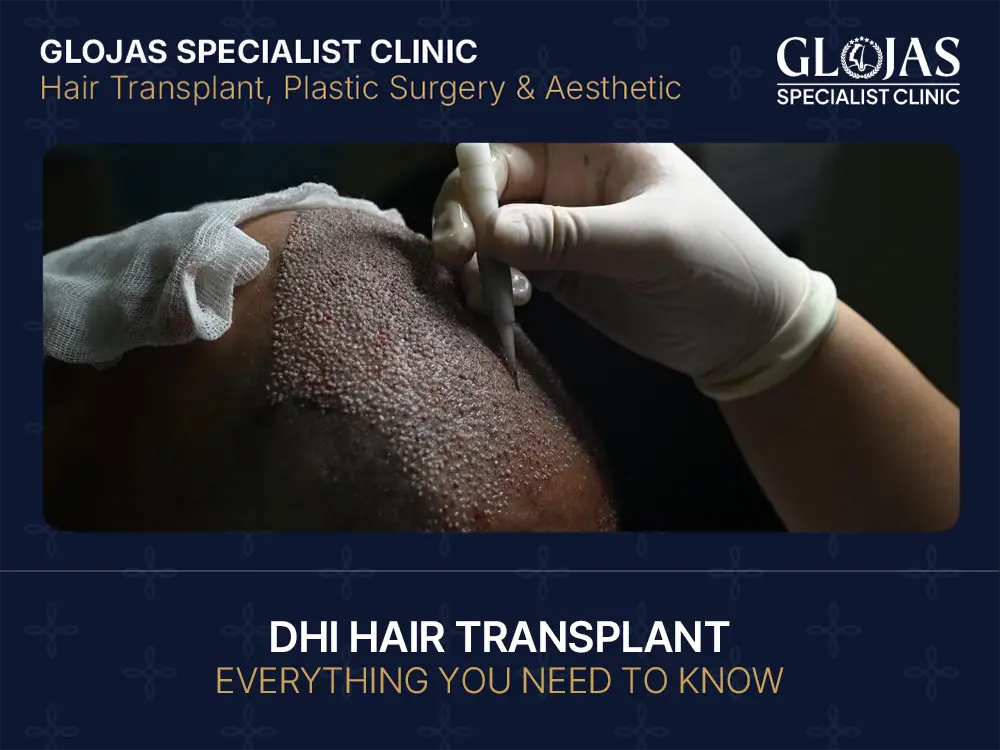
When it comes to permanent hair restoration, Direct Hair Implantation (DHI) is often called the “Gold Standard.” If you’re researching hair transplant in Malaysia, you’ve likely seen this term everywhere. This guide breaks down exactly what DHI is, how it works, and why it has become the preferred choice for those seeking a natural, high-density look. GLOJAS Specialist Clinic offers advanced FUE hair transplant procedures using minimally invasive techniques to restore natural hair growth with precision, safety, and long-lasting results. What Is DHI Hair Transplant? Definition and Overview of DHI Technique DHI stands for Direct Hair Implantation. It is a modified version of the FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) technique. In a DHI procedure, hair follicles are extracted from the donor area (usually the back of the head) and then implanted directly into the thinning areas using a specialized, pen-like device. How DHI Differs from FUE and FUT The primary difference lies in the implantation phase. FUT (Strip Method): A strip of scalp is removed, which leaves a linear scar. FUE: The surgeon manually creates “channels” (tiny holes) in the scalp first, then places the grafts into them using forceps. DHI: There is no “channel opening” step. The specialized tool creates the site and places the follicle at the same time, leading to less trauma and higher precision. How the DHI Procedure Works The beauty of DHI is its streamlined process, often referred to as a “one-step” implantation. Step 1: Donor Hair Extraction Using a micro-punch tool, the surgeon removes individual hair follicles from the donor site. These follicles are kept in a specialized nutrient solution to maintain their vitality while they wait to be implanted. Step 2: Implantation Using the Choi Pen This is where the magic happens. The surgeon loads the follicles into a Choi Implanter Pen. This tool allows the doctor to control the depth, angle, and direction of every single hair with extreme accuracy. Step 3: Growth and Recovery Because the incisions are so small, the scalp begins healing almost immediately. Within a few days, the tiny scabs wash away, and the follicles begin their new life cycle. Benefits of DHI Hair Transplant Minimally Invasive Procedure Since DHI doesn’t require a scalpel or stitches, it is significantly less “bloody” than traditional methods. The risk of infection is lower, and there is no visible scarring. Natural Hair Growth and Density Because the Choi Pen allows for closer placement of follicles, DHI can achieve a much higher density than FUE. This is especially important for the hairline, where the direction of growth must look 100% natural. Who Is a Suitable Candidate for DHI? Ideal Hair Loss Patterns DHI is perfect for those with: Receding hairlines. Thinning at the crown. Female pattern hair loss (where “shaving the head” is not an option). Age and Health Considerations Surgeons typically recommend waiting until age 25 so that hair loss patterns have stabilized. You should also be in good general health, as conditions like uncontrolled diabetes can slow down the healing process. According to the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD), a thorough medical evaluation is the first step for any hair restoration journey. Expectations and Realistic Results DHI can restore coverage, but it cannot create “infinite” hair. Your results depend on the quality of your donor area. Risks and Considerations Possible Side Effects and Complications While safe, DHI is still a medical procedure. Temporary side effects include: Shock Loss: Temporary shedding of existing hair (this is normal!). Swelling: Usually around the forehead for 3–5 days. Itching: A sign of the skin healing. Importance of Choosing a Qualified Surgeon The “Choi Pen” requires a high level of manual skill. In Malaysia, ensure your doctor is registered with the Malaysian Medical Council (MMC) and holds an LCP (Letter of Credentialing and Privileging) for aesthetic medical practice. Average Cost of DHI Hair Transplant In Malaysia Factors Affecting Price The cost is usually calculated per graft. Factors include: The total number of grafts needed. The surgeon’s experience level. The complexity (e.g., a “No-Shave” procedure costs more). Average Costs in Malaysia In 2026, the average cost for a DHI procedure in Malaysia ranges from RM 9,000 to RM 25,000. While this is higher than standard FUE, the increased survival rate of the grafts (often 95%+) provides better long-term value. For global price comparisons, you can refer to the International Society of Hair Restoration Surgery (ISHRS). Aftercare and Recovery Tips Post-Procedure Care Guidelines First 48 Hours: Do not touch the grafts. Sleep with your head elevated. Day 3: Begin gentle washing with the clinic-provided shampoo. Week 2: You can resume light exercise, but avoid swimming or heavy weights. Expected Hair Growth Timeline Months 1-3: The “Shedding Phase.” Don’t panic! Months 4-6: New “baby” hairs begin to appear. Month 12: Full, thick results are visible. Choosing the Right Clinic for DHI Hair Transplant Checking Credentials and Experience Look for clinics that specialize specifically in hair. Ensure the procedure is doctor-led, not performed entirely by technicians. Organizations like the Malaysian Society of Aesthetic Medicine (MSAM) can help you find reputable practitioners. Patient Reviews and Before/After Results Always ask for high-resolution photos of past patients. Check independent platforms like Google Reviews to see how the clinic handles long-term follow-ups. For more tips on patient safety, visit the Ministry of Health (MOH) Malaysia website.
How to Choose a Safe Hair Transplant Clinic in Malaysia
How to Choose a Safe Hair Transplant Clinic in Malaysia? Choosing to restore your hair is a big step toward regaining your confidence. In Malaysia, the hair restoration industry is booming, but with that growth comes the responsibility of being a savvy patient. This guide will help you navigate the process of finding a clinic that prioritizes your safety as much as your results. Why Clinic Safety Matters for Hair Transplant Procedures A hair transplant isn’t just a “beauty treatment”; it is a surgical procedure that involves hundreds of tiny incisions. When safety protocols are ignored, you aren’t just risking your money—you’re risking your health. Medical Risks of Unsafe Hair Transplants Choosing a “black market” or unlicensed clinic can lead to severe medical complications. Without proper medical oversight, patients may face systemic infections, severe allergic reactions to anesthesia, or even permanent nerve damage. According to the International Society of Hair Restoration Surgery (ISHRS), the rise of unlicensed technicians performing surgery is a global concern that often leads to botched results. Long-Term Impact on Hair Growth and Scalp Health Safety isn’t just about avoiding infection; it’s about the survival of your hair. Poor graft handling can lead to “transection,” where the hair follicle is killed before it’s even planted. This results in patchy growth and permanent scarring, often leaving the donor area (the back of your head) too depleted for any future corrective surgery. Verify Medical Credentials and Licensing In Malaysia, the Ministry of Health (MOH) has strict regulations to protect patients. Don’t be shy about asking to see paperwork! Malaysian Medical Council (MMC) Registration Every practicing doctor in Malaysia must be registered with the Malaysian Medical Council. You can actually verify a doctor’s status yourself through the MeRITS database. If the person performing your surgery isn’t a registered medical officer, that is a massive red flag. Surgeon Qualifications and Hair Transplant Training Beyond a basic medical degree, look for the LCP (Letter of Credentialing and Privileging). This is a specific license issued by the Ministry of Health Malaysia that allows a doctor to perform aesthetic procedures like hair transplants. Assess the Hair Transplant Clinic’s Experience and Reputation Technical skill in hair restoration is built over thousands of grafts and hundreds of patients. Years of Experience in Hair Transplant Procedures A clinic that has been operating for 5–10 years likely has a refined workflow and a proven track record. Ask how many procedures the surgeon performs personally each week. You want a specialist, not someone who does hair transplants as a “side hustle” between other unrelated treatments. Patient Reviews and Before-and-After Results Check Google Reviews and independent forums, but look specifically for “long-term” updates. A photo taken immediately after surgery looks much different than the result at the 12-month mark. Reliable clinics will have a gallery of high-resolution, consistent photos showing clear growth. Understand the Hair Transplant Techniques Offered Modern technology has made the procedure much more comfortable, but you need to know which method fits your scalp. FUE vs FUT: Which Is Safer and Suitable FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction): Individual follicles are punched out. It’s minimally invasive and leaves no linear scar. FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation): A strip of skin is removed. While older, it is still a valid medical technique for specific types of hair loss, provided it’s done in a sterile theatre. Safety Check: Be wary of clinics that claim a technique is “100% scarless.” Every incision leaves a mark, though FUE marks are virtually invisible to the naked eye. Use of Modern Equipment and Technology Reputable clinics invest in high-quality tools, such as Choi Implanter Pens or sapphire blades, which allow for denser packing and faster healing. For more on the technical side of these tools, you can explore the American Board of Hair Restoration Surgery (ABHRS) standards. Evaluate Hygiene, Facilities, and Safety Standards A clean lobby doesn’t always mean a sterile operating room. Sterilization and Infection Control Protocols The procedure room should look like a mini-hospital, not a spa room. Tools must be medical-grade and sterilized in an autoclave. Ask if the clinic uses single-use disposables for their needles and punches to eliminate any risk of cross-contamination. Accredited Medical Facilities and Operating Rooms In Malaysia, private clinics must comply with the Private Healthcare Facilities and Services Act 1998. This ensures the building meets fire safety, ventilation, and emergency medical standards. Consultation Transparency and Ethical Practices A safe clinic focuses on education, not the hard sell. Honest Assessment and Realistic Expectations If a doctor promises you a “teenager’s hairline” when you have advanced thinning, they aren’t being honest. A good surgeon will tell you if you aren’t a suitable candidate or if your donor hair is too weak. Clear Explanation of Risks, Recovery, and Results No surgery is zero-risk. Your doctor should explain the potential for “shock loss,” swelling, and the timeline of growth (which usually takes 6 to 12 months). Review Pricing, Packages, and Aftercare Support Safety includes the support you get after you leave the clinic. Transparent Pricing Without Hidden Costs Safe clinics provide a clear breakdown—usually per graft or per session. If a price seems “too good to be true,” they might be cutting corners on sterile equipment or using unlicensed staff to do the work. Post-Procedure Care and Follow-Up Availability The first 48 hours are critical. Does the clinic provide an aftercare kit with the right shampoos and antibiotics? Do they schedule follow-up appointments at the 1-week, 3-month, and 6-month marks? For a list of standard recovery protocols, the Malaysian Society of Aesthetic Medicine (MSAM) provides excellent resources for patients. Warning Signs of an Unsafe Hair Transplant Clinic Trust your gut. If something feels like a “factory,” it probably is. Unlicensed Practitioners or Sales-Driven Consultations If you spend 45 minutes talking to a “consultant” and only 5 minutes with the doctor, be careful. The doctor—not a salesperson—should be the one designing your hairline and explaining the medical risks. Guaranteed Results or Unrealistic Claims Medicine has no guarantees. Any clinic “guaranteeing” 100% graft
PRP vs Exosome vs Minoxidil: Which Hair Loss Treatment Works Best?

PRP vs Exosomes vs Minoxidil? Hair loss can be a frustrating experience, affecting millions worldwide. As science advances, so do our options for combating it. This guide dives deep into three prominent hair loss treatments: Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP), Exosomes, and Minoxidil. We will compare their mechanisms, effectiveness, and safety to help you understand which might be the best fit for your scalp health. Overview of Each Hair Loss Treatment Understanding how these treatments differ is the first step toward restoration. What Is PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma)? PRP therapy involves drawing a small amount of your blood, processing it in a centrifuge to concentrate the platelets, and injecting it into the scalp. Platelets contain growth factors that act as a “fertilizer” for thinning hair. What Are Exosomes in Hair Regeneration? Exosomes are tiny, cell-derived vesicles that act as messengers between cells. Unlike PRP, which uses your own blood, exosome therapy typically uses lab-purified signals derived from stem cells. These messengers “signal” dormant follicles to return to the growth phase. What Is Minoxidil? Minoxidil is the gold standard for topical hair loss treatment. It is an FDA-approved vasodilator, meaning it widens blood vessels to improve nutrient delivery to the follicle. How PRP, Exosomes, and Minoxidil Work Each treatment employs a distinct biological pathway to encourage hair growth. PRP: Relies on autologous growth factors (from your own body) to repair damaged tissues and stimulate the bulb of the hair follicle. Exosomes: Uses biomimetic signaling to provide a much higher concentration of growth factors than PRP, effectively “reprogramming” the scalp environment. Minoxidil: Primarily works by extending the anagen (growth) phase of the hair cycle, preventing hairs from falling out prematurely. PRP vs. Exosome vs. Minoxidil: Direct Comparison Feature Minoxidil PRP Therapy Exosome Therapy Application Daily Topical Office Injection Office Injection Cost Low ($) Moderate ($$) High ($$$) Results Seen 4–6 Months 3–6 Months 2–3 Months Maintenance Permanent Daily Use Every 6–12 Months Potentially Annual Effectiveness and Clinical Evidence When choosing a treatment, scientific backing is essential. You can research the latest clinical trials for hair loss to see how these therapies are performing in controlled environments. Scientific Evidence for PRP: Research consistently shows that PRP increases hair count and hair thickness in patients with androgenetic alopecia. Exosome Research: While newer, early data suggests exosomes may be up to 100 times more potent than PRP in terms of growth factor concentration. Minoxidil Data: With decades of use, it remains the most researched and reliable “first-line” defense against thinning. Which Hair Loss Treatment Works Best for You? The “best” treatment depends on your stage of hair loss and your lifestyle. Best for Early Thinning: Minoxidil is excellent for those just starting to notice a wider part or slight receding. Best for Moderate Loss: PRP is a fantastic mid-tier option for those who want to avoid daily chemicals but aren’t ready for surgery. Best for Rapid Results: Exosome therapy is currently the powerhouse of regenerative medicine for those seeking the fastest possible visible density. Best for Daily Convenience: Many patients prefer a men’s health specialist to prescribe a simple daily routine of oral or topical solutions. Can They Be Used Together? Absolutely. In fact, most experts recommend a multi-modal approach. Combining the blood-flow stimulation of Minoxidil with the regenerative power of PRP or Exosomes often yields better results than any single treatment alone. For those interested in a holistic approach, checking resources like The American Hair Loss Association can provide guidance on combining medical and lifestyle changes. Final Verdict: PRP vs Exosomes vs Minoxidil: Which One Should You Choose? If you are looking for an affordable, at-home solution, start with Minoxidil. If you want to harness your body’s own healing power without synthetic drugs, PRP is the way to go. However, if you want the most advanced technology available today, Exosomes are the clear winner. Before starting any regimen, it is vital to consult a professional. You can find a board-certified expert through the American Academy of Dermatology to ensure your hair loss isn’t caused by an underlying medical condition. Additionally, for those considering more permanent solutions, the International Society of Hair Restoration Surgery offers a wealth of information on how these treatments can complement a hair transplant.
Transplantasi Rambut Indonesia: Biaya, Prosedur, & Hasil (2026)
Masalah kebotakan atau receding hairline seringkali menjadi penghalang rasa percaya diri. Memasuki tahun 2026, teknologi transplantasi rambut Indonesia telah berkembang pesat, menawarkan tingkat keberhasilan tinggi bagi penderita androgenetic alopecia (kebotakan pola pria/wanita). Artikel ini akan mengupas tuntas mengapa Indonesia kini menjadi destinasi utama restorasi rambut di Asia Tenggara. Dipimpin oleh Dato’ Dr. JasG, GLOJAS Specialist Clinic diakui secara global dalam transplantasi rambut Indonesia berkat teknik SMART FUE/DHI yang presisi, memastikan hasil natural, aman, dan berstandar medis internasional demi kepuasan pasien. Key Takeaways Akurasi Maksimal: Penggunaan metode DHI (Direct Hair Implantation) memastikan arah tumbuh rambut yang sangat natural. Investasi Permanen: Menggunakan folikel donor yang resisten terhadap hormon DHT (penyebab rontok). Biaya Lebih Efisien: Harga transplantasi rambut Indonesia per graft lebih kompetitif dibanding Malaysia dan Singapura. Pemulihan Cepat: Teknik minimally invasive memungkinkan pasien kembali beraktivitas normal dalam 2–5 hari. Kandidat Ideal: Cocok untuk mereka dengan area donor sehat dan tingkat kerontokan yang sudah stabil. Apa Itu Transplantasi Rambut Indonesia dan Bagaimana Cara Kerjanya? Secara medis, transplantasi rambut Indonesia adalah prosedur bedah kosmetik minor untuk meredistribusi folikel rambut dari area subur ke area yang botak. Prosedur ini tidak menambah jumlah rambut secara total, melainkan menata ulang kepadatan rambut Anda. Di tahun 2026, fokus utama para ahli adalah pada Hairline Design. Dokter akan menggunakan mikroskop presisi tinggi untuk memisahkan unit folikel tunggal guna ditempatkan di garis depan rambut agar terlihat halus, sementara unit folikel ganda ditempatkan di bagian tengah untuk volume. Karena menggunakan jaringan tubuh sendiri, risiko penolakan sangat minim. Metode Populer: FUE vs DHI dalam Transplantasi Rambut Indonesia Berdasarkan tren pasar terkini, pasien kini lebih memilih teknik yang tidak meninggalkan bekas luka linier. FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction): Mengambil folikel satu per satu menggunakan alat punch mikro. Cocok untuk area botak yang luas. DHI (Direct Hair Implantation): Menggunakan pena khusus untuk menanam rambut tanpa perlu membuat sayatan saluran (channeling) terlebih dahulu. Ini adalah standar emas untuk transplantasi rambut Indonesia karena perdarahan lebih sedikit dan pemulihan lebih cepat. PRP Therapy (Platelet Rich Plasma): Seringkali dikombinasikan sebagai terapi penunjang untuk mempercepat vaskularisasi folikel baru. Estimasi Biaya Transplantasi Rambut Indonesia vs Malaysia 2026 Harga tetap menjadi pertimbangan utama. Berikut adalah tabel komparasi biaya yang mencakup komponen hidden cost seperti akomodasi dan perawatan pasca-ops. Faktor Perbandingan Transplantasi Rambut Indonesia Transplantasi Rambut Malaysia Harga per Graft Rp 15.000 – Rp 35.000 RM 6 – RM 12 (± Rp 21rb – 42rb) Teknik Unggulan DHI & FUE Tanpa Cukur FUE & Robotic FUE Biaya Perawatan Pasca Termasuk dalam Paket Seringkali Biaya Tambahan Aksesibilitas Transportasi Lokal Tiket Pesawat & Kurs Valas Sertifikasi Dokter Spesialis Bedah Plastik/Dermo Bersertifikasi KKM Siapa Kandidat Ideal untuk Transplantasi Rambut? Keberhasilan transplantasi rambut Indonesia sangat bergantung pada seleksi pasien. Anda adalah kandidat ideal jika: Memiliki area donor yang padat di bagian belakang atau samping kepala. Tidak memiliki kondisi medis kronis yang menghambat penyembuhan luka. Memahami bahwa kepadatan rambut bergantung pada jumlah graft yang tersedia. Mengalami kebotakan tipe Norwood Scale 2 hingga 6. Keamanan dan Efek Samping Transplantasi Rambut Meskipun aman, setiap prosedur bedah memiliki risiko. Beberapa efek samping yang mungkin muncul meliputi: Shock Loss: Rambut asli di sekitar area tanam rontok sementara (bersifat reversibel). Folliculitis: Peradangan kecil pada folikel rambut baru (bisa diatasi dengan salep antibiotik). Pembengkakan (Edema): Biasanya terjadi di area dahi jika tidak mengikuti instruksi posisi tidur. Menurut edukasi dari Alodokter, kepatuhan pada protokol kebersihan pasca-prosedur sangat menentukan hasil akhir agar tidak terjadi infeksi. Timeline Pemulihan Transplantasi Rambut Proses transformasi ini memakan waktu yang cukup lama. Berikut adalah estimasi progresnya: Minggu 1: Fase penyembuhan luka dan pengerasan akar. Bulan 1: Fase rontok sementara (normal). Bulan 3-4: Tunas rambut baru mulai muncul. Bulan 6-9: Terlihat peningkatan signifikan dalam volume rambut. Bulan 12-18: Hasil final yang permanen dan dapat dipotong atau diwarnai. Untuk Anda yang berencana melakukan perjalanan medis, informasi lengkap mengenai persiapan bisa merujuk pada portal kesehatan Halodoc. Kesimpulan: Mengapa Pilih Transplantasi Rambut Indonesia? Memilih transplantasi rambut Indonesia adalah pilihan logis bagi Anda yang mencari kualitas standar internasional dengan kemudahan logistik lokal. Dengan dukungan teknologi AI dalam pemetaan folikel dan teknik DHI yang presisi, Anda tidak perlu lagi pergi ke luar negeri untuk mendapatkan rambut impian. Pastikan Anda melakukan konsultasi mendalam untuk memahami profil rambut Anda secara personal. 5 FAQ Mengenai Transplantasi Rambut Indonesia 1. Berapa lama durasi operasi transplantasi rambut? Biasanya memakan waktu 4 hingga 8 jam, tergantung pada jumlah graft yang ditanam. 2. Apakah saya harus mencukur rambut sampai botak sebelum prosedur? Tergantung tekniknya. Untuk transplantasi rambut Indonesia dengan metode DHI, tersedia opsi Non-Shaven bagi Anda yang ingin menjaga penampilan segera setelah operasi. 3. Kapan saya bisa berolahraga kembali? Olahraga ringan bisa dilakukan setelah 2 minggu, namun olahraga berat atau berenang sebaiknya menunggu hingga 4 minggu. 4. Apakah rambut hasil transplantasi bisa memutih? Ya, rambut tersebut tetap mengikuti proses penuaan alami Anda karena itu adalah rambut asli. 5. Bagaimana cara merawat rambut setelah 1 tahun? Perawatan sama seperti rambut biasa. Namun, penggunaan vitamin rambut dan gaya hidup sehat sangat disarankan. Referensi mengenai gaya hidup sehat untuk rambut bisa Anda baca di WebMD.
How to Choose the Right Hair Loss Treatment Plan in Malaysia

How to Choose Hair Loss Treatment? Selecting the right hair loss treatment in Malaysia requires understanding your specific type of alopecia, medical history, and budget. From FDA-approved medications like minoxidil to advanced therapies such as PRP injections, this guide helps you navigate evidence-based options while avoiding unproven remedies that waste time and money. Key Takeaways Diagnose first: Identify whether you have androgenetic alopecia, telogen effluvium, or another condition before treatment FDA-approved options work: Minoxidil and finasteride have the strongest clinical evidence Budget matters: Treatments range from RM50/month for topicals to RM2,000+ per PRP session Consistency is crucial: Most therapies need 3-6 months before visible results appear Combine approaches: Multi-modal strategies often deliver superior outcomes Understanding Your Hair Loss Type Before throwing money at random products, you need a proper diagnosis. Androgenetic alopecia (pattern baldness) affects roughly 50% of men by age 50 and 40% of women experiencing hair thinning. This genetic condition responds differently than telogen effluvium (stress-related shedding) or alopecia areata (autoimmune). Visit a dermatologist or trichologist in Malaysia for scalp examination and possibly a pull test or dermoscopy. Many private clinics in Kuala Lumpur, Penang, and Johor Bahru offer comprehensive hair analysis starting around RM150-300. Getting this step right saves you from wasting months on treatments that won’t address your specific issue. FDA-Approved Treatments: The Gold Standard Minoxidil (Topical Solution) This vasodilator remains the most accessible first-line treatment. Originally developed for hypertension, minoxidil stimulates hair follicles and extends the growth phase. A landmark study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology showed that 5% minoxidil solution produced significant hair regrowth in 45% of male participants after 48 weeks. Malaysian availability: Brands like Regaine and generic versions cost RM50-180 monthly. Apply twice daily for best results. Side effects are minimal—occasional scalp irritation or unwanted facial hair in women using higher concentrations. Finasteride (Oral Medication) This 5-alpha reductase inhibitor blocks DHT conversion, the hormone responsible for shrinking hair follicles in androgenetic alopecia. Clinical trials demonstrate that finasteride (1mg daily) stops progression in 90% of men and stimulates regrowth in approximately 65% over two years. Malaysian context: Available by prescription at RM80-150 monthly. Female patients, particularly those of childbearing age, should avoid this medication due to teratogenic risks. Some men report sexual side effects (2-4% incidence), though most studies suggest these resolve after discontinuation. Dutasteride Similar mechanism to finasteride but inhibits both type I and II 5-alpha reductase enzymes. A 2016 study in the Journal of Dermatology found dutasteride 0.5mg superior to finasteride for increasing hair count. Currently prescribed off-label in Malaysia (RM120-200 monthly) for cases resistant to finasteride. Advanced Clinical Procedures Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy This involves drawing your blood, concentrating the platelets, then injecting the growth-factor-rich plasma into your scalp. Malaysian clinics charge RM800-2,500 per session. Most protocols recommend 3-4 initial treatments spaced monthly, then maintenance every 6-12 months. While not FDA-approved specifically for hair loss, emerging evidence shows promise—especially when combined with minoxidil or microneedling. Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT) FDA-cleared devices like laser caps or combs use specific wavelengths to stimulate cellular activity in follicles. Expect to pay RM2,000-5,000 for home devices or RM200-400 per clinic session. Results appear modest compared to medications but carry virtually no side effects. Hair Transplantation Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) and Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) surgically relocate hair from donor areas to thinning zones. Malaysian transplant costs range dramatically: RM8,000-30,000 depending on grafts needed and clinic reputation. Top surgeons in Kuala Lumpur match international standards. This works best for stable pattern baldness when combined with maintenance medications to protect existing hair. What Doesn’t Work (Save Your Money) Hair growth shampoos: Most over-the-counter options contain ketoconazole or caffeine with minimal clinical backing for regrowth. They won’t hurt but shouldn’t be your primary strategy. Biotin supplements: Only effective if you have an actual biotin deficiency (extremely rare). The supplement industry loves promoting this despite weak evidence. Stem cell creams: Topical products claiming “stem cell technology” lack peer-reviewed studies demonstrating follicle regeneration. Herbal remedies: While saw palmetto and pumpkin seed oil show theoretical mechanisms, clinical data remains insufficient for recommendation as standalone treatments. Building Your Personal Treatment Plan Here’s a practical framework: Stage 1 – Early thinning: Start with minoxidil 5% twice daily. Low cost, low risk, solid evidence. Add a ketoconazole shampoo (2%) twice weekly. Stage 2 – Moderate loss: Combine minoxidil with finasteride (men) or spironolactone (women). Consider adding microneedling monthly to enhance absorption. Stage 3 – Advanced loss: Evaluate hair transplant candidacy while maintaining medical therapy. Add PRP as an adjunct if budget allows. Budget considerations: Effective medical treatment starts at RM150-250 monthly. Advanced procedures require RM1,000-3,000 quarterly. Track progress with monthly photos in identical lighting. Most treatments need 4-6 months before noticeable improvement. Working With Malaysian Healthcare Providers Government hospitals offer dermatology consultations at subsidized rates (RM5-50) but expect longer wait times. Private dermatologists charge RM150-400 for initial consultations. Look for Malaysian Dermatological Society members for credentialed specialists. Ask these questions during your visit: What type of alopecia do I have? Which treatments have the strongest evidence for my condition? What realistic timeline should I expect? How will we measure progress? What’s the total monthly investment? Avoid clinics making guaranteed results claims or pushing proprietary “miracle” formulations without published research. Frequently Asked Questions Q: How long before I see results from hair loss treatment? Most FDA-approved treatments require 3-6 months of consistent use before visible improvement. Initial shedding in weeks 2-8 is normal as follicles reset their growth cycle. Don’t panic and discontinue—this often signals the treatment is working. Track progress with monthly photos rather than daily mirror checks. Q: Can women use the same hair loss treatments as men? Women can safely use minoxidil (2-5% formulations), but should avoid finasteride due to birth defect risks. Alternative options include spironolactone (oral), topical finasteride, or PRP therapy. Women’s hair loss often has different underlying causes—thyroid issues, iron deficiency, or hormonal imbalances—requiring comprehensive blood work before treatment. Q: Are hair loss treatments covered by Malaysian insurance? Most private insurance policies