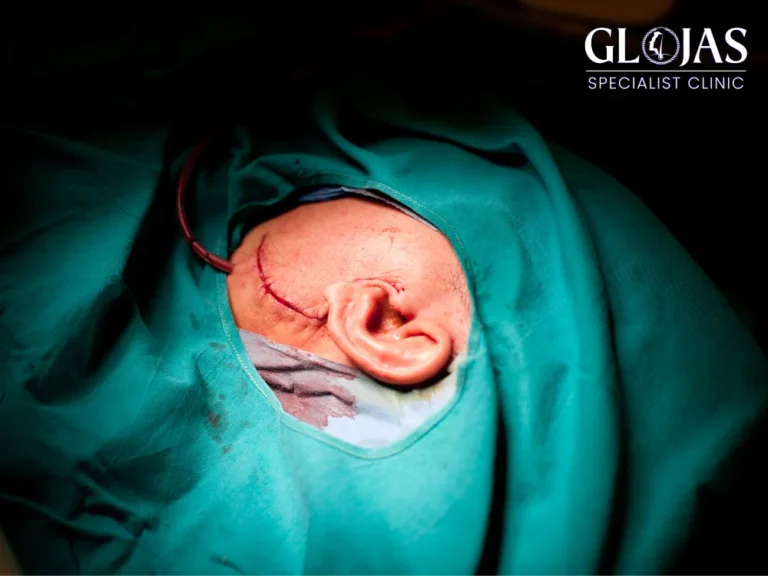
Ear operations, also known as otoplasty or ear surgery, are life-changing procedures that can improve both appearance and functionality. Whether addressing cosmetic concerns or resolving medical issues, an ear operation can enhance a person’s confidence and quality of life. This article provides an in-depth look into ear operations, including types, benefits, recovery, and more, making it easier for you to make an informed decision.
What Is an Ear Operation?
An ear operation is a surgical procedure performed on the ear to correct structural deformities, enhance appearance, or address medical conditions affecting hearing or ear functionality. These procedures can be cosmetic or medically necessary, depending on the patient’s needs.
Common ear operations include:
- Otoplasty (ear pinning): Corrects protruding ears.
- Tympanoplasty: Repairs a perforated eardrum.
- Cochlear Implant Surgery: Helps restore hearing in individuals with severe hearing loss.
- Reconstructive Ear Surgery: Repairs deformities caused by trauma or congenital conditions.
Each type of ear operation serves a unique purpose and requires specialized care.
Who Needs an Ear Operation?
An ear operation can benefit individuals of all ages, depending on their specific concerns:
1. Children
- Correcting congenital ear deformities, such as microtia or lop ear.
- Resolving issues like chronic ear infections that may affect hearing or development.
2. Adults
- Improving the appearance of prominent ears for increased confidence.
- Addressing hearing loss due to injury or disease.
A consultation with a qualified otolaryngologist or plastic surgeon will help determine if an ear operation is the right choice for you or your child.
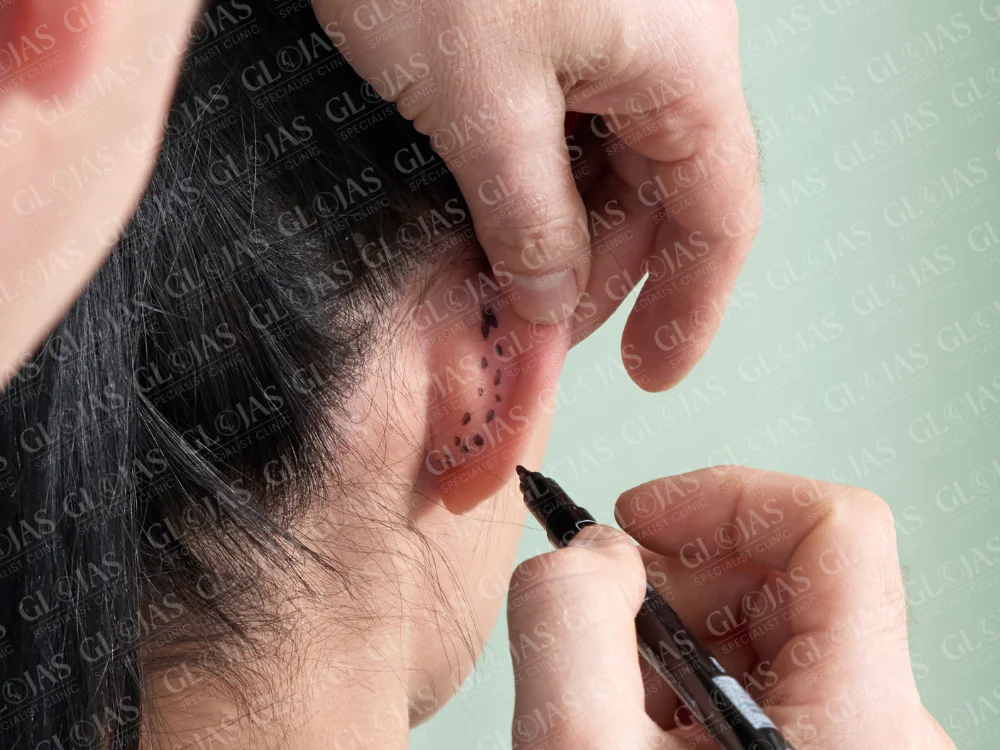
Benefits of an Ear Operation
Undergoing an ear operation offers a range of advantages, including:
- Enhanced Appearance: Correcting ear shape or size can lead to a more balanced and harmonious facial appearance.
- Improved Hearing: Medical procedures like tympanoplasty or cochlear implants can restore or enhance hearing abilities.
- Boosted Confidence: Addressing cosmetic concerns helps patients feel more comfortable in social settings.
- Resolution of Chronic Issues: Treating ear infections or injuries prevents long-term complications.
- Permanent Results: Most ear operations provide lasting or lifelong benefits with minimal maintenance.
Types of Ear Operations
1. Otoplasty (Cosmetic Ear Surgery)
Otoplasty focuses on reshaping and repositioning the ears for aesthetic purposes. Commonly performed on children and adults, it addresses issues such as:
- Protruding ears.
- Asymmetrical ears.
- Enlarged or irregular ear lobes.
2. Tympanoplasty (Eardrum Repair)
This procedure repairs a perforated eardrum caused by trauma, infection, or chronic ear disease. Tympanoplasty improves hearing and reduces the risk of recurring infections.
3. Cochlear Implant Surgery
For individuals with severe hearing loss, cochlear implants bypass damaged inner ear structures, transmitting sound directly to the auditory nerve. This life-changing surgery is often performed on both adults and children.
4. Reconstructive Ear Surgery
Reconstructive surgery addresses deformities from birth defects (e.g., microtia) or injuries, such as burns or accidents. Advanced techniques, including cartilage grafting, can rebuild the ear structure for a natural appearance.
5. Mastoidectomy
This procedure removes infected or diseased mastoid cells located behind the ear, typically caused by chronic ear infections. It helps prevent the spread of infection and protects nearby structures.
How Is an Ear Operation Performed?
The process of an ear operation depends on the type of surgery. Here’s a general overview of what to expect:
1. Consultation
During the consultation, the surgeon will evaluate your condition, discuss your goals, and recommend the most suitable procedure.
2. Pre-Surgical Preparation
You may need to undergo medical tests, avoid certain medications, and stop smoking to prepare for the surgery.
3. The Procedure
- Anesthesia: General or local anesthesia is administered for comfort.
- Incisions: Small incisions are made, often hidden in natural creases or folds.
- Corrections: The surgeon reshapes cartilage, repairs tissue, or implants necessary devices based on the procedure type.
- Closure: Stitches or surgical adhesives close the incisions, ensuring minimal scarring.
4. Post-Surgical Care
After surgery, bandages or dressings are applied to protect the area and promote healing.
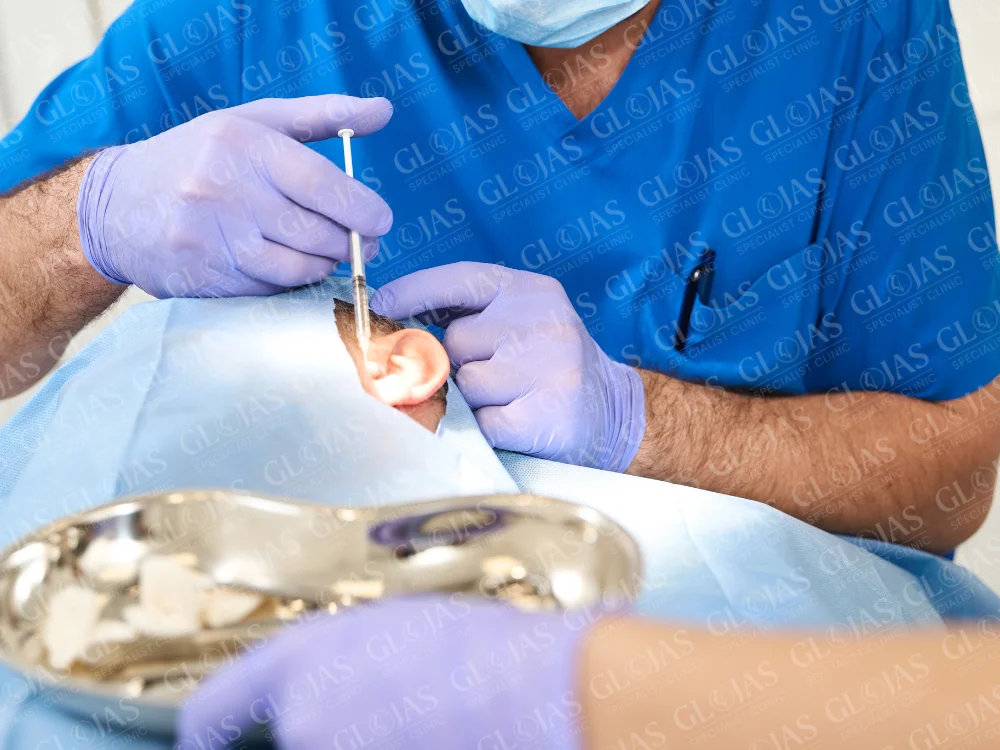
Recovery After an Ear Operation
The recovery timeline varies depending on the type and complexity of the ear operation. Here’s what to expect:
Immediate Recovery
- Swelling, bruising, and mild discomfort are common and subside within a few days.
- Pain management is usually achieved with prescribed medications.
Activity Restrictions
- Avoid strenuous activities for 2–4 weeks.
- Refrain from sleeping on the operated ear until fully healed.
Long-Term Healing
- Most patients see initial results within a week, but complete healing can take up to 6 months.
- Scars typically fade and become less noticeable over time.
Tips for a Smooth Recovery
- Keep the surgical area clean and dry.
- Follow your surgeon’s instructions for dressing changes and suture care.
- Attend all follow-up appointments to monitor progress.
Risks and Complications of Ear Operations
As with any surgical procedure, there are potential risks, including:
- Infection.
- Scarring or poor wound healing.
- Changes in sensation (temporary or permanent).
- Asymmetry or dissatisfaction with the results.
Choosing a skilled, board-certified surgeon significantly reduces these risks and ensures the best possible outcome.
How Much Does an Ear Operation Cost?
The cost of an ear operation depends on the procedure type, surgeon’s expertise, and location. Here’s a general estimate:
Procedure Type | Cost Range |
Otoplasty (Cosmetic Surgery) | $3,000 – $5,000 |
Tympanoplasty (Eardrum Repair) | $2,000 – $4,000 |
Cochlear Implant Surgery | $20,000 – $50,000 |
Reconstructive Ear Surgery | $4,000 – $10,000 |
Insurance may cover medically necessary procedures like tympanoplasty or cochlear implants. Always check with your provider beforehand.
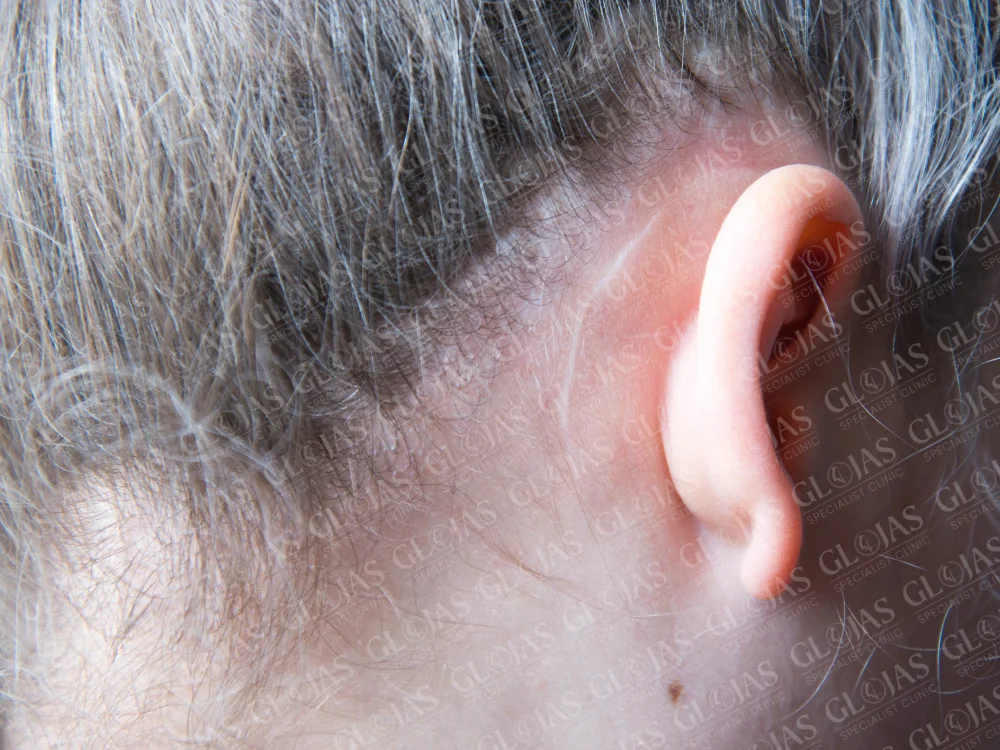
FAQs About Ear Operation
1. Is ear operation painful?
Most patients experience mild discomfort after surgery, which is manageable with pain medications. Modern surgical techniques prioritize minimal pain and quick recovery.
2. Can children undergo ear operations?
Yes, children as young as five years old can safely undergo otoplasty or other necessary ear procedures. Early correction can prevent social and psychological challenges later in life.
3. How long does an ear operation take?
The duration varies depending on the procedure. Otoplasty typically takes 1–2 hours, while more complex surgeries, like cochlear implants, may take up to 4 hours.
4. Are the results of ear surgery permanent?
Yes, most ear operations provide permanent results. However, maintaining healthy habits and following post-operative care instructions is essential for lasting success.
5. Will there be visible scars after surgery?
Most scars are minimal and strategically placed in inconspicuous areas, such as behind the ear or within natural folds.
6. Can ear operations improve hearing?
Yes, procedures like tympanoplasty and cochlear implants are specifically designed to restore or enhance hearing.
Conclusion
Ear operations, whether cosmetic or medical, offer transformative benefits for patients of all ages. By understanding the various types of procedures, benefits, and recovery expectations, you can take the first step toward achieving better functionality, enhanced appearance, and increased confidence. Consult with a qualified surgeon to explore your options and make an informed decision about your ear operation journey.