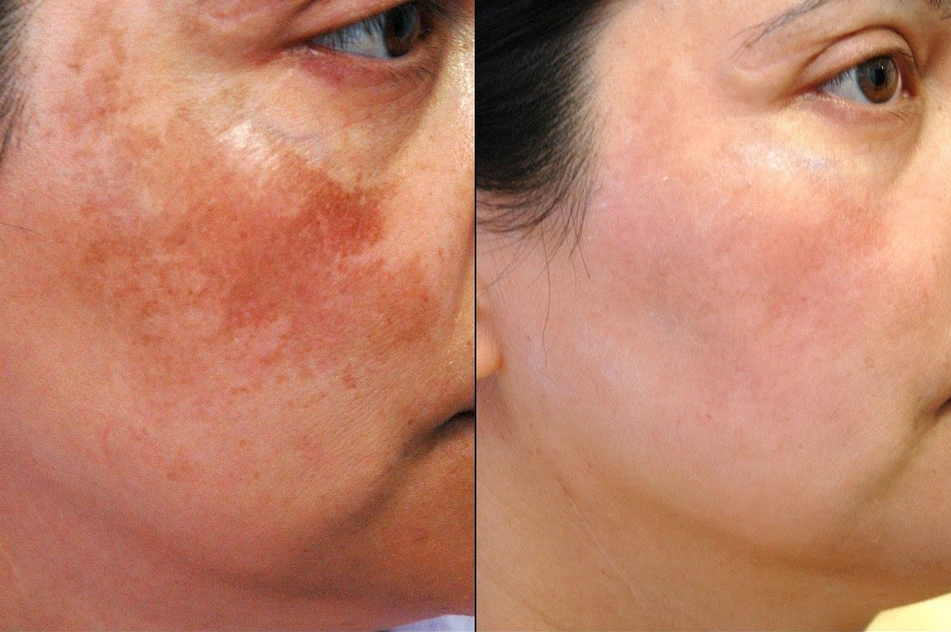
Hyperpigmentation is one of the most common skin concerns globally, affecting people of all ages and skin types. Whether it is a lingering spot from a teenage breakout or the “mask of pregnancy” known as melasma, these darkened patches of skin occur when your body produces excess melanin.
While usually harmless, an uneven skin tone can be a source of frustration. Understanding the biological triggers and the latest dermatological breakthroughs—from Tranexamic Acid to Exosome therapy—is the first step toward reclaiming a radiant, balanced complexion.
GLOJAS Specialist Clinic offers world-class hyperpigmentation treatments, combining LCP-certified expertise with advanced Pico Laser and Q-Switch technology to deliver safe, radiant, and natural-looking results for all skin types.
5 Key Takeaways for Managing Hyperpigmentation
Sun Protection is Non-Negotiable: UV exposure is the primary trigger for melanin overproduction; a sunscreen for melasma prevention with tinted iron oxides is your best defense.
Identify Your Type: Treatment varies significantly between post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), melasma, and solar lentigines (sun spots).
Patience is Mandatory: Skin cells take about 28–40 days to turnover; most brightening treatments require 8–12 weeks for visible results.
Ingredient Synergy: Combining tyrosinase inhibitors (like Vitamin C or Alpha Arbutin) with exfoliants yields faster results than using a single active.
Consult a Professional: For deep-seated dermal pigmentation, clinical treatments like chemical peels or Pico Lasers are more effective than over-the-counter creams.
What Exactly is Hyperpigmentation?
At its core, hyperpigmentation is a physiological response. Think of melanin as your skin’s natural umbrella. When the skin is “attacked” by sun, heat, or injury, it opens these umbrellas to protect itself.
Our skin contains specialized cells called melanocytes, which produce melanin—the pigment responsible for our skin, hair, and eye color. When these cells become overactive or damaged, they deposit clumps of pigment in the epidermis (surface) or dermis (deep layer).
Common Types of Skin Discoloration
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH): These are the “stains” left behind after an injury or skin inflammation. This is extremely common after cystic acne dark spots, eczema, or psoriasis flare-ups.
Melasma: Often called “the mask of pregnancy,” this is driven by hormonal melasma fluctuations (estrogen and progesterone). It is notoriously difficult to treat because it can be triggered by heat as well as light.
Solar Lentigines: Commonly known as age spots or liver spots, these are the direct result of cumulative UV damage over years of sun exposure.
The Science of Brightening: Key Ingredients
To effectively treat dark spots, you need to understand the melanogenesis pathway. Most topical treatments work by inhibiting tyrosinase, an enzyme required for melanin production. Using a “cocktail” approach—layering different types of inhibitors—is often more effective than using one high-strength product.
The Gold Standards & New Innovations
Vitamin C (L-Ascorbic Acid): The best Vitamin C serum for dark spots should be used every morning. It acts as a shield, neutralizing free radicals that trigger pigment production.
Tranexamic Acid for Skin: This is the “rising star” of 2026 skincare. It is particularly effective for melasma because it slows down the inflammatory process that signals melanocytes to fire up.
Alpha Arbutin vs Hydroquinone: Many people are moving toward Alpha Arbutin. It is a natural derivative of bearberry that provides the brightening power of hydroquinone without the risk of “rebound” darkening or irritation.
Niacinamide (Vitamin B3): This acts as a gatekeeper. It does not stop melanin from being made, but it prevents the pigment from being transferred into your skin cells.
Azelaic Acid: This is a favorite for a hyperpigmentation routine for Black skin. It is gentle, kills acne-causing bacteria, and targets only the “abnormal” melanocytes while leaving your natural skin tone alone.
For those looking for a deep dive into the clinical efficacy of these ingredients, the American Academy of Dermatology provides extensive resources on dermatological grading and safety.
Professional Procedures vs. At-Home Care
While a consistent evening routine is the foundation of skin health, sometimes the pigment sits too deep for topical serums to reach. This is especially true for dermal melasma or long-standing sun damage.
Clinical Interventions
If over-the-counter solutions fail, dermatologists often recommend:
Chemical Peels: These use high concentrations of Glycolic or Salicylic acid to “unglue” the top layer of pigmented skin.
Pico Laser for Brown Spots: Unlike older lasers that use heat (which can worsen melasma), Pico lasers use pressure to shatter pigment clusters into tiny particles that your body then flushes away.
Exosome Therapy for Pigmentation: This is the latest frontier in regenerative medicine. Exosomes are tiny “messenger” bubbles that tell your skin cells to repair themselves and stop overproducing pigment.
Microneedling: Often paired with Glutathione for skin brightening, this creates “micro-channels” that allow your brightening serums to penetrate 80% deeper than they would on their own.
According to the Skin Cancer Foundation, many spots mistaken for simple hyperpigmentation can actually be early signs of sun damage, making professional screening vital.
Prevention: The “Always-On” Strategy
The most effective way to treat hyperpigmentation is to prevent it from forming in the first place. This requires a “360-degree” approach to photoprotection.
Broad-Spectrum SPF: You must ensure your sunscreen protects against both UVA (aging/pigment) and UVB (burning) rays. For melasma sufferers, a sunscreen for melasma prevention containing iron oxides is best because it blocks blue light from screens.
Antioxidant Loading: Apply a Vitamin C serum every morning under your sunscreen. This creates a double barrier against environmental pollutants.
Internal Support: Research into a hormonal melasma diet suggests that anti-inflammatory foods (like salmon, walnuts, and leafy greens) can help stabilize the skin’s response to hormonal shifts.
Avoid Picking: Forcing a blemish to pop causes trauma to the basement membrane of the skin. This almost guarantees a dark spot will follow, especially in those with deeper Fitzpatrick skin types.
For a comprehensive list of safe sunscreens and their ratings, check the Environmental Working Group (EWG) Skin Deep Database to ensure your products are free from endocrine disruptors.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Does hyperpigmentation ever go away on its own?
PIH (acne marks) can fade over 6–12 months without treatment, but deeper issues like melasma or sun spots generally require active intervention to disappear.
2. Can I use Niacinamide and Retinol together?
Yes! In fact, Niacinamide and Retinol together are a powerhouse duo. The Niacinamide strengthens the skin barrier, making the Retinol more effective and less irritating.
3. Why is my hyperpigmentation getting darker in the summer?
Heat and UV rays stimulate melanocytes. Even if you are wearing sunscreen, the infrared heat from the sun can trigger melasma flare-ups. This is why “cooling” the skin is just as important as protecting it.
4. Is hyperpigmentation different for darker skin tones?
While everyone can get it, people with higher Fitzpatrick skin types (deeper skin tones) are more prone to PIH. Their melanocytes are more “reactive,” meaning even a small scratch can leave a long-lasting mark.
5. What is the fastest way to get rid of dark spots?
A combination of a prescription-strength retinoid, Tranexamic acid, and a professional Pico Laser treatment is typically the fastest route, though this must be done under medical supervision.
