In Malaysia, male pattern baldness is a super common conversation starter (or ender) for guys of all ages. Whether you’re just starting to thin or you’re ready to take action, let’s break down what’s actually happening to your hair and what you can do about it.
GLOJAS Specialist Clinic Kuala Lumpur offers world-class male pattern baldness treatment in Malaysia, specializing in SMART™ FUE transplants and PRP therapy to deliver natural, permanent results for thinning hair.
What Is Male Pattern Baldness
Simply put, it’s the most common cause of hair loss in men. In a tropical climate like Malaysia, where heat and humidity can make hair look flat anyway, noticing that “see-through” scalp can be a bit of a wake-up call.
Definition of Androgenetic Alopecia
Medical professionals call this condition Androgenetic Alopecia. It’s a mouthful, but it basically means your hair loss is driven by a mix of genetics and hormones. Unlike temporary hair loss caused by stress or diet, this one is progressive—meaning it doesn’t usually stop on its own.
How Male Pattern Baldness Develops
It’s not an overnight disappearance. It’s a process called miniaturization. Your hair follicles, which used to produce thick, healthy strands, start shrinking. Over time, they produce shorter, thinner hairs until they eventually stop producing hair altogether.
Causes of Male Pattern Baldness
Why is this happening to you? It’s usually a “perfect storm” of biology.
Genetic Factors & Family History
You can thank (or blame) your parents for this one. If your dad or your maternal grandfather had a receding hairline, there’s a high chance your DNA has already mapped out a similar path. You can learn more about how genetics influence hair loss to see where you stand.
DHT (Dihydrotestosterone) Sensitivity
This is the main villain in the story. DHT is a byproduct of testosterone. If you are genetically predisposed, DHT attaches to your hair follicles and tells them to pack their bags and shrink.
Hormonal & Age-Related Factors
While DHT is the trigger, age is the accelerator. As we get older, the cumulative effect of DHT exposure makes thinning more visible. In Malaysia, environmental factors like UV exposure can also stress already-weakened hair.
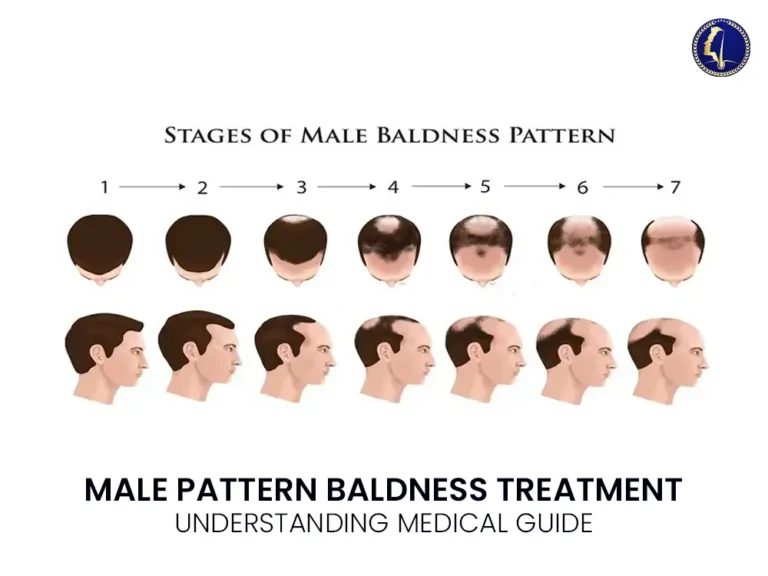
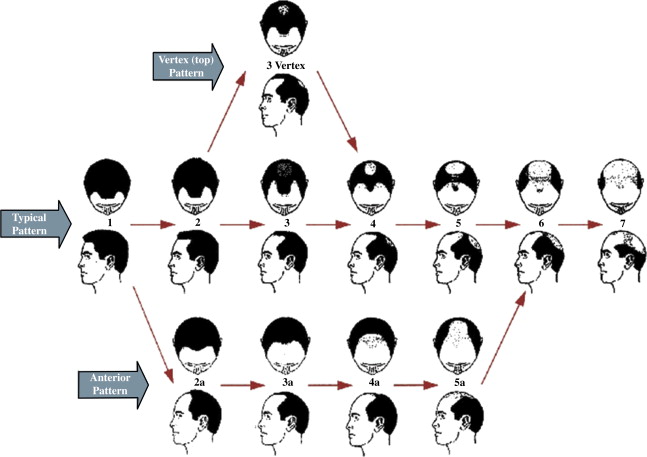
Stages of Male Pattern Baldness
Knowing where you are in the process helps determine which treatment will actually work.
Norwood Scale Explained
The Norwood Scale is the gold standard for classifying hair loss. It ranges from Stage 1 (minimal loss) to Stage 7 (severe baldness where only a wreath of hair remains on the sides).
Early vs Advanced Hair Loss
Early (Stages 1-3): You’ll notice a “V” or “M” shape at the hairline. This is the best time to start preventative treatments.
Advanced (Stages 4-7): The crown (top of the head) starts thinning significantly, eventually meeting the receding hairline.
Signs & Symptoms
Receding Hairline
This usually starts at the temples. You might notice your “widow’s peak” becoming more prominent.
Crown Thinning
Often called the “monk’s patch,” this is thinning at the very top of your head. You might only notice it through a rear-view mirror or in photos taken from above.
Diffuse Scalp Thinning
Some guys don’t get a clear receding line but instead experience a general decrease in density across the entire top of the scalp.
Diagnosis of Male Pattern Baldness
Before buying every “anti-hair loss” shampoo in the pharmacy, get a proper diagnosis.
Clinical Scalp Examination
A doctor or hair specialist will check your hair loss pattern and scalp health to rule out other issues like fungal infections or scarring alopecia.
Trichoscopy & Hair Density Analysis
This involves using a specialized camera to look at your scalp under high magnification. It allows doctors to see exactly how many follicles are miniaturizing and measure your hair density.
Male Pattern Baldness Treatment Options in Malaysia
The good news? Malaysia has world-class hair restoration tech.
Medications (Finasteride, Minoxidil)
These are the “Big Two.” Minoxidil (topical) helps blood flow to the follicles, while Finasteride (oral) blocks DHT. You can check out the FDA-approved hair loss medications to understand how they work.
PRP Hair Treatment
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) involves drawing a bit of your own blood, spinning it to concentrate the growth factors, and injecting it back into your scalp. It’s like “fertilizer” for your hair.
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
This uses medical-grade lasers to stimulate cellular activity in the follicles. It’s painless and often done via “laser caps” or in-clinic devices.
Hair Transplant Overview
If the follicle is completely dead, meds won’t bring it back. That’s where a transplant comes in—moving healthy hair from the back of your head to the bald spots.
Hair Transplant for Male Pattern Baldness
FUE Hair Transplant
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) is the most popular method in Malaysia. Individual follicles are plucked out one by one and moved. No linear scars!
FUT Hair Transplant
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) involves removing a strip of skin from the back. It’s better for guys needing a massive amount of hair in one session, but it does leave a thin scar.
DHI Hair Transplant
Direct Hair Implantation (DHI) is an advanced version of FUE where a specialized tool (a Choi pen) is used to control the depth and angle of every single hair for a very natural look.
Treatment Results & Timeline
Patience is key. Hair grows slow!
When Hair Regrowth Starts
With meds or PRP, you might see “fuzz” in 3 to 6 months. For transplants, the transplanted hair actually falls out first (shock loss) before growing back permanently around the 6-to-9-month mark.
Long-Term Maintenance
Hair loss is a marathon. Even after a transplant, you’ll likely need to stay on some form of maintenance (like Minoxidil) to keep the non-transplanted hair from falling out.
Who Is a Suitable Candidate for Treatment
Ideal Candidates
The best candidates are those in the early-to-mid stages of hair loss with a healthy “donor area” (the hair on the back and sides).
Limitations & Expectations
If you are completely bald (Norwood 7), a transplant might not give you a full “teenager” mane, but it can definitely frame your face again. Setting realistic goals is vital.
Risks & Side Effects
Medication Side Effects
Finasteride can occasionally cause changes in libido, while Minoxidil might cause scalp irritation or dryness. Always consult a doctor first.
Procedure-Related Risks
Transplants are minor surgeries. Risks include temporary swelling, redness, or minor infections, though these are rare with proper surgical standards.
Male Pattern Baldness Prevention & Hair Care
Early Intervention Strategies
The best time to save a tree is before it falls. If you notice more hair in the shower drain, start a scalp care routine now.
Scalp Care & Lifestyle Factors
In Malaysia’s heat, sweat and oil can clog follicles. Use a clarifying shampoo and try to manage stress levels, as high cortisol can accelerate thinning. For more on overall hair health, the WebMD hair care guide offers great foundational tips.
Choosing a Hair Loss Clinic in Malaysia
Don’t just go for the cheapest price. Your face is at stake!
Doctor Credentials & Experience
Ensure the clinic is LCP-certified (Letter of Credentialing and Privileging) by the Ministry of Health Malaysia. You want a doctor who specializes in hair, not just a generalist.
Technology & Treatment Standards
Check if they use modern tools like the Choi Implanter or high-tech trichoscopy. Read reviews and look at “Before & After” photos of real Malaysian patients.
Frequently Asked Questions About Male Pattern Baldness
Can Male Pattern Baldness Be Reversed?
If caught early, you can regrow a significant amount. If the area is completely smooth and shiny, you can’t “regrow” it with meds, but you can “restore” it with a transplant.
At What Age Does It Start?
It can start as early as the late teens. However, most men in Malaysia begin noticing it in their mid-20s or early 30s.
Is Treatment Permanent?
Hair transplants are generally considered permanent because the hair moved from the back is resistant to DHT. However, you must continue preventative hair loss treatments to protect the rest of your natural hair.