Reconstructive Surgery: Procedures & Recovery Guide in Malaysia
If you’ve ever found yourself looking in the mirror and wishing a part of your body functioned as well as it used to—or if life has thrown you a curveball in the form of an accident or illness—you’re likely exploring the world of reconstructive surgery. Malaysia has rapidly become a global hub for this medical specialty, blending world-class surgical expertise with recovery settings that feel more like a vacation than a hospital stay. Led by NSR-registered surgeons, GLOJAS Specialist Clinic provides expert reconstructive surgery in Malaysia, specializing in advanced scar revision and functional restoration with a focus on natural-looking, life-changing results. Introduction to Reconstructive Surgery Reconstructive surgery isn’t just about “fixing” things; it’s about restoring your quality of life. Whether it’s helping a child speak clearly through cleft palate repair or helping a woman feel whole again after a mastectomy, this field is the backbone of modern plastic surgery. In Malaysia, the surgical community is highly regulated, ensuring that patients receive care that meets international benchmarks. What Is Reconstructive Surgery? At its heart, reconstructive surgery is a medical necessity. It focuses on repairing abnormal structures of the body caused by congenital defects, developmental abnormalities, trauma, infection, tumors, or disease. While the goal often includes improving appearance, the primary mission is to restore function. For example, a surgeon might use a skin graft to treat a severe burn, not just to make the area look better, but to ensure the patient can move their limb without pain or restriction. Difference Between Reconstructive and Cosmetic Surgery It’s easy to get these two mixed up, but the distinction is actually quite simple: Reconstructive Surgery: Focuses on restoring function and a “normal” appearance to parts of the body that are medically impaired. Examples include breast reconstruction after cancer or hand surgery for carpal tunnel. Cosmetic Surgery: This is elective. It aims to enhance or “upgrade” structures that are already functioning normally but don’t meet a person’s aesthetic goals. Think breast augmentation for size or a facelift for anti-aging. Common Reconstructive Surgery Procedures in Malaysia Malaysia’s healthcare system is particularly adept at several key reconstructive areas, often utilizing advanced microsurgery to achieve natural-looking results. Breast Reconstruction Breast cancer is a significant health concern in Malaysia, and the surgical response has evolved beautifully. Surgeons here offer both implant-based reconstruction and autologous (flap) reconstruction. Flap surgery is particularly popular, where the surgeon uses your own tissue—often from the abdomen or back—to create a new breast that feels and behaves like natural tissue. According to Prudential Malaysia, immediate reconstruction (done at the same time as the mastectomy) is a growing trend that helps reduce the emotional trauma of the procedure. Facial Reconstruction From repairing fractures after a motorcycle accident to removing skin cancers and rebuilding the nose or jaw, facial reconstruction is a delicate art. Surgeons in Kuala Lumpur and Penang often specialize in craniofacial surgery, which addresses complex bone structures. The goal is to restore symmetry and vital functions like breathing, chewing, and blinking. Hand and Limb Reconstruction Our hands are our primary tools for interacting with the world. Reconstructive surgeons in Malaysia handle everything from reattaching severed fingers (replantation) to treating congenital “webbed” fingers. They also work on lower limb salvage, using complex tissue transfers to save legs that might otherwise face amputation due to severe trauma or diabetic complications. Skin Grafts and Scar Revision Burn care is a major pillar of the reconstructive field. Surgeons use skin grafts (taking skin from a donor site) or tissue expansion (growing extra skin) to cover large wounds. For older injuries, scar revision techniques—including laser therapy or surgical excision—help minimize the visibility of scars and improve the skin’s flexibility. Choosing a Reconstructive Surgeon in Malaysia Your results are only as good as the hands performing the procedure. Here is how to vet your options. Qualifications and Certifications In Malaysia, a qualified plastic surgeon must be registered with the National Specialist Register (NSR). Look for credentials like: MSPRS: Malaysian Society of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. MAPACS: Malaysian Association of Plastic, Aesthetic and Craniomaxillofacial Surgeons. FRCS: Fellow of the Royal College of Surgeons (often from the UK, Edinburgh, or Ireland). Top Hospitals and Clinics Most major reconstructive work happens in JCI-accredited (Joint Commission International) hospitals. Facilities like Gleneagles, Prince Court, and Pantai Hospital are renowned for their specialized plastic surgery departments and high-tech operating theaters. Patient Reviews and Success Rates Don’t just take the brochure’s word for it. Check independent forums and ask for before-and-after photos of patients with similar conditions. A reputable surgeon will be transparent about their success rates and potential “re-do” statistics. Cost of Reconstructive Surgery in Malaysia One of Malaysia’s biggest draws is the “value for money” factor. You get Western-standard medical care at a fraction of the price found in the US or UK. Average Prices by Procedure Procedure Estimated Cost (RM) Estimated Cost (USD) Breast Reconstruction (Implant) RM 15,000 – RM 25,000 $3,500 – $5,800 Cleft Lip/Palate Repair RM 8,000 – RM 15,000 $1,800 – $3,500 Scar Revision RM 3,000 – RM 10,000 $700 – $2,300 Note: These are baseline estimates. Prices vary by hospital and complexity. Factors Affecting Cost Your final bill isn’t just the surgeon’s fee. It includes: Anesthesia fees: Based on the length of the surgery. Hospital stay: Reconstructive cases often require 2–5 days of monitoring. Materials: The cost of implants, specialized mesh, or hardware like plates and screws. Insurance and Financing Options Unlike cosmetic surgery, reconstructive procedures are often covered by medical insurance because they are deemed medically necessary. Policies like Prudential’s PRULady specifically provide benefits for facial or breast reconstruction following accidents or cancer. Always get a “Letter of Guarantee” from your insurer before the surgery. Safety, Risks, and Recovery Every surgery has a “downside” to manage. Being informed is your best defense against complications. Potential Complications While rare in the hands of experts, risks include infection, hematoma (blood pooling), or flap failure (where the transferred tissue doesn’t get enough blood flow). In Malaysia, the Malaysian Medical Council sets
Cosmetic Surgery: Procedures, Clinics & Costs Guide in Malaysia

The pursuit of confidence has no borders, and these days, Malaysia is at the heart of the global map for aesthetic transformations. Whether it’s the allure of world-class medical facilities or the incredibly competitive pricing, cosmetic surgery in Malaysia has evolved from a niche luxury to a mainstream wellness choice. GLOJAS Specialist Clinic is a multi-award-winning leader for cosmetic surgery in Malaysia, offering board-certified expertise in facial rejuvenation, breast augmentation, and body contouring for natural, life-changing results. Introduction to Cosmetic Surgery In the modern era, looking as good as you feel isn’t just about vanity—it’s about self-actualization. Malaysia’s medical landscape has embraced this, offering everything from minor “tweakments” to full-scale transformations. What Is Cosmetic Surgery? Often referred to as aesthetic surgery, cosmetic surgery is a unique discipline of medicine focused on enhancing appearance through surgical and medical techniques. It can be performed on all areas of the head, neck, and body. Because the treated areas function properly but lack aesthetic appeal, cosmetic surgery is almost always elective. Differences Between Cosmetic and Reconstructive Surgery While the terms are often used interchangeably, they serve different masters: Cosmetic Surgery: Focused entirely on enhancing a patient’s appearance. Improving aesthetic appeal, symmetry, and proportion are the primary goals. Reconstructive Surgery: Aims to restore function and normal appearance after trauma, infection, or birth disorders. As noted by the Mayo Clinic, reconstructive work is often considered a medical necessity, whereas cosmetic work is a personal choice. Popular Cosmetic Surgery Procedures in Malaysia Malaysia has built a reputation for specific “signature” procedures that attract thousands of international patients annually. Facial Procedures (Rhinoplasty, Facelift, Eyelid Surgery) The “Asian Rhinoplasty” is a specialized field here, focusing on bridge augmentation and tip refinement. Blepharoplasty (eyelid surgery) is also high on the list for those seeking a more alert, youthful gaze. For those looking to turn back the clock, the Deep Plane Facelift has become a 2026 favorite for providing structural lifting without that “wind-tunnel” look. Body Contouring (Liposuction, Tummy Tuck, Breast Surgery) Post-weight-loss transformations are surging. With the rise of GLP-1 medications, many are seeking a tummy tuck (abdominoplasty) or liposuction to remove stubborn skin and fat. In the realm of breast surgery, the trend has shifted toward “ballerina breasts”—smaller, more athletic implants that complement an active lifestyle. Non-Surgical Treatments (Botox, Fillers, Laser Therapy) If you’re not ready for the operating room, Malaysia’s “Medispas” offer advanced biostimulators like Sculptra or Radiesse. These aren’t just fillers; they encourage your skin to produce its own collagen over time, leading to a more natural, gradual rejuvenation. Choosing a Cosmetic Surgeon in Malaysia Your safety depends entirely on the hands you choose. In Malaysia, the “Golden Rule” is to verify before you book. Qualifications and Certifications Every legitimate surgeon must be registered with the Malaysian Medical Council (MMC). Specifically, for aesthetic work, ensure your doctor holds the Letter of Credentialing and Privileging (LCP). This is a mandatory certification from the Ministry of Health that proves the doctor has the specialized training to perform these procedures. Top Clinics and Hospitals Look for facilities with international stamps of approval. Many Malaysian hospitals are accredited by the Joint Commission International (JCI), which is the global gold standard for patient safety and quality of care. Patient Reviews and Success Rates In the age of social media, “Before & After” galleries are your best friend. Look for consistency in results and read through independent forums to get the “unfiltered” patient experience. Cost of Cosmetic Surgery in Malaysia One of the biggest draws to Malaysia is the price tag. You can expect to save anywhere from 40% to 70% compared to Western prices. Average Prices by Procedure Procedure Estimated Price (RM) Estimated Price (USD) Rhinoplasty RM 10,000 – RM 18,000 $2,300 – $4,200 Breast Augmentation RM 15,000 – RM 30,000 $3,500 – $7,000 Liposuction (per area) RM 8,000 – RM 15,000 $1,800 – $3,500 Facelift (Full) RM 30,000 – RM 45,000 $7,000 – $10,500 Factors Affecting Cost The final bill depends on the surgeon’s prestige, the type of anesthesia used, and whether you’re staying in a boutique clinic or a full-scale private hospital. High-quality implants (like Motiva or Mentor) will also influence the total cost of breast procedures. Financing and Payment Options Most top-tier clinics offer 0% interest installment plans for locals. International patients usually pay via credit card or bank transfer, often opting for “all-inclusive” packages that cover surgery, hospital stay, and initial recovery accommodation. Safety, Risks, and Recovery Surgery is a marathon, not a sprint. The recovery phase is just as important as the procedure itself. Potential Complications No surgery is risk-free. Common issues include hematoma, infection, or scarring. According to the International Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery (ISAPS), the best way to mitigate these risks is to follow your surgeon’s pre-op and post-op instructions to the letter. Pre- and Post-Operative Care Stop smoking at least two weeks before. Smoking constricts blood vessels and can lead to skin necrosis (tissue death). Post-op, you’ll likely need compression garments to minimize swelling and help the skin adhere to its new contours. Recovery Timelines Initial Rest: 2–3 days of pure downtime. Back to Work: 1–2 weeks for most facial surgeries; 2 weeks for body work. Final Results: While you’ll look great in a month, true final results (especially in rhinoplasty) can take up to a full year to settle. Latest Trends and Innovations in Cosmetic Surgery The industry is moving toward “regenerative” medicine—helping the body heal itself for more natural results. Advanced Surgical Techniques Fat Grafting is the hero of 2026. Instead of synthetic fillers, surgeons are using your own processed fat to restore volume to the face or breasts. It’s natural, permanent, and reduces the risk of rejection. Minimally Invasive Procedures Pico Lasers and Ultherapy (which uses ultrasound to lift the skin) are the go-to for busy professionals who want a refresh during their lunch break. These treatments require zero downtime and provide a “filtered” skin effect. Popular Treatments Among Locals and Tourists While locals love V-shape face contouring and
Plastic Surgery: Cosmetic & Reconstructive Solutions in Malaysia

Thinking about a glow-up in the tropics? You aren’t alone. Malaysia has fast become a global hotspot for aesthetic transformations, blending high-tech medical facilities with prices that don’t require a second mortgage. Whether you’re looking for a subtle “did-she-or-didn’t-she” refresh or a life-changing reconstructive procedure, the Malaysian plastic surgery scene is buzzing with innovation and expertise. GLOJAS Specialist Clinic is a premier destination for plastic surgery in Malaysia, offering award-winning body contouring and hair restoration. Led by board-certified surgeons, they deliver safe, natural-looking results with world-class medical expertise. Overview of Plastic Surgery Plastic surgery isn’t just about vanity; it’s a sophisticated branch of medicine that balances artistry with complex biological engineering. In Malaysia, the industry is strictly regulated to ensure that “looking good” goes hand-in-hand with “staying safe.” What Is Plastic Surgery? At its core, plastic surgery is a surgical specialty involving the restoration, reconstruction, or alteration of the human body. The term comes from the Greek word plastikos, meaning “to mold” or “to give shape.” It’s divided into two main categories: cosmetic surgery, aimed at enhancing appearance, and reconstructive surgery, which fixes functional defects caused by trauma, birth disorders, or disease. Common Types of Procedures The spectrum of care in Malaysia is vast. Most patients seek out: Facial Contouring: Rhinoplasty, blepharoplasty (eyelid surgery), and facelifts. Body Sculpting: Liposuction, tummy tucks (abdominoplasty), and “Mommy Makeovers.” Breast Surgery: Augmentation, lifts, or reduction. Skin Treatments: High-end lasers and medical-grade injectables. Popular Plastic Surgery Procedures in Malaysia From the bustling clinics of Kuala Lumpur to the medical hubs in Penang, certain procedures have become local favorites due to the high success rates and specialist expertise available. Cosmetic Surgery Options Cosmetic surgery is currently seeing a shift toward “natural-looking” results. According to the American Society of Plastic Surgeons, 2026 trends emphasize regenerative sculpting over dramatic, “frozen” changes. In Malaysia, Breast Augmentation (using Motiva or Mentor implants) and Rhinoplasty (nose reshaping) remain top-tier requests for those seeking a harmonious silhouette. Reconstructive Surgery Services Malaysia’s public and private sectors excel in reconstructive work. This includes cleft lip and palate repairs, breast reconstruction following a mastectomy, and intricate microsurgery for trauma victims. These services focus on restoring both form and function, often covered by different insurance criteria than elective cosmetic work. Minimally Invasive Treatments Not everyone wants to go under the knife. The rise of “tweakments” is massive here. Procedures like Botox, Dermal Fillers, and Ultherapy (non-surgical skin tightening) offer immediate results with zero downtime. Recently, Profhilo and Pico Lasers have gained traction for their ability to improve skin bio-remodelling and texture without surgical incisions. Choosing the Right Plastic Surgeon in Malaysia Your face and body are permanent; your surgeon selection should be, too. Malaysia has a rigorous system to filter out “cowboy” practitioners. Qualifications and Certifications First things first: your surgeon must be registered with the Malaysian Medical Council (MMC). For aesthetic procedures, look for the Letter of Credentialing and Privileging (LCP). Ideally, your surgeon should be a member of the Malaysian Association of Plastic, Aesthetic and Craniomaxillofacial Surgeons (MAPACS), which ensures they have undergone 5–6 years of specialized training beyond their medical degree. Top Clinics and Hospitals Malaysia is home to world-class facilities like Beverly Wilshire Medical Centre, Gleneagles, and Prince Court Medical Centre. These institutions often hold international accreditations, ensuring they meet global hygiene and safety benchmarks. Patient Reviews and Success Rates Don’t just take the brochure’s word for it. Check independent platforms for patient testimonials and ask to see Before & After galleries. A reputable surgeon will show you a range of outcomes, not just their “perfect” cases. Cost of Plastic Surgery in Malaysia One of the biggest draws to Malaysia is the cost-to-quality ratio. You can typically save 40% to 70% compared to prices in Australia, the UK, or the USA. Average Prices by Procedure While prices vary by clinic and surgeon expertise, here are some 2026 estimates: Procedure Estimated Cost (MYR) Estimated Cost (USD) Rhinoplasty RM 12,000 – RM 25,000 $2,800 – $5,800 Breast Augmentation RM 15,000 – RM 30,000 $3,500 – $7,000 Liposuction (per area) RM 8,000 – RM 18,000 $1,800 – $4,200 Double Eyelid Surgery RM 6,000 – RM 12,000 $1,400 – $2,800 Factors Affecting Cost Surgeon’s Experience: High-demand specialists charge more. Facility Fees: Private hospitals vs. boutique aesthetic clinics. Anesthesia: General anesthesia is more expensive than local sedation. Implant Quality: Premium brands like Motiva Joy often come at a surcharge. Financing and Payment Options Many Malaysian clinics offer installment plans through major banks (like Maybank or CIMB) or medical financing fintech apps. For international patients, credit card payments are standard, but always check for “medical tourism” packages that might include post-op accommodation. Safety, Risks, and Recovery Every surgery carries a degree of risk. The key is how those risks are managed by your medical team. Potential Complications Common risks include infection, scarring, hematoma, or anesthesia reactions. According to International Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery (ISAPS), choosing a board-certified surgeon reduces the risk of major complications significantly because they are trained to handle emergencies mid-procedure. Pre- and Post-Operative Care Preparation is half the battle. You’ll likely be asked to stop smoking and avoid blood thinners (like aspirin) two weeks before surgery. Post-op, you’ll need to wear compression garments and attend follow-up sessions to monitor healing and remove sutures. Recovery Timelines Socially Ready: Most patients feel comfortable going out after 10–14 days. Light Activity: 2–3 weeks. Full Gym/Strenuous Exercise: 6 weeks. Trends and Innovations in Malaysian Plastic Surgery Malaysia is staying ahead of the curve with tech that makes “getting work done” less scary and more precise. Latest Techniques and Technology Deep Plane Facelifts are the new gold standard in Malaysia for 2026, offering structural lifting rather than just skin stretching. We’re also seeing more 3D Imaging (like Crisalix) during consultations, allowing you to “try on” your new look digitally before the first incision. Non-Surgical Advancements The “GLP-1 Makeover” is a rising trend. As more people use medications for weight loss, there is a surge in demand for non-surgical
Pubertal Gynecomastia: What Every Teen and Parent Needs to Know
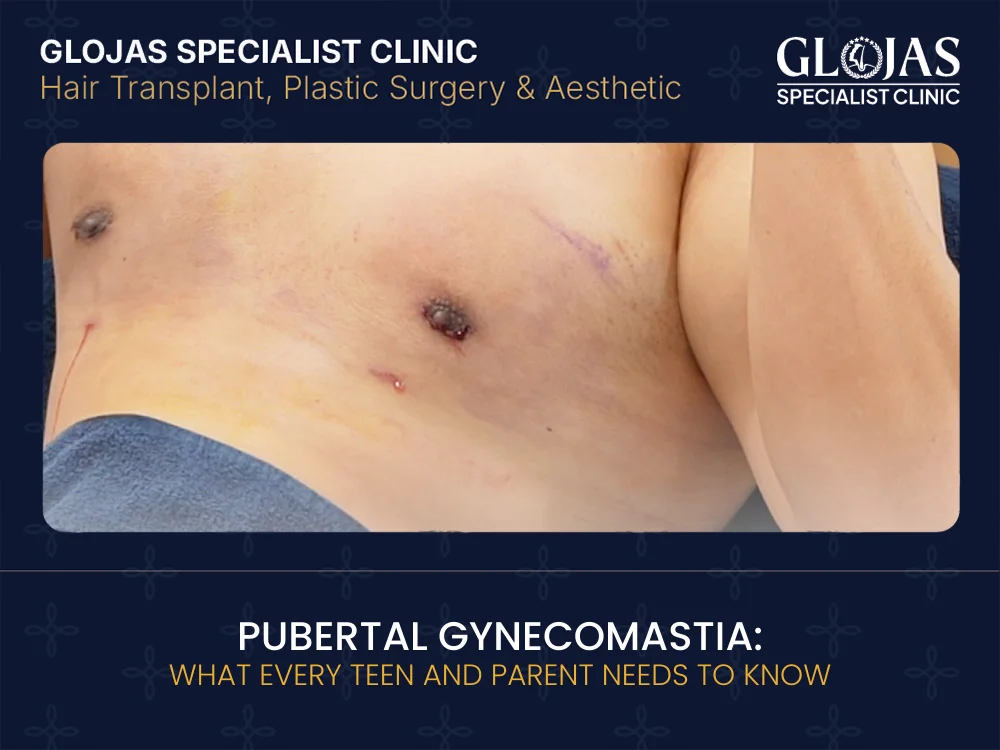
Pubertal gynecomastia is a common condition affecting many teenage boys during puberty. This guide breaks down what it is, why it happens, how it’s diagnosed, and when to seek help — all in an easy‑to‑understand, factual way for teens and families. Understanding Pubertal Gynecomastia Pubertal gynecomastia refers to the benign enlargement of male breast tissue during adolescence. It is usually seen between ages 12–18 and happens because of natural hormonal changes involving estrogen and testosterone during puberty. Though it can feel worrying, it is typically temporary and not a sign of serious illness. What Is Gynecomastia? Gynecomastia is the medical term for benign breast tissue growth in males. It differs from pseudogynecomastia, which involves mostly fat accumulation without glandular enlargement. In pubertal gynecomastia, the growth is due to increased breast gland tissue, not just fat. Key Entities in Pubertal Gynecomastia Breast gland tissue Hormones (estrogen, testosterone) Endocrine system Mammary ducts & lobules Why It Happens: Hormonal Causes During puberty, boys experience shifts in hormone levels. Normally, testosterone levels rise, but for a period, estrogen (the hormone often associated with breast growth) can also temporarily increase or become more active relative to testosterone. This hormone imbalance can trigger the growth of breast tissue. Signs and Symptoms Pubertal gynecomastia is a common condition during adolescence, usually caused by temporary hormonal imbalances—specifically, a relative increase in estrogen compared to testosterone. Recognizing the signs early can help distinguish it from other conditions that may require medical attention. Typical signs include: Swelling around the nipple area – This is often the first noticeable change. The tissue directly beneath the nipple may appear enlarged or puffy. Firm or rubbery tissue under the areola – Unlike general fat accumulation, the growth in gynecomastia feels firm or rubbery to the touch. It is usually concentric around the nipple. Unilateral or bilateral enlargement – Gynecomastia may affect just one breast (unilateral) or both breasts (bilateral). In some cases, one side may be slightly larger than the other. Mild tenderness or sensitivity – Some adolescents experience discomfort, soreness, or tenderness, particularly when touched or during physical activity. Other less common symptoms may include: Slight asymmetry as the tissue develops unevenly Occasional itching or tingling around the nipple due to stretching skin Timeline: Symptoms usually peak within 6–12 months after onset and tend to gradually resolve over 1–2 years as hormone levels stabilize during puberty. In most cases, the swelling diminishes naturally without medical intervention, though persistent or severe cases may require evaluation by a healthcare professional. Common Ages and Who Gets It Pubertal gynecomastia is a very common phenomenon during adolescence, affecting a substantial proportion of boys. Studies suggest that up to 65% of adolescent males may experience some degree of breast tissue enlargement during puberty. Typical age range: Most cases appear between ages 13 and 16, which corresponds with the rapid hormonal changes of early to mid-adolescence. In some boys, gynecomastia may develop slightly earlier (11–12 years) or later (17–18 years), depending on the timing of puberty and individual growth patterns. Who is more likely to develop it: Rapid pubertal changes: Boys who experience fast growth or sudden hormonal shifts are more prone to temporary breast tissue enlargement. Body composition: Higher body fat can make breast tissue more noticeable. In some cases, what appears as gynecomastia may be a combination of fatty tissue and glandular growth, sometimes called “pseudo-gynecomastia.” Family history: Genetics can play a role. If a father, brother, or other close male relatives experienced pubertal gynecomastia, there may be a higher likelihood of occurrence. Certain medications or supplements: Drugs such as some anti-androgens, steroids, or medications for acne, heart conditions, or mental health, as well as herbal supplements containing phytoestrogens, can contribute to breast tissue growth in boys. Key point: Pubertal gynecomastia is generally temporary and self-limiting, with most cases resolving within 1–2 years as hormone levels stabilize. While it can affect boys of different ages and body types, awareness of risk factors can help parents and teens distinguish normal development from conditions that require medical evaluation. How Doctors Diagnose Pubertal Gynecomastia An evaluation usually includes: Medical history review — questions about onset, pain, medications. Physical exam — checking breast tissue size and consistency. Hormone tests — if atypical symptoms occur. Imaging (rarely) — ultrasound or mammogram to rule out other causes. Diagnosis focuses on distinguishing true glandular growth from fat tissue or rare serious conditions. When to Seek Medical Advice While pubertal gynecomastia is usually a normal, temporary condition that resolves on its own, it’s important to monitor changes carefully. You should contact a healthcare provider if any of the following occur: Rapid or severe breast enlargement – Sudden or pronounced growth may indicate an underlying hormonal imbalance or other medical condition that requires evaluation. Significant pain or discomfort – Mild tenderness is common, but severe pain, persistent soreness, or discomfort that interferes with daily activities should be assessed by a doctor. Hard, fixed lumps or irregular masses – Most pubertal gynecomastia feels soft or rubbery, so firm, immovable lumps may signal other conditions, including tumors, that need prompt medical attention. Signs of infection – Redness, warmth, swelling, or discharge from the nipple can indicate an infection or inflammation and should not be ignored. Symptoms persisting beyond 2 years – If breast tissue does not regress naturally after a couple of years, evaluation is recommended to rule out persistent hormonal imbalances or other causes. Hormone-related symptoms – Delayed or early puberty, unusual growth patterns, or changes in body hair may suggest an underlying endocrine issue that requires investigation. Additional Considerations:Even though most cases of pubertal gynecomastia are harmless, seeking advice can provide reassurance and guidance on management, lifestyle adjustments, or treatment if necessary. A healthcare provider may perform: Physical examination Hormonal testing Imaging (e.g., ultrasound) if a lump is suspicious Bottom line: Medical consultation is recommended whenever there is uncertainty, rapid changes, or persistent discomfort, as early assessment can prevent complications and ease anxiety. Treatments and Management Options In many cases, no active treatment is
10 Cara Kecilkan Punggung Secara Berkesan di Malaysia

Nak pakai seluar jeans kegemaran tapi sangkut di bahagian punggung? Jangan risau, anda tidak bersendirian. Ramai rakyat Malaysia mencari cara kecilkan punggung yang bukan sahaja berkesan, tapi juga selamat dan praktikal untuk gaya hidup kita yang kaya dengan makanan sedap! Ingin cara kecilkan punggung yang pantas dan selamat? GLOJAS Specialist Clinic menawarkan teknologi terkini untuk membentuk kontur badan idaman anda dengan hasil yang nampak semula jadi dan memukau oleh doktor pakar. Apa Itu Punggung Besar & Punca Utama Punggung yang besar selalunya disebabkan oleh pengumpulan tisu adiposa (lemak) di bahagian bawah badan. Walaupun bentuk badan “pear” dianggap sihat oleh sesetengah pakar, namun lemak yang berlebihan boleh membuatkan kita rasa kurang yakin. Faktor Genetik & Bentuk Badan Genetik memainkan peranan besar dalam menentukan di mana badan anda menyimpan lemak. Jika ahli keluarga anda cenderung mempunyai pinggul yang lebar, kemungkinan besar anda juga akan mewarisi struktur tulang dan taburan lemak yang sama. Lemak Berlebihan di Kawasan Punggung Lemak subkutaneus adalah lemak yang berada tepat di bawah kulit. Kawasan punggung dan paha merupakan “kawasan simpanan” utama bagi wanita kerana faktor biologi untuk persediaan kehamilan dan penyusuan. Gaya Hidup, Diet & Kurang Aktiviti Fizikal Tabiat suka makan makanan berlemak (seperti nasi lemak atau roti canai setiap pagi) tanpa melakukan aktiviti fizikal akan menyebabkan kalori berlebihan disimpan sebagai lemak. Pekerjaan pejabat yang memerlukan anda duduk terlalu lama juga boleh melemahkan otot gluteus. Hormon & Perubahan Berat Badan Hormon estrogen sangat mempengaruhi pengumpulan lemak di bahagian bawah badan. Perubahan hormon semasa akil baligh, kehamilan, atau menopaus boleh menyebabkan saiz punggung berubah secara drastik. Cara Kecilkan Punggung Secara Semula Jadi Tiada jalan pintas yang ajaib, tetapi kombinasi pergerakan yang betul boleh membuahkan hasil yang sangat memuaskan. Senaman Fokus Untuk Mengecilkan Punggung Untuk “tone up” otot, anda perlu melakukan senaman kekuatan. Squats, lunges, dan glute bridges adalah senaman wajib. Walaupun ia tidak membakar lemak secara setempat (spot reduction), otot yang pejal akan membuatkan punggung nampak lebih kecil dan kemas. Senaman Kardio Paling Berkesan Kardio adalah kunci untuk membakar kalori keseluruhan. Berlari, berbasikal, atau mendaki (hiking) adalah antara senaman membakar lemak yang paling efektif untuk mengecilkan bahagian bawah badan. Regangan & Postur Badan Kadangkala, punggung nampak lebih besar disebabkan oleh Anterior Pelvic Tilt (punggung tertonggok ke belakang). Melakukan regangan hip flexors secara rutin boleh membetulkan postur dan memberikan ilusi badan yang lebih ramping. Tempoh & Kekerapan Senaman Yang Disarankan Konsistensi adalah kunci. Cuba sasarkan sekurang-kurangnya 150 minit aktiviti intensiti sederhana seminggu mengikut saranan World Health Organization untuk kesihatan optimum. Pemakanan Untuk Kecilkan Punggung Abs are made in the kitchen! Begitu juga dengan punggung yang idaman. Makanan Yang Perlu Dikurangkan Kurangkan pengambilan gula ringkas, minuman manis, dan makanan diproses. Garam berlebihan juga perlu dielakkan kerana ia menyebabkan “water retention” yang membuatkan badan nampak bengkak. Diet Rendah Lemak & Kalori Fokus kepada pengambilan protein tanpa lemak, sayur-sayuran hijau, dan karbohidrat kompleks seperti nasi perang atau oat. Diet seimbang membantu badan membakar simpanan lemak sedia ada untuk tenaga. Contoh Pelan Pemakanan Harian Sarapan: Telur hancur dengan roti bijirin penuh. Makan Tengah Hari: Ayam bakar, ulam-ulaman, dan separuh senduk nasi putih. Makan Malam: Sup ikan dengan sayur sawi. Peranan Air & Metabolisme Minum air secukupnya membantu melancarkan sistem pencernaan dan meningkatkan kadar metabolisme. Air juga membantu otot berfungsi dengan lebih baik semasa bersenam. Rawatan Estetik Untuk Kecilkan Punggung di Malaysia Bagi mereka yang mahukan hasil lebih pantas tanpa pembedahan, teknologi moden kini ada jawapannya. Fat Reduction Non-Surgical Rawatan non-invasif semakin popular di klinik estetik sekitar Kuala Lumpur dan Selangor. Ia tidak memerlukan waktu pemulihan yang lama (no downtime). Teknologi Pelangsingan Badan (RF, Ultrasound, Cryolipolysis) Cryolipolysis (CoolSculpting): Membekukan sel lemak sehingga mati dan disingkirkan secara semula jadi oleh badan. Radiofrequency (RF): Menggunakan haba untuk menegangkan kulit dan mengurangkan selulit. Ultrasound: Memecahkan dinding sel lemak menggunakan gelombang bunyi. Kelebihan & Kekangan Rawatan Tanpa Pembedahan Kelebihannya ialah prosedur ini tidak menyakitkan dan selamat. Namun, kekangannya ialah anda mungkin memerlukan beberapa sesi untuk nampak hasil yang ketara dan kosnya boleh menjadi agak tinggi. Pembedahan Untuk Mengecilkan Punggung Jika kaedah semula jadi dan estetik ringan tidak mencukupi, prosedur perubatan adalah pilihan terakhir. Liposuction Punggung Liposuction adalah prosedur pembedahan untuk menyedut keluar lemak degil secara terus. Ini adalah cara paling drastik untuk mengubah bentuk badan dalam masa singkat. Siapa Calon Yang Sesuai Calon terbaik adalah individu yang mempunyai berat badan stabil tetapi mempunyai lemak degil yang tidak hilang dengan diet atau senaman. Anda juga perlu berada dalam tahap kesihatan yang baik. Proses, Risiko & Tempoh Pemulihan Seperti mana-mana pembedahan, terdapat risiko jangkitan atau lebam. Pemulihan biasanya mengambil masa 2 hingga 4 minggu sebelum anda boleh kembali melakukan aktiviti lasak. Anda boleh merujuk portal MyHealth KKM untuk maklumat lanjut mengenai prosedur kosmetik di Malaysia. Hasil Sebelum & Selepas Rawatan Hasil liposuction adalah sangat ketara, namun ia memerlukan penjagaan rapi seperti memakai compression garment untuk memastikan kulit mengecut dengan cantik. Cara Mengecilkan Punggung Dengan Selamat Keselamatan harus menjadi keutamaan anda sebelum memulakan mana-mana regimen baru. Kesilapan Biasa Yang Perlu Dielakkan Ramai orang tersilap dengan mengambil produk “kurus” yang tidak berdaftar. Produk ini selalunya mengandungi bahan terlarang yang boleh merosakkan buah pinggang. Kepentingan Nasihat Pakar Sebelum memulakan senaman berat atau rawatan estetik, berbincanglah dengan doktor atau pakar kecergasan bertauliah untuk memastikan kaedah tersebut sesuai dengan kondisi jantung dan sendi anda. Keselamatan & Jangkaan Realistik Fahami bahawa badan manusia memerlukan masa untuk berubah. Jangan terpedaya dengan iklan “kecilkan punggung dalam 3 hari”. Matlamat yang sihat adalah penurunan yang konsisten dan kekal. Berapa Lama Untuk Nampak Hasil Mengecilkan Punggung Sabar itu separuh daripada kejayaan! Faktor Yang Mempengaruhi Keputusan Kadar metabolisme, umur, dan tahap aktiviti harian mempengaruhi kepantasan anda nampak hasil. Orang muda biasanya nampak kesan lebih cepat berbanding mereka yang lebih berusia. Senaman vs Rawatan Estetik Senaman memerlukan masa (3-6 bulan), manakala rawatan estetik seperti CoolSculpting mungkin menampakkan hasil dalam masa 8-12 minggu selepas satu sesi. Konsistensi & Penjagaan Jangka Panjang Walaupun anda sudah berjaya mengecilkan punggung, lemak boleh kembali jika anda tidak menjaga pemakanan. Jadikan gaya hidup sihat sebagai rutin harian, bukan sekadar “projek jangka pendek”. Soalan Lazim Tentang Cara Kecilkan Punggung
Yo-Yo Dieting in Malaysia: Causes, Effects & How to Stop the Weight Cycle

Let’s be real: we’ve all been there. You see a wedding on the calendar or a beach trip to Langkawi, and suddenly, it’s all about the “cabbage soup diet” or skipping rice for two weeks. You lose five kilos, feel like a champ, and then—boom. A few months later, the weight is back, plus a little extra. Break the yo-yo dieting cycle at GLOJAS Specialist Clinic. We offer medically supervised weight loss solutions, including Ozempic and Mounjaro or even Liposuction Surgery, to help you achieve sustainable results safely. What Is Yo-Yo Dieting? Yo-Yo Dieting Meaning and Definition Yo-yo dieting is the process of losing weight, typically through restrictive means, only to regain it shortly after. It’s a cyclical pattern that feels like a never-ending loop of “starting again on Monday.” Why Yo-Yo Dieting Is Also Called Weight Cycling Scientists often call it weight cycling because your body weight moves up and down like a wave. It’s not just a fluctuation of a few grams; it’s the repeated loss and gain of significant body mass, which can take a toll on your internal systems. How Common Is Yo-Yo Dieting in Malaysia? Diet Culture and Weight Loss Trends in Malaysia With Malaysia having one of the highest obesity rates in Southeast Asia, the pressure to “slim down fast” is intense. From detox teas sold on Instagram to extreme “no-carb” challenges, diet culture is booming in KL and beyond. Crash Diets vs Sustainable Weight Loss The problem is that most Malaysians opt for crash diets—short-term fixes for long-term problems. Sustainable weight loss is about shifting habits over years, not weeks, yet the allure of a “7-day transformation” remains hard to resist. What Causes Yo-Yo Dieting? Extreme Calorie Restriction and Fad Diets When you slash your calories too low, your body enters “starvation mode.” You’ll lose weight, sure, but your brain will eventually scream for energy, leading to a massive binge. Unrealistic Weight Loss Goals Trying to lose 10kg in a month isn’t just difficult; it’s biologically unsustainable. When we don’t hit these impossible targets, we give up entirely and revert to old habits. Emotional Eating and Stress Factors Work stress in busy hubs like PJ or Penang often leads to “healing” with food. According to the American Psychological Association, stress-related eating is a primary driver of weight fluctuations. Lack of Long-Term Weight Maintenance Plan Most people focus on the loss phase but have zero plan for the maintenance phase. Without a strategy for how to eat once the goal is reached, the weight inevitably creeps back. Signs You Are Experiencing Yo-Yo Dieting Repeated Weight Loss and Rapid Weight Regain If your wardrobe has three different sizes of jeans to accommodate your “up” and “down” months, you’re likely in the cycle. Constant Diet Hopping One month it’s Keto, the next it’s Intermittent Fasting, followed by a juice cleanse. If you can’t stick to one method for more than three weeks, it’s a red flag. Feeling Stuck in a Weight Loss Cycle That feeling of “I’ve been dieting for ten years but I’m heavier than when I started” is the classic hallmark of the yo-yo effect. Health Effects of Yo-Yo Dieting Impact on Metabolism and Fat Storage Every time you lose weight and regain it, your body becomes more “efficient” at storing fat as a survival mechanism. Muscle Loss and Reduced Metabolic Rate When you lose weight rapidly, you don’t just lose fat; you lose muscle. Since muscle burns more calories at rest, losing it effectively slows down your metabolism. Hormonal Imbalance and Appetite Regulation Weight cycling messes with leptin (the fullness hormone) and ghrelin (the hunger hormone). This makes you feel hungrier more often, even when you’ve eaten enough. Mental Health Effects and Body Image Issues The “failure” of regaining weight can lead to depression and low self-esteem. The National Eating Disorders Association highlights how chronic dieting can distort body perception and lead to disordered eating patterns. Long-Term Cardiovascular and Metabolic Risks Studies suggest that frequent weight fluctuations can put extra stress on the heart and increase the risk of Type 2 diabetes. Does Yo-Yo Dieting Make It Harder to Lose Weight? Metabolic Adaptation Explained Your body is smart. If you keep starving it, it lowers its Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) to save energy. This is why the last 5kg are always the hardest to shed. Insulin Resistance and Weight Regain Repeatedly gaining weight, especially around the midsection, can lead to insulin resistance, making it much harder for your body to process carbohydrates efficiently. Set Point Theory and Body Weight Regulation The Set Point Theory suggests your body has a “preferred” weight range. Rapid dieting fights against this biological thermostat, usually resulting in the body “fighting back” to return to its previous weight. Who Is Most at Risk of Yo-Yo Dieting? Overweight and Obese Individuals Those with more weight to lose are often targets for aggressive marketing of “fast-acting” supplements that trigger the cycle. Post-Pregnancy Weight Loss New moms often feel pressured to “bounce back” instantly, leading to restrictive diets that aren’t compatible with the demands of motherhood or breastfeeding. Busy Professionals and Sedentary Lifestyles in Malaysia The “office life” in Malaysia—long hours followed by late-night Mamak sessions—creates a perfect storm for erratic eating patterns. How to Stop Yo-Yo Dieting Permanently Adopting Sustainable Eating Habits Stop looking for a “diet” and start looking for a lifestyle. If you can’t imagine eating this way in five years, don’t start it today. Balanced Malaysian Diet for Long-Term Weight Control You don’t have to quit Malaysian food. Switch to Nasi Campur with more ulam and veggies, choose grilled over fried, and opt for Teh O Ais Limau (less sugar) instead of Teh Tarik. Importance of Protein, Fibre, and Portion Control Protein keeps you full, and fibre (from veggies and whole grains) keeps your digestion on track. Understanding portions is the “secret sauce” to eating what you love without the guilt. Building Consistent Exercise Routines Focus on strength training. Building muscle helps counteract the metabolic slowdown caused
Liposuction FAQs: Answers to Common Patient Questions

Liposuction FAQs in Malaysia If you’ve been hitting the gym in KL or eating clean in Penang but still can’t nudge those stubborn pockets of fat, you’ve probably searched for “liposuction in Malaysia.” It’s one of the most popular body contouring tools for a reason. But before you dive in, let’s clear up the confusion with this ultimate FAQ guide. What is liposuction? Liposuction is a surgical procedure designed to remove specific areas of “stubborn” fat that don’t respond to traditional diet and exercise. It’s not a weight-loss tool, but rather a body sculpting method to refine your silhouette. How does liposuction work? The surgeon makes tiny incisions in the target area and inserts a thin tube called a cannula. This tube is connected to a vacuum that suctions out the fat cells. Modern techniques often use ultrasound or laser energy to “melt” the fat first, making it easier to remove. Who is a good candidate for liposuction? The ideal candidate is someone within 30% of their ideal weight with firm, elastic skin. You should be in good health and have realistic goals. If you have significant loose skin, you might need a lift (like a tummy tuck) instead. What areas of the body can liposuction treat? Pretty much anywhere fat likes to hide! Common spots include: Abdomen and waist (love handles) Thighs and buttocks Upper arms and “bra fat” Chin and neckline Male chest (for gynecomastia) Is liposuction safe? When performed by a board-certified plastic surgeon in an accredited facility, it is very safe. However, like any surgery, it carries risks. The American Society of Plastic Surgeons emphasizes that choosing a qualified surgeon is the most important factor in ensuring safety. How much does liposuction cost in Malaysia? In 2026, prices in Malaysia are quite competitive. You can generally expect: Small areas (Chin/Arms): RM 6,000 – RM 12,000 Medium areas (Abdomen/Thighs): RM 12,000 – RM 22,000 Full Body/Multi-area: RM 25,000 – RM 45,000+ Costs vary based on the clinic’s location and the technology used (like VASER). How long does liposuction take? Usually between 1 to 3 hours, depending on how many areas are being treated and the volume of fat being removed. What is the recovery time after liposuction? Most people return to light desk work within 3 to 7 days. However, you’ll need to avoid strenuous exercise for about 4 to 6 weeks while your body heals internally. When will I see the results of liposuction? You’ll see a difference immediately, but the “wow” factor happens after the swelling goes down. Most patients see final results between 3 to 6 months post-op. Will liposuction leave scars? The incisions are tiny (usually less than 1cm). While they leave small marks, these are typically placed in natural skin folds or hidden areas and fade significantly over time. Does liposuction hurt? The procedure itself is done under anesthesia (local or general), so you won’t feel a thing. Afterward, it feels like a very intense workout—soreness and tenderness are normal for the first week. How long does swelling last after liposuction? The bulk of the swelling subsides within 4 to 6 weeks, but minor residual swelling can linger for a few months as the skin molds to your new contour. Can liposuction remove cellulite? Unfortunately, no. Liposuction removes deep fat, while cellulite is caused by bands of connective tissue near the surface. It may even make cellulite look slightly more prominent if the skin is thin. Will fat come back after liposuction? The fat cells removed are gone forever. However, if you gain significant weight, the remaining fat cells in your body can still expand. Staying active is key! Is liposuction a weight loss solution? Definitely not. It’s for contouring, not shedding kilograms. In fact, most surgeons will only remove a maximum of about 5 liters of fat in one session for safety reasons. Can liposuction be combined with other cosmetic procedures? Yes! It’s often paired with a Fat Transfer (moving the fat to the breasts or buttocks) or a Tummy Tuck to remove excess skin. What are the risks and side effects of liposuction? Common side effects include bruising, swelling, and temporary numbness. Rare risks include infection, fluid accumulation (seromas), or contour irregularities. How do I choose the best liposuction clinic in Malaysia? Check the Malaysian Medical Council (MMC) to ensure the doctor is registered. Look for the LCP (Letter of Credentialing and Privileging), which is the official MOH license for aesthetic procedures. Is liposuction covered by insurance in Malaysia? In 99% of cases, no. It’s considered an elective cosmetic procedure. However, if it’s for a medical condition like lipoedema, you might have a case, though this is rare. What types of liposuction are available in Malaysia? Tumescent: The standard “wet” technique. VASER: Uses ultrasound to liquefy fat (very popular in KL). Laser-Assisted (Cool Lipo): Uses heat to break down fat. PAL (Power-Assisted): Uses a vibrating cannula for faster removal. Do I need to shave before liposuction? Usually, no. If hair removal is needed, the clinic staff will often handle it right before surgery to minimize the risk of nicks or infection. How should I prepare for liposuction in Malaysia? Stop smoking at least two weeks before, avoid blood-thinning supplements (like Vitamin E or Aspirin), and arrange for someone to drive you home from the clinic. What should I expect during a liposuction consultation? The surgeon will assess your skin elasticity, measure your fat deposits, and discuss which liposuction technique is best for your body type. Can men get liposuction in Malaysia? Absolutely. Men frequently get lipo for the abdomen, love handles, and “man boobs” (gynecomastia). Can liposuction be done without surgery? True liposuction is surgical. However, non-invasive alternatives like Cryolipolysis (fat freezing) exist, though they offer much more subtle results than surgery. How long do liposuction results last? They are permanent as long as you maintain a stable weight. Think of it as a permanent change to your body’s “blueprint.” What is the best age for liposuction? There’s no
Understanding Keloid Scars: A Guide to Removal and Care In Malaysia

Dealing with a scar that just won’t quit? You aren’t alone. In Malaysia, where our skin is often exposed to humidity and a variety of environmental factors, keloid scars are a common concern. Whether it’s a piercing gone wrong or a reminder of a past surgery, getting that smooth skin back is a top priority for many. GLOJAS Specialist Clinic Kuala Lumpur offers premier keloid scar treatment in Malaysia, utilizing expert steroid injections and advanced laser technology to effectively flatten scars and restore skin confidence. What Is a Keloid Scar? Definition and Medical Overview A keloid is essentially an overgrowth of scar tissue. Unlike a normal scar that stays within the lines of the original wound, a keloid is a “rule-breaker.” It keeps growing even after the wound has healed, creating a raised, firm, and often shiny bump on the skin. According to the American Academy of Dermatology, these are benign (non-cancerous) but can be quite stubborn to manage. How Keloid Scars Form When your skin is injured, your body rushes to produce collagen to bridge the gap. In some people, the “off switch” for collagen production fails. The body keeps pumping out protein, leading to a thickened, rubbery lesion that can eventually become larger than the initial injury. Keloid Scar vs Hypertrophic Scar It’s easy to mix them up! A hypertrophic scar stays within the boundaries of the original wound and often flattens over time. A keloid, however, spreads like wildfire beyond the original cut and rarely disappears on its own without medical intervention. Causes and Risk Factors of Keloid Scars Genetic and Skin Type Factors Genetics play a huge role. If your parents have keloids, you’re more likely to develop them. Research on keloid genetics suggests that certain genes influence how our skin responds to trauma. Common Triggers (Acne, Surgery, Piercing, Burns) Anything that breaks the skin can trigger a keloid. This includes: Acne: Especially deep cystic acne on the jawline or back. Piercings: Earlobes are a prime target. Surgery: C-section scars or heart surgery incisions. Burns: Deep thermal or chemical burns. Who Is Most Prone to Keloid Scars in Malaysia In Malaysia, we see a higher prevalence among individuals with darker skin tones, including those of Malay, Indian, and certain Chinese descents. Higher melanin levels are often linked to a more aggressive fibroproliferative response (aka, more scar tissue). Common Areas Affected by Keloid Scars Keloid Scars on Face and Jawline This is often the most distressing area. Jawline keloids are frequently caused by severe acne and can affect one’s confidence significantly. Chest, Shoulders, and Upper Back The skin here is under constant tension from movement, which makes it a “hot zone” for keloid growth after minor scratches or surgery. Ear Keloid Scars (Piercing-Related) Ever noticed a firm “grape-like” lump after an ear piercing? That’s a classic ear keloid. They can grow on the lobe or the cartilage (industrial piercings). Symptoms and Complications of Keloid Scars Pain, Itching, and Discomfort Keloids aren’t just a cosmetic issue. They can be itchy, tender, or even cause sharp pains as they grow and tighten the surrounding skin. Cosmetic and Psychological Impact Beyond the physical, keloids can affect mental well-being. Many people feel self-conscious about visible scars, leading to a search for effective aesthetic solutions. Progressive Growth and Recurrence Risk The trickiest part? If you cut a keloid out without the right follow-up, it might come back even bigger. This “rebound effect” is why professional treatment is vital. Diagnosis of Keloid Scars Clinical Examination by Specialist Most dermatologists in Malaysia can diagnose a keloid just by looking at it. They’ll check the texture, color, and whether it has spread beyond the original wound site. When Biopsy Is Required If the scar looks unusual or is growing rapidly in an odd way, a doctor might perform a skin biopsy to rule out more serious skin conditions. You can learn more about skin biopsy procedures to understand what to expect. Differentiating Keloid from Other Scar Types The specialist will distinguish it from hypertrophic scars or dermatofibromas to ensure the treatment plan actually works. Keloid Scar Treatment Options in Malaysia Steroid Injection for Keloid Scar The “gold standard.” Corticosteroid injections help flatten the scar and reduce itching by breaking down the excess collagen. Laser Treatment for Keloid Scar Vascular lasers (like Pulsed Dye Laser) target the blood vessels feeding the scar, reducing redness and shrinking the tissue. Cryotherapy (Freezing Treatment) This involves using liquid nitrogen to freeze the keloid from the inside out. It’s effective for smaller keloids, though it may cause some skin lightening. Surgical Removal of Keloid Scar For very large keloids, surgery is an option, but it is always paired with other treatments (like injections) to prevent the scar from returning. Combination Therapy for Severe Keloids The best results usually come from a “cocktail” approach—combining lasers, injections, and silicone sheets. Advanced Medical and Aesthetic Treatments Silicone Gel and Pressure Therapy Applying silicone sheets or pressure earrings helps hydrate the scar and physically prevents it from rising. Radiofrequency and Energy-Based Devices Newer tech uses radiofrequency to remodel the collagen deep within the skin without the downtime of traditional surgery. Post-Treatment Scar Modulation Therapy This involves ongoing care to ensure the skin remains supple and the collagen fibers stay organized. Recovery and Aftercare for Keloid Scar Treatment Healing Timeline and Expected Results Don’t expect an overnight miracle. Most treatments require 4 to 8 sessions spaced weeks apart. You’ll notice the scar softening first, followed by flattening. Reducing Recurrence After Treatment The secret to success is consistency. Skipping an injection session can allow the keloid to start growing again. Post-Treatment Lifestyle and Skincare Advice Keep the area out of the sun! UV rays can darken the scar permanently. Using a high-quality SPF is non-negotiable. Keloid Scar Treatment Results and Success Rates Visible Improvement and Symptom Relief Most patients see a 50% to 80% reduction in scar height and almost total relief from itching and pain. Factors Affecting Treatment Outcome Your age, skin type, and
Man Boobs in Malaysia: Causes, Treatments & Prevention Guide

Let’s be honest—it’s a topic many Malaysian men think about but few want to discuss over teh tarik. Whether you call them “man boobs,” “moobs,” or use the medical terms, carrying extra tissue in the chest area can be a major hit to your confidence, especially during a beach trip to Langkawi or a session at the gym. In this guide, we’re breaking down everything you need to know about this common condition, from the science behind it to the local treatment options available in Malaysia. What Are Man Boobs? Definition & Medical Context In simple terms, “man boobs” refers to an enlargement of the male breast tissue. While it’s often played off as a joke in movies, for many men, it’s a source of genuine physical and emotional discomfort. Medically, it usually falls into one of two categories based on what exactly is causing the volume. Gynecomastia vs Pseudogynecomastia: What’s the Difference? It’s important to distinguish between the two because the treatments are very different: Gynecomastia: This is the growth of actual glandular breast tissue. It’s usually caused by a hormonal imbalance (too much estrogen or too little testosterone). If you feel a firm lump behind the nipple, it’s likely gynecomastia. Pseudogynecomastia: This is simply fat accumulation in the chest area, common in men who are overweight. There is no hard glandular tissue involved; it’s just soft adipose tissue. How Common Are Man Boobs in Malaysia? You aren’t alone. Data suggests that up to 30% to 60% of men worldwide experience some form of gynecomastia in their lifetime. In Malaysia, rising obesity rates—with Malaysia often cited as one of the heaviest nations in Southeast Asia—have led to a significant increase in pseudogynecomastia cases among local men. Causes of Man Boobs Understanding the “why” is the first step toward the “how” of fixing it. Hormonal Imbalance & Endocrine Factors The male body produces both testosterone and estrogen. When the ratio flips and estrogen becomes too high, breast tissue grows. This is common during puberty (when hormones are haywire) and later in life as testosterone naturally dips. Weight Gain, Obesity & Fat Distribution Malaysia is a food paradise, but our love for nasi lemak and char kway teow can lead to weight gain. Fat cells don’t just sit there; they actually produce aromatase, an enzyme that converts testosterone into estrogen, creating a vicious cycle of breast tissue growth. Medications & Drug-Induced Causes Certain medications can trigger chest growth as a side effect. According to the Mayo Clinic, common culprits include certain antidepressants, blood pressure medications, and even some antibiotics. Underlying Medical Conditions In some cases, moobs are a symptom of something else, such as: Kidney or liver failure. Thyroid issues. Hypogonadism (low testosterone). Symptoms & When to See a Doctor Physical Signs to Watch For The most obvious sign is swollen breast tissue. This might happen in just one breast (unilateral) or both (bilateral). You might notice the area looks “pointy” or feels softer than the surrounding muscle. Pain, Tenderness & Other Symptoms True gynecomastia often comes with sensitivity or tenderness. If your chest feels sore when your shirt rubs against it or when you apply pressure, it’s a sign that glandular tissue is active. Red Flags: Serious Conditions to Rule Out While rare, male breast cancer does exist. According to the American Cancer Society, you should see a doctor immediately if you notice: A hard, fixed lump. Nipple discharge. Skin dimpling or puckering on the chest. Diagnosis: How Man Boobs Are Evaluated Medical History & Physical Exam Your GP or a specialist (like an endocrinologist) will ask about your diet, gym supplements (like steroids, which are a major cause), and medications. They will perform a physical exam to feel the consistency of the tissue. Blood Tests & Hormone Panels Doctors often order blood work to check your levels of testosterone, estrogen, and prolactin. This helps determine if an internal hormonal shift is the root cause. Ultrasound & Imaging Studies If the doctor feels a suspicious lump, they may recommend an ultrasound or a mammogram. This is the gold standard for distinguishing between fat, glandular tissue, and potentially harmful tumors. Treatment Options for Man Boobs in Malaysia Lifestyle Changes: Diet & Exercise If the cause is pseudogynecomastia (fat), the first line of defense is a caloric deficit. Focus on high-protein Malaysian favorites like ayam bakar while skipping the sugary teh ais. High-intensity interval training (HIIT) is particularly effective for overall fat loss. Medications & Hormone Therapy If an imbalance is found, doctors might prescribe medications like Tamoxifen. While these are often used for breast cancer, they can help block estrogen’s effect on male chest tissue. Always consult a certified medical professional before starting any hormonal treatment. Surgical Solutions: Liposuction & Reduction Surgery For permanent glandular tissue or stubborn fat that won’t budge, surgery is an option. Liposuction: Removes excess fat. Excision: Removes the actual gland. Many plastic surgery clinics in Kuala Lumpur and Penang specialize in “Male Chest Contouring.” Cost Considerations & Local Clinics In Malaysia, the cost for gynecomastia surgery can range from RM 8,000 to RM 20,000, depending on the complexity and the clinic. Private hospitals like Gleneagles or specialized aesthetic clinics in Bangsar are popular choices for these procedures. Prevention & Healthy Habits Nutrition Strategies to Reduce Chest Fat Focus on “anti-estrogenic” foods. Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and cauliflower contain compounds that help the body process estrogen. The Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health emphasizes that a balanced diet rich in whole grains and lean proteins is key to maintaining a healthy hormonal profile. Exercise Routines for Targeted Results You can’t “spot reduce” fat, but you can build the muscle underneath to create a firmer look. Incorporate: Bench Presses (Flat and Incline). Push-ups. Chest Flies. Avoiding Substances That Can Contribute to Man Boobs Be wary of: Alcohol: Heavy drinking can affect the liver’s ability to clear estrogen. Anabolic Steroids: A very common cause among Malaysian bodybuilders. Certain Herbal Supplements: Some oils, like lavender or tea tree
How Gynecomastia Works: Medical Explanation in Malaysia

How Gynecomastia Works? Medical Explained Ever noticed some extra “padding” in the chest area that just won’t go away, no matter how many bench presses you do? You aren’t alone. In Malaysia, many men deal with this condition, often feeling a bit self-conscious about it. Let’s break down the science of what’s actually happening under the skin. What Is Gynecomastia? Medical Definition of Gynecomastia At its core, gynecomastia is the non-cancerous enlargement of male breast tissue. It’s not just “man boobs” or extra weight; it is a clinical condition where the glandular tissue—the firm stuff behind the nipple—grows due to a specific biological trigger. Gynecomastia vs Chest Fat (Pseudogynecomastia) It’s easy to confuse the two. Pseudogynecomastia is simply an accumulation of fat in the chest, often seen in guys carrying a few extra kilos. However, true gynecomastia involves the growth of actual breast glands. You can usually tell the difference by touch: fat feels soft, while glandular tissue feels like a firm, rubbery lump. How Gynecomastia Works in the Male Body Hormonal Imbalance Between Estrogen and Testosterone The male body produces both testosterone (the “male” hormone) and estrogen (the “female” hormone). Normally, testosterone keeps estrogen in check. Gynecomastia happens when the balance of these hormones tips. If your testosterone levels drop or your estrogen levels spike, the breast tissue receives a signal to start growing. How Breast Gland Tissue Develops and Enlarges When estrogen dominates, it binds to receptors in the breast area. This stimulates the ductal structures to branch out and the surrounding stroma to thicken. This is why the area right under the areola often feels tender, sensitive, or swollen during the early stages. Why Gynecomastia Can Be Unilateral or Bilateral Hormones travel through the whole body, but they don’t always affect both sides equally. While bilateral gynecomastia affects both breasts, unilateral gynecomastia (affecting just one side) is also very common. This usually happens because one side’s tissue is simply more sensitive to hormonal signals than the other. Biological Causes Behind How Gynecomastia Works Puberty-Related Hormonal Changes Puberty is a hormonal rollercoaster. Up to 60% of boys experience some form of breast swelling during their teens because their bodies are still figuring out the right testosterone-to-estrogen ratio. Luckily, for most Malaysian teenagers, this usually settles down on its own within a year or two. Age-Related Hormonal Decline As men get older, testosterone levels naturally begin to dip. At the same time, body fat often increases, and fat cells actually convert testosterone into estrogen. This “double whammy” makes gynecomastia in older men quite common as the hormonal gap widens. Medical and Metabolic Triggers Sometimes, it isn’t just age or puberty. Certain medications—like some anti-anxiety meds, hair loss treatments, or steroids—can disrupt how the body processes hormones. Additionally, underlying issues with the liver or kidneys can lead to unwanted growth. Types of Gynecomastia and How Each Works Glandular Gynecomastia This is “true” gynecomastia. It is characterized by firm, fibrous tissue directly under the nipple. It is strictly caused by the growth of the breast gland itself rather than weight gain. Fat-Dominant Gynecomastia Mostly seen in men with higher BMIs, this type is primarily composed of adipose (fat) tissue. While it looks like gynecomastia, there is very little actual glandular tissue present upon examination. Mixed Gynecomastia This is the most common type we see in clinics. It’s a combination of both excess fat and enlarged glandular tissue. To fix this, both the fat and the gland usually need to be addressed simultaneously. How Gynecomastia Progresses Over Time Early Development Stage In the first 6 to 12 months (the florid phase), the tissue is actively growing. This is often the stage where guys experience pain or a “burning” sensation in the chest. Stable and Fibrotic Stage If the hormonal issue isn’t fixed, the tissue becomes “fibrotic.” The soft, growing gland turns into tough, scarred tissue. At this point, the American Society of Plastic Surgeons notes that the growth is likely permanent and won’t shrink with diet or exercise alone. How Gynecomastia Is Clinically Diagnosed Physical and Hormonal Assessment A doctor will start with a physical exam to feel the consistency of the tissue. They may also order blood tests to check your testosterone, estrogen, and thyroid levels to rule out underlying health issues. Imaging to Confirm Glandular Enlargement In some cases, an ultrasound or mammogram is used to get a clear picture of what’s inside. This helps the doctor confirm if it’s fat, a gland, or in very rare cases, something more serious that requires attention. How Gynecomastia Resolves or Persists Natural Regression vs Permanent Tissue Growth If the cause is puberty, the tissue usually disappears within six months to two years. However, if the tissue has been there for more than a year and has become fibrotic, it rarely goes away on its own. Factors That Influence Reversibility Several things determine if the condition will reverse: Duration: The longer it’s there, the more “set” the tissue becomes. Cause: If it’s caused by a medication you’ve stopped, it might shrink. Lifestyle: Reducing alcohol and avoiding certain supplements can help prevent it from worsening. How Treatment Targets the Mechanism of Gynecomastia Medical Management Based on Hormonal Cause If caught very early, doctors might prescribe Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs) like Tamoxifen. These drugs block estrogen from “talking” to the breast tissue, potentially halting the growth before it becomes permanent. Surgical Correction of Glandular Tissue For most men, the gold standard is surgery. This involves liposuction to remove the fat and a small incision to physically excise the firm gland. Since the gland is removed, the results are typically permanent. If you’re curious about the specific surgical techniques used today, you can find more details at WebMD.