Pubertal Gynecomastia: What Every Teen and Parent Needs to Know
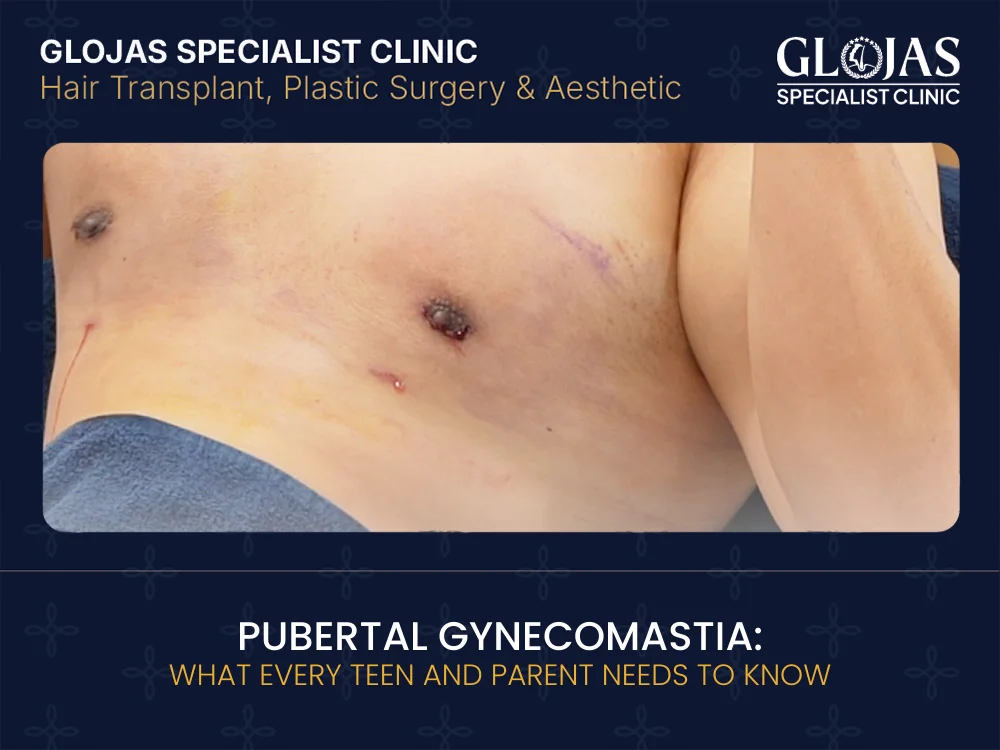
Pubertal gynecomastia is a common condition affecting many teenage boys during puberty. This guide breaks down what it is, why it happens, how it’s diagnosed, and when to seek help — all in an easy‑to‑understand, factual way for teens and families. Understanding Pubertal Gynecomastia Pubertal gynecomastia refers to the benign enlargement of male breast tissue during adolescence. It is usually seen between ages 12–18 and happens because of natural hormonal changes involving estrogen and testosterone during puberty. Though it can feel worrying, it is typically temporary and not a sign of serious illness. What Is Gynecomastia? Gynecomastia is the medical term for benign breast tissue growth in males. It differs from pseudogynecomastia, which involves mostly fat accumulation without glandular enlargement. In pubertal gynecomastia, the growth is due to increased breast gland tissue, not just fat. Key Entities in Pubertal Gynecomastia Breast gland tissue Hormones (estrogen, testosterone) Endocrine system Mammary ducts & lobules Why It Happens: Hormonal Causes During puberty, boys experience shifts in hormone levels. Normally, testosterone levels rise, but for a period, estrogen (the hormone often associated with breast growth) can also temporarily increase or become more active relative to testosterone. This hormone imbalance can trigger the growth of breast tissue. Signs and Symptoms Pubertal gynecomastia is a common condition during adolescence, usually caused by temporary hormonal imbalances—specifically, a relative increase in estrogen compared to testosterone. Recognizing the signs early can help distinguish it from other conditions that may require medical attention. Typical signs include: Swelling around the nipple area – This is often the first noticeable change. The tissue directly beneath the nipple may appear enlarged or puffy. Firm or rubbery tissue under the areola – Unlike general fat accumulation, the growth in gynecomastia feels firm or rubbery to the touch. It is usually concentric around the nipple. Unilateral or bilateral enlargement – Gynecomastia may affect just one breast (unilateral) or both breasts (bilateral). In some cases, one side may be slightly larger than the other. Mild tenderness or sensitivity – Some adolescents experience discomfort, soreness, or tenderness, particularly when touched or during physical activity. Other less common symptoms may include: Slight asymmetry as the tissue develops unevenly Occasional itching or tingling around the nipple due to stretching skin Timeline: Symptoms usually peak within 6–12 months after onset and tend to gradually resolve over 1–2 years as hormone levels stabilize during puberty. In most cases, the swelling diminishes naturally without medical intervention, though persistent or severe cases may require evaluation by a healthcare professional. Common Ages and Who Gets It Pubertal gynecomastia is a very common phenomenon during adolescence, affecting a substantial proportion of boys. Studies suggest that up to 65% of adolescent males may experience some degree of breast tissue enlargement during puberty. Typical age range: Most cases appear between ages 13 and 16, which corresponds with the rapid hormonal changes of early to mid-adolescence. In some boys, gynecomastia may develop slightly earlier (11–12 years) or later (17–18 years), depending on the timing of puberty and individual growth patterns. Who is more likely to develop it: Rapid pubertal changes: Boys who experience fast growth or sudden hormonal shifts are more prone to temporary breast tissue enlargement. Body composition: Higher body fat can make breast tissue more noticeable. In some cases, what appears as gynecomastia may be a combination of fatty tissue and glandular growth, sometimes called “pseudo-gynecomastia.” Family history: Genetics can play a role. If a father, brother, or other close male relatives experienced pubertal gynecomastia, there may be a higher likelihood of occurrence. Certain medications or supplements: Drugs such as some anti-androgens, steroids, or medications for acne, heart conditions, or mental health, as well as herbal supplements containing phytoestrogens, can contribute to breast tissue growth in boys. Key point: Pubertal gynecomastia is generally temporary and self-limiting, with most cases resolving within 1–2 years as hormone levels stabilize. While it can affect boys of different ages and body types, awareness of risk factors can help parents and teens distinguish normal development from conditions that require medical evaluation. How Doctors Diagnose Pubertal Gynecomastia An evaluation usually includes: Medical history review — questions about onset, pain, medications. Physical exam — checking breast tissue size and consistency. Hormone tests — if atypical symptoms occur. Imaging (rarely) — ultrasound or mammogram to rule out other causes. Diagnosis focuses on distinguishing true glandular growth from fat tissue or rare serious conditions. When to Seek Medical Advice While pubertal gynecomastia is usually a normal, temporary condition that resolves on its own, it’s important to monitor changes carefully. You should contact a healthcare provider if any of the following occur: Rapid or severe breast enlargement – Sudden or pronounced growth may indicate an underlying hormonal imbalance or other medical condition that requires evaluation. Significant pain or discomfort – Mild tenderness is common, but severe pain, persistent soreness, or discomfort that interferes with daily activities should be assessed by a doctor. Hard, fixed lumps or irregular masses – Most pubertal gynecomastia feels soft or rubbery, so firm, immovable lumps may signal other conditions, including tumors, that need prompt medical attention. Signs of infection – Redness, warmth, swelling, or discharge from the nipple can indicate an infection or inflammation and should not be ignored. Symptoms persisting beyond 2 years – If breast tissue does not regress naturally after a couple of years, evaluation is recommended to rule out persistent hormonal imbalances or other causes. Hormone-related symptoms – Delayed or early puberty, unusual growth patterns, or changes in body hair may suggest an underlying endocrine issue that requires investigation. Additional Considerations:Even though most cases of pubertal gynecomastia are harmless, seeking advice can provide reassurance and guidance on management, lifestyle adjustments, or treatment if necessary. A healthcare provider may perform: Physical examination Hormonal testing Imaging (e.g., ultrasound) if a lump is suspicious Bottom line: Medical consultation is recommended whenever there is uncertainty, rapid changes, or persistent discomfort, as early assessment can prevent complications and ease anxiety. Treatments and Management Options In many cases, no active treatment is
Hair Planting in Malaysia Cost: Complete Guide

Hair loss affects millions, and many people are searching for a reliable, permanent solution. One of the most popular options in Southeast Asia is a hair transplant — especially when priced reasonably and delivered by experienced surgeons. In this guide, we’ll dive deep into the hair planting in Malaysia cost, the factors that affect pricing, what to expect, and how to plan your procedure smartly. Understanding Hair Planting in Malaysia Cost The hair planting in Malaysia cost depends on your graft count, technique, clinic reputation, and surgeon experience. Clinics usually price procedures per graft — which means how many hair follicle units you need influences the final total. Most patients undergoing hair restoration in Malaysia can expect an approximate price range of: FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction): ~RM 8 – RM 15 per graft FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation): ~RM 5 – RM 12 per graft Advanced Techniques (e.g., DHI or robotic FUE): Premium pricing RM 12+ per graft Total typical procedure totals often fall between RM 12,000 to RM 35,000+, but more extensive sessions can even reach RM 45,000–RM 60,000 in high‑end clinics with advanced tech. Why Malaysia Offers Competitive Value Malaysia is recognized as a top destination for medical tourism due to its combination of quality care, skilled English-speaking surgeons, modern clinics, and relatively affordable pricing compared to Western countries. For example: In the United States or Europe, hair transplants can cost 2–3 times more for similar graft counts. Regional competitors like Thailand or India may offer slightly lower prices, but Malaysia often balances affordability with high international standards. Patients benefit from not just Hair Planting in Malaysia Cost savings, but also professional care, modern facilities, and post-op support, making the investment in Malaysia a practical and reliable choice. 💡 Key Takeaway:When planning a hair transplant in Malaysia, it’s important to consider both price and quality. Cheaper procedures may compromise results, while premium clinics offer higher survival rates, better hairline design, and long-term satisfaction. Knowing the pricing structure up front ensures realistic expectations and a smooth, confident experience. How Hair Planting in Malaysia Cost Works 1. Cost Per Graft Model Most clinics quote a per graft price, not a flat fee. Each graft contains a small group of hair follicles — typically 1 to 4 hairs — and the total number needed is based on how much coverage you want. 2. Procedure Type FUE: Minimally invasive, less scarring, quicker healing — popular and priced higher. FUT: Strip method, more economical per graft in some cases but leaves a linear scar. DHI: Direct Hair Implantation with implanter pens — a more advanced, premium option. 3. Clinic Reputation & Location Clinics in major cities like Kuala Lumpur or Penang may charge more due to higher operational Hair Planting in Malaysia Cost and access to advanced equipment. 4. Surgeon Expertise Seasoned surgeons with credible certifications and strong results often command higher fees — and that’s usually worth it for natural look and higher graft survival. 5. Package Inclusions Some clinics include: Consultation appointments Medications and follow‑ups PRP (Platelet‑Rich Plasma) therapy add‑ons…while others may charge extras for these. Always ask what’s included in your quote. Typical Hair Planting in Malaysia Cost Breakdown (Realistic Examples) Understanding Hair Planting in Malaysia Cost can help you budget and compare clinics effectively. Prices depend on the technique used, the number of grafts required, the surgeon’s experience, and the clinic’s facilities. Below is a general guide based on graft count: Graft Count FUE Estimate FUT Estimate DHI Estimate 1,000 RM 8,000 – 12,000 RM 5,000 – 8,000 RM 12,000 – 18,000 2,000 RM 15,000 – 25,000 RM 8,000 – 13,000 RM 24,000 – 36,000 3,000+ RM 25,000 – 35,000+ RM 12,000 – 18,000 RM 36,000 – 54,000+ Note: These ranges are estimates. Final costs vary depending on clinic reputation, surgeon expertise, and your individualized consultation. 💡 Tip for Patients:When comparing costs, don’t just look for the cheapest option. A lower price may mean fewer guarantees on graft survival, less experienced surgeons, or limited follow-up care. Investing in a reputable clinic often leads to better long-term results and fewer complications. Hair Planting in Malaysia Cost: Is It Worth the Investment? Hair transplantation is not just a cosmetic procedure—it’s a long-term investment in your appearance, confidence, and overall quality of life. Unlike temporary solutions such as topical treatments, shampoos, or medications that require ongoing use, a hair transplant offers a more permanent solution to hair loss. While the upfront cost may seem significant, many patients find that over time, it can actually be more cost-effective than constantly buying non-surgical products or undergoing repeated therapies. 📌 Long-Term Benefits:A successful transplant can restore a natural-looking hairline and density, which often translates to improved self-esteem and a more youthful appearance. For many, the psychological benefits—feeling confident in social and professional settings—are priceless. 📌 High-Quality Care in Malaysia:Malaysia has become a popular destination for medical tourism, especially for hair transplantation. Clinics here often meet international standards, equipped with advanced technology and staffed by highly trained, English-speaking surgeons. Patients can expect professional consultations, modern facilities, and personalized care plans. 📌 Cost-Effectiveness Compared to Other Treatments:While non-surgical options like PRP, laser therapy, or hair growth products can add up over the years, a one-time transplant procedure may ultimately save money. Most patients only need maintenance treatments occasionally, rather than ongoing monthly expenses. 📌 Convenience and Support:Many Malaysian clinics provide comprehensive packages including pre-op consultation, surgery, and post-op follow-up. This makes the entire process smoother and less stressful for both local and international patients. 📌 Consider It a Lifestyle Investment:Think of a hair transplant not merely as a procedure, but as an investment in yourself. Improved confidence, reduced stress over hair loss, and the ability to enjoy a fuller, natural-looking head of hair are benefits that extend well beyond the monetary cost. In summary, while hair transplantation in Malaysia may require careful budgeting, the long-term rewards—in terms of appearance, self-confidence, and life satisfaction—often outweigh the initial expense. Choosing the Right Clinic and Surgeon Selecting the right clinic
Pico Laser Downtime: What to Expect After Treatment
Modern aesthetic treatments promise visible results with minimal interruption to daily life. One of the most common questions patients ask is about Pico Laser downtime. While pico laser technology is known for being gentle, understanding what happens after treatment helps set realistic expectations and ensures proper skin recovery. This guide explains downtime, recovery stages, factors that affect healing, and how pico laser compares to other laser treatments. What Is Pico Laser Downtime? Pico Laser downtime refers to the short recovery period after a pico laser treatment, during which the skin may experience redness, mild swelling, or sensitivity. Because pico laser delivers ultra-short pulses in picoseconds, it minimizes heat damage to surrounding tissue. As a result, downtime is significantly shorter than traditional laser treatments, allowing most patients to return to normal activities within one to two days. Why Pico Laser Has Minimal Downtime Pico laser technology works differently from older laser systems. Instead of relying mainly on heat, it uses photoacoustic energy to break pigment and stimulate collagen. Key reasons downtime is reduced: Ultra-short pulse duration (picoseconds) Less thermal injury to the skin Faster cellular recovery Lower risk of inflammation This makes pico laser downtime suitable for busy individuals who want results without extended recovery. Common Skin Reactions After Pico Laser Treatment Pico Laser is a non-ablative, high-precision laser, meaning it targets pigment and stimulates collagen without damaging the skin’s surface. Because of this, most post-treatment reactions are mild, short-lived, and completely normal—they actually indicate that your skin is responding to the laser energy. 1. Mild RednessImmediately after treatment, it’s common to experience mild redness, similar to a mild sunburn. This usually appears in the treated areas and typically subsides within 24–48 hours. In some cases, sensitive skin may remain slightly pink for up to 72 hours. 2. Slight SwellingA temporary swelling or puffiness may occur, especially around delicate areas like under the eyes or the cheeks. This usually resolves within a day or two and can be minimized with cool compresses if needed. 3. Warm or Tight Skin SensationYou may feel a warmth or tightness in the treated areas. This sensation is normal and indicates the laser is stimulating collagen and repairing skin tissues. It typically eases within hours after the session. 4. Temporary Dryness or FlakingAs the laser stimulates skin renewal, minor dryness or flaking may occur in the days following treatment. Gentle moisturizing and avoiding harsh scrubs or chemical exfoliants help maintain comfort and support healing. 5. Rare or Mild Bruising or Pinpoint Red SpotsIn some cases, tiny red dots or mild bruising can appear, particularly if the treatment involved multiple passes over the same area. These usually fade within a few days. Timeline for Recovery: Reaction Typical Duration Tips for Comfort Redness 24–48 hours Use gentle moisturizer, avoid heat exposure Swelling 24–48 hours Apply cold compress if needed Warm/tight sensation Few hours Avoid strenuous activity immediately after Dryness/flaking 2–5 days Hydrate and use soothing creams Pinpoint redness 1–3 days Avoid scratching, let skin heal naturally Key Takeaway:Most reactions are temporary and indicate that your skin is healing and responding to the treatment. With proper aftercare—like hydration, sun protection, and gentle skincare—these effects resolve quickly, allowing you to enjoy the benefits of Pico Laser with minimal downtime. Pico Laser Downtime Timeline First 24 Hours Redness and sensitivity are most noticeable Skin may feel warm or slightly swollen Makeup is usually avoided for the first day Day 2–3 Redness fades significantly Skin texture may feel dry or rough Most patients resume work and social activities Day 4–7 Skin tone appears brighter and more even Collagen stimulation continues beneath the surface Minimal visible signs of treatment remain Unlike aggressive resurfacing lasers, pico laser does not cause open wounds or heavy peeling. Factors That Affect Pico Laser Downtime While Pico Laser is known for minimal downtime, the recovery period can vary slightly between individuals. Several factors influence how your skin responds after treatment and how quickly it returns to normal. Understanding these factors can help set realistic expectations and optimize results. 1. Skin Sensitivity and TypeIndividuals with sensitive or reactive skin may experience longer-lasting redness or mild swelling after treatment. Darker skin types are also more prone to temporary pigmentation changes, so extra caution and gentler settings may be required to minimize downtime. 2. Treatment Intensity and SettingsThe energy level, pulse duration, and spot size chosen by the clinician directly affect how the skin reacts. Higher intensity settings can provide faster or more dramatic results but may also slightly increase redness or swelling for a day or two. 3. Target ConcernDifferent skin issues respond differently to Pico Laser: Pigmentation (sunspots, freckles): Usually mild redness for a few hours to a day. Melasma: May require lower energy and multiple sessions to avoid post-inflammatory pigmentation, which can slightly extend downtime. Acne scars & texture improvement: Treatments that involve multiple passes may cause temporary sensitivity or minor pinpoint redness for 1–2 days. 4. Number of Passes During TreatmentEach area treated requires “passes” of the laser. More passes increase the energy delivered to the skin, potentially intensifying results but also slightly extending recovery time. A skilled clinician balances the number of passes to maximize improvement while minimizing downtime. 5. Post-Treatment Skincare RoutineProper aftercare is crucial for reducing downtime and preventing complications. Gentle cleansing, adequate hydration, and strict sun protection can help the skin heal faster. Using harsh products or skipping sunscreen can prolong redness or irritation. Key Takeaway:Most patients experience mild redness, slight swelling, or temporary sensitivity, which typically resolves within 24–48 hours. Patients with sensitive skin or darker skin tones may notice slightly longer recovery, but downtime remains minimal compared to traditional laser treatments. Following your clinician’s advice closely ensures a smoother and faster recovery while maximizing the results of Pico Laser treatment. How Pico Laser Downtime Compares to Other Laser Treatments Pico Laser vs Q-Switched Laser Pico laser: shorter downtime, less heat damage Q-switched laser: higher risk of redness and pigmentation issues Pico Laser vs Fractional CO2 Laser Pico laser: minimal downtime
Is Liposuction Safe? Risk and Complication

Liposuction has been performed worldwide for decades. It is one of the most common cosmetic procedures for removing stubborn fat. Still, many people ask the same important question: Is liposuction safe? The short answer is yes—when done correctly, on the right patient, by a qualified doctor. Like any medical procedure, liposuction carries risks. Understanding these risks helps you make a confident and informed decision. This guide explains liposuction safety, potential complications, risk factors, and how to reduce them, using clear, evidence-based information. Is Liposuction Safe? What You Need to Know First Liposuction safe outcomes depend on three key factors: patient selection, surgical technique, and provider experience. Modern liposuction techniques have significantly improved safety, recovery time, and results compared to earlier methods. When performed by a trained and licensed surgeon in an accredited facility, liposuction is considered a low-risk cosmetic procedure for healthy individuals. What Is Liposuction? A Brief Overview Liposuction is a cosmetic surgical procedure that removes localized fat deposits that do not respond to diet or exercise. How Liposuction Works Small incisions are made in the skin A cannula loosens fat cells Fat is suctioned out Body contours are reshaped Common Types of Liposuction Tumescent liposuction Power-assisted liposuction (PAL) Ultrasound-assisted liposuction (UAL) Laser-assisted liposuction All modern techniques focus on controlled fat removal and patient safety. Why Liposuction Safety Has Improved Over Time Liposuction today is much safer than it was decades ago due to: Advanced surgical tools Better anesthesia protocols Improved fluid management Stricter patient screening Accredited surgical facilities According to global cosmetic surgery data, serious complications are rare when guidelines are followed. Who Is a Safe Candidate for Liposuction? Liposuction safety begins with proper patient selection. While the procedure is widely performed and generally safe, it is not suitable for everyone. The best outcomes—both medically and aesthetically—occur in patients who meet specific health and lifestyle criteria. Ideal Candidates You may be considered a safe candidate if you meet most of the following: Good overall healthNo active or uncontrolled medical conditions that could interfere with healing or anesthesia. Stable body weightIdeally within 20–30% of your target weight, with weight stability for several months. Liposuction is a body-contouring procedure, not a weight-loss solution. No serious chronic illnessesConditions such as controlled hypertension or mild asthma may be acceptable, depending on medical clearance. Non-smoker or willing to stop smokingSmoking increases the risk of poor wound healing, infection, and complications. Most surgeons require smoking cessation before and after surgery. Good skin elasticityFirm, elastic skin helps the body adapt smoothly to new contours after fat removal. Realistic expectationsUnderstanding what liposuction can and cannot achieve is key to patient satisfaction. Who May Not Be Suitable Liposuction may be unsafe or ineffective for individuals with the following: Severe obesityLiposuction is not designed to treat obesity or replace long-term weight management. Poor skin elasticitySignificant skin laxity may result in sagging or uneven contours after fat removal. Uncontrolled diabetesIncreases risks of infection, delayed healing, and poor surgical outcomes. Heart or lung diseaseThese conditions raise anesthesia and surgical risks. Bleeding disorders or use of certain medicationsCan increase the risk of excessive bleeding and complications. Weakened immune system or poor healing capacityMay compromise recovery and results. Why Medical Evaluation Is Critical A thorough pre-operative medical assessment is essential before liposuction. This typically includes: Medical history review Physical examination Blood tests and, when needed, cardiac or imaging evaluations Discussion of goals, risks, and expected outcomes This evaluation ensures patient safety and helps the surgeon determine whether liposuction is appropriate—or if alternative treatments would be safer and more effective. Is Liposuction Safe Under Local or General Anesthesia? Both anesthesia types can be safe when properly administered. Local Anesthesia Common for small areas Lower systemic risk Faster recovery General Anesthesia Used for larger treatment areas Requires anesthesiology monitoring Safe in accredited facilities The choice depends on treatment extent and patient health. Common Liposuction Risks (Usually Mild and Temporary) Most side effects are part of normal healing. Expected Short-Term Effects Swelling Bruising Soreness Temporary numbness Fluid drainage These symptoms usually resolve within weeks. Potential Liposuction Complications (Less Common) While uncommon, complications can occur. Possible Complications Infection Seroma (fluid accumulation) Irregular contours Prolonged swelling Delayed healing Proper technique and aftercare greatly reduce these risks. Rare but Serious Liposuction Risks Serious complications are rare but important to understand. Rare Risks Include Blood clots Fat embolism Excessive fluid loss Organ injury Adverse anesthesia reaction These risks increase when: Large fat volumes are removed Procedures are done in unlicensed facilities Surgery is performed by unqualified providers This is why choosing a certified surgeon is critical. How Much Fat Can Be Safely Removed? Safety guidelines limit fat removal to prevent complications. Small-volume liposuction: very low risk Large-volume liposuction: higher risk, requires monitoring Many surgeons follow strict volume limits Removing more fat does not mean better results. Safety always comes first. Is Liposuction Safe for Different Body Areas? Commonly Treated Areas Abdomen Thighs Arms Flanks Chin and neck Each area has different safety considerations, but liposuction is generally safe when performed properly. Post-Operative Care and Its Role in Safety Post-operative care is a critical part of liposuction safety. Even when surgery is performed flawlessly, poor aftercare can increase the risk of complications and compromise final results. Following your surgeon’s instructions closely supports proper healing, reduces swelling, and helps achieve smooth, long-lasting outcomes. Why Aftercare Matters After liposuction, your body needs time to heal and adapt to the new contours. Proper aftercare helps to: Minimize swelling and bruising Reduce the risk of infection and fluid buildup Support skin retraction and even contours Speed up recovery and improve comfort Neglecting post-operative care can delay healing and lead to avoidable complications. Important Aftercare Steps Wear compression garmentsCompression garments help control swelling, prevent fluid accumulation, and support the skin as it adjusts. They are usually worn continuously for the first few weeks, then part-time as advised by your surgeon. Attend all follow-up visitsScheduled follow-ups allow your surgeon to monitor healing, remove stitches or drains if needed, and detect early signs of complications before
Liposuction vs CoolSculpting: Which is Right for You?
Stubborn fat can be frustrating. Even with a healthy diet and regular exercise, some areas simply refuse to slim down. This is why body contouring treatments like Liposuction vs CoolSculpting remain highly popular worldwide. But choosing between them is not always simple. This guide breaks down Liposuction vs CoolSculpting in detail—how they work, how fast results appear, risks, recovery, costs, and who each treatment is best suited for—so you can make a confident, informed decision. Liposuction vs CoolSculpting: What’s the Fundamental Difference? When comparing Liposuction vs CoolSculpting, the main difference lies in invasiveness and fat removal method. Liposuction is a surgical procedure that physically removes fat cells, while CoolSculpting is a non-invasive treatment that freezes fat cells so the body can eliminate them naturally. Both target localized fat, but the experience, results, and recovery time differ significantly. What Is Liposuction? Liposuction is a cosmetic surgical procedure designed to remove stubborn fat deposits from specific areas of the body. How Liposuction Works Small incisions are made in the skin A thin tube (cannula) is inserted Fat cells are loosened and suctioned out Body contours are reshaped immediately Common Liposuction Techniques Tumescent liposuction Ultrasound-assisted liposuction (UAL) Power-assisted liposuction (PAL) Laser-assisted liposuction Liposuction has been performed safely for decades and is considered the gold standard for fat removal. What Is CoolSculpting? CoolSculpting is a non-surgical fat reduction treatment based on a technology called cryolipolysis. How CoolSculpting Works Controlled cooling targets fat cells Fat cells freeze and undergo natural cell death The body gradually removes them through the lymphatic system No needles, incisions, or anesthesia CoolSculpting is FDA-cleared and widely used for patients who prefer non-invasive options. Treatment Areas: What Can Each Address? Liposuction Treatment Areas Abdomen Flanks (love handles) Thighs Arms Chin and neck Back Chest (including gynecomastia) CoolSculpting Treatment Areas Abdomen Flanks Thighs Upper arms Double chin Bra fat Banana roll Liposuction can treat larger volumes of fat and more areas in a single session. Liposuction vs CoolSculpting: Speed of Results Liposuction Results Timeline Fat removal is immediate Swelling reduces over 4–8 weeks Final results visible in 3–6 months CoolSculpting Results Timeline Initial changes in 3–4 weeks Optimal results at 2–3 months Continued improvement up to 6 months Winner for faster, noticeable results: Liposuction Amount of Fat Removed: Liposuction vs CoolSculpting? Factor Liposuction CoolSculpting Fat removal per session High Moderate Sculpting precision High Moderate Large fat deposits Excellent Limited Small pockets of fat Excellent Good Liposuction removes fat cells directly, while CoolSculpting typically reduces 20–25% of fat thickness per session in treated areas. Downtime and Recovery: Liposuction vs CoolSculpting Liposuction Recovery Downtime: 5–14 days Compression garments required Swelling and bruising common Exercise restricted initially CoolSculpting Recovery Little to no downtime Mild redness or numbness Resume normal activities immediately CoolSculpting is often called a “lunchtime procedure”, while liposuction requires recovery planning. Pain and Comfort Level: Liposuction vs CoolSculpting Liposuction: Performed under local or general anesthesia. Post-procedure soreness is expected. CoolSculpting: Sensation of intense cold, pressure, and temporary numbness during treatment. Pain tolerance and comfort preference play a role in decision-making. Safety and Risks Liposuction Risks Infection Bleeding Fluid accumulation Irregular contours Anesthesia-related risks When performed by a qualified surgeon, complications are uncommon. CoolSculpting Risks Temporary numbness or tingling Redness or bruising Rare risk of paradoxical adipose hyperplasia Both procedures are considered safe when properly indicated. Cost Comparison Treatment Cost Structure Total Cost Liposuction One-time surgical fee Higher upfront CoolSculpting Per applicator/session Adds up over time CoolSculpting may seem more affordable initially, but multiple sessions can approach the cost of liposuction. Longevity of Results: Liposuction vs CoolSculpting Liposuction Liposuction removes fat cells permanently from targeted areas, creating immediate and noticeable contour changes. Key points to understand: Fat cells removed do not regenerate in treated areas Weight gain can still occur, causing remaining fat cells (in treated or untreated areas) to enlarge Results are typically long-lasting, especially when body weight remains stable Body proportions may change if significant weight gain occurs, even though treated areas usually accumulate less fat than before With a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and healthy habits, liposuction results can be maintained for many years or even decades. CoolSculpting CoolSculpting also permanently eliminates fat cells, but the process and timeline are different. What to expect: Destroyed fat cells do not return once the body naturally clears them Fat reduction is gradual, becoming visible over several weeks to months Results are more subtle compared to liposuction, as less fat is removed per session Maintenance treatments may be required, especially if weight fluctuates or new fat pockets develop CoolSculpting works best for long-term refinement when combined with consistent lifestyle habits. The Role of Lifestyle in Maintaining Results Regardless of the treatment chosen: Neither liposuction nor CoolSculpting prevents future weight gain Neither treatment replaces weight management, proper nutrition, or exercise Maintaining a stable weight helps preserve body contours and symmetry Ideal Candidate for Liposuction Liposuction is best suited for individuals who want significant, visible fat reduction in specific areas of the body. It is a surgical procedure, so proper candidate selection is crucial for both safety and results. You may be a good candidate for liposuction if you: Have moderate to large fat deposits that do not respond well to diet and exercise Desire dramatic and immediate results, often noticeable once swelling subsides Are close to your ideal body weight, as liposuction is a body-contouring procedure, not a weight-loss solution Have good skin elasticity, which helps the skin retract smoothly after fat removal Can tolerate downtime, including temporary swelling, bruising, and recovery time Are in good overall health, with no uncontrolled medical conditions that may affect healing Have realistic expectations, understanding that results enhance body contours rather than create perfection Liposuction is ideal for areas such as the abdomen, flanks, thighs, arms, and chin when more aggressive fat removal is required. Ideal Candidate for CoolSculpting CoolSculpting is a non-invasive fat reduction treatment that works by freezing fat cells. It is best for patients seeking subtle improvements without surgery. CoolSculpting may suit you if
CO2 Laser vs Microneedling: Which One Delivers Faster Results for Wrinkles?
Wrinkles are a natural part of aging, but modern aesthetic treatments now offer effective ways to soften lines and restore smoother skin. Among the most talked-about options are CO2 laser vs microneedling—two clinically proven procedures with very different approaches. This guide compares how they work, how fast results appear, and which option may be best for different skin goals. CO2 Laser vs Microneedling: Understanding the Core Difference When comparing CO2 Laser vs Microneedling, the main difference lies in how deeply and aggressively each treatment stimulates skin renewal. CO2 laser uses controlled thermal energy to resurface the skin, while microneedling relies on mechanical micro-injuries to trigger collagen production. Both aim to reduce wrinkles, improve texture, and boost collagen, but they vary significantly in intensity, downtime, and speed of visible results. What Is CO2 Laser Treatment? Fractional CO2 laser is a gold-standard resurfacing treatment used in dermatology and aesthetic medicine. It works by delivering precise columns of laser energy into the skin, removing damaged tissue and stimulating deep collagen remodeling. How CO2 Laser Works Vaporizes micro-columns of old skin Triggers wound healing response Stimulates collagen and elastin production Promotes new, smoother skin growth Wrinkles CO2 Laser Treats Best Deep facial wrinkles Static wrinkles (visible at rest) Crow’s feet and forehead lines Severe photoaging CO2 laser is often recommended for patients seeking dramatic skin rejuvenation with long-lasting results. What Is Microneedling? Microneedling, also known as collagen induction therapy, uses fine needles to create controlled microchannels in the skin. These tiny injuries stimulate the body’s natural healing process, increasing collagen and elastin over time. How Microneedling Works Creates micro-injuries in the dermis Activates fibroblast cells Improves skin texture gradually Enhances absorption of serums or PRP Wrinkles Microneedling Treats Best Fine lines Early signs of aging Mild textural irregularities Preventative anti-aging care Microneedling is popular due to its minimal downtime and suitability for most skin types. Which CO2 Laser vs Microneedling Delivers Faster Results for Wrinkles? If speed is your priority, CO2 laser delivers faster and more noticeable wrinkle reduction compared to microneedling. CO2 Laser Results Timeline Initial improvement: 7–14 days Visible wrinkle reduction: 3–4 weeks Continued collagen remodeling: up to 6 months Microneedling Results Timeline Subtle glow: 5–7 days Gradual improvement: 4–6 weeks Optimal results: after 3–6 sessions Winner for faster results: CO2 Laser Microneedling requires multiple treatments spaced weeks apart, while CO2 laser often produces significant improvement after one session. Downtime and Recovery Comparison CO2 Laser vs Microneedling Downtime is a key factor when choosing between CO2 laser vs microneedling. CO2 Laser Downtime Redness and swelling: 7–14 days Skin peeling and crusting Pinkness may last several weeks Strict sun avoidance required Microneedling Downtime Mild redness: 24–72 hours Minimal peeling Quick return to daily activities Microneedling wins for convenience, while CO2 laser requires planned recovery time. Safety and Skin Type Considerations CO2 Laser vs Microneedling CO2 Laser Best for Fitzpatrick skin types I–III Higher risk of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) in darker skin tones Requires experienced practitioner Microneedling Safe for all skin types (I–VI) Lower risk of pigmentation issues Suitable for sensitive skin For patients with darker skin tones, microneedling is often the safer first-line option. Pain Level and Comfort CO2 Laser: Moderate discomfort; usually performed with topical or local anesthesia Microneedling: Mild to moderate discomfort; numbing cream is typically sufficient Pain tolerance and comfort expectations should be discussed during consultation. Cost Comparison CO2 Laser vs Microneedling The total cost of treatment depends on the clinic’s expertise, device technology, treatment depth, and area treated. Prices below reflect typical ranges in Malaysia and may vary. CO2 Laser Estimated cost: RM3,000 – RM8,000 per session Number of sessions: Usually 1 session (occasionally a second for severe concerns) What you’re paying for: Deep skin resurfacing Strong collagen remodeling Significant improvement in wrinkles and scars Downtime considerations: Longer recovery period, which may add indirect costs (time off work, aftercare products) Overall value:Although the upfront cost is higher, CO2 laser can be more cost-effective long term for patients seeking dramatic improvement, as fewer sessions are required. Microneedling Estimated cost: RM500 – RM1,500 per session Number of sessions: Typically 3–6 sessions, spaced 4–6 weeks apart What you’re paying for: Gradual collagen stimulation Improved skin texture and tone Minimal downtime Downtime considerations: Very minimal, usually no disruption to daily routine Overall value:Microneedling has a lower entry cost, making it more accessible, but the total cost can accumulate over time due to multiple sessions. Which Is More Cost-Effective? CO2 laser: Higher upfront investment, faster and more dramatic results, fewer treatments Microneedling: Lower per-session cost, gradual improvement, higher cumulative cost over time Bottom line:If your goal is deep correction with fewer visits, CO2 laser may offer better long-term value. If you prefer budget flexibility and minimal downtime, microneedling may be the more practical choice. Longevity of Results CO2 Laser vs Microneedling The duration of results depends on treatment depth, skin condition, age, lifestyle, and post-treatment care. Proper skincare and sun protection play a major role in maintaining outcomes for both options. CO2 Laser Results duration: Often several years Why results last longer:CO2 laser triggers deep collagen remodeling, which continues to improve skin quality for months after treatment. Best for: Deep wrinkles Severe photoaging Acne scars and skin laxity Maintenance: Daily sun protection Medical-grade skincare Optional light maintenance treatments after 1–2 years Patients who follow good aftercare habits often enjoy long-lasting wrinkle reduction and firmer skin, particularly in areas with deeper lines. Microneedling Results duration: Shorter-term, typically 6–12 months Why maintenance is needed:Microneedling stimulates collagen at a more superficial level, producing gradual but less permanent structural changes. Best for: Fine lines Early aging Texture and pore refinement Maintenance: Repeat sessions every 6–12 months Consistent skincare to support collagen health Microneedling works best as a long-term maintenance treatment rather than a one-time corrective procedure. Key Takeaway CO2 laser delivers longer-lasting improvement, especially for deeper wrinkles and advanced skin aging. Microneedling provides subtle, natural enhancement that requires ongoing sessions to maintain results. Choosing between them depends on how dramatic and long-lasting you want your results to
CO2 Laser vs Erbium YAG: Which skin resurfacing treatment is right for your skin type?

Laser skin resurfacing has become one of the most effective ways to treat wrinkles, scars, and uneven skin texture. Among the most commonly compared options are CO2 Laser vs Erbium YAG. While both are powerful resurfacing lasers, they differ in depth, recovery time, and suitability for different skin types. This guide explains how each laser works and helps you decide which option aligns best with your skin needs. CO2 Laser vs Erbium YAG: Understanding the Key Differences When comparing CO2 Laser vs Erbium YAG, the primary difference lies in how deeply each laser penetrates the skin and how much heat it delivers. CO2 laser provides deeper thermal stimulation, while Erbium YAG offers more precise ablation with less heat spread. These differences directly affect results, downtime, and safety across skin types. Both lasers are widely used in dermatology and aesthetic medicine, but they are chosen for different clinical goals. What Is CO2 Laser Skin Resurfacing? CO2 laser skin resurfacing uses a carbon dioxide laser with a wavelength of 10,600 nm. This wavelength is strongly absorbed by water in the skin, allowing controlled removal of damaged tissue while stimulating deep collagen remodeling. How CO2 Laser Works Creates microthermal zones in the skin Removes damaged surface layers Delivers heat into the dermis Triggers long-term collagen production Skin Concerns Best Treated with CO2 Laser Deep wrinkles and folds Acne and surgical scars Severe sun damage Skin laxity CO2 laser is often considered the gold standard for dramatic skin rejuvenation. What Is Erbium YAG Laser Resurfacing? Erbium YAG laser operates at a wavelength of 2,940 nm, which is even more selectively absorbed by water. This allows precise ablation with minimal thermal damage to surrounding tissue. How Erbium YAG Works Removes thin layers of skin with accuracy Causes less heat diffusion Promotes faster epithelial healing Reduces risk of prolonged redness Skin Concerns Best Treated with Erbium YAG Fine lines and mild wrinkles Superficial scars Uneven skin tone Mild photoaging Erbium YAG is favored for patients seeking resurfacing with shorter downtime. Depth of Treatment: CO2 Laser vs Erbium YAG Depth is a major deciding factor. CO2 Laser: Penetrates deeper into the dermis, offering stronger collagen remodeling Erbium YAG: Treats more superficially with controlled ablation For advanced aging or deep scars, CO2 laser delivers more dramatic improvement. For early aging or texture refinement, Erbium YAG may be sufficient. Downtime and Recovery Comparison CO2 Laser vs Erbium YAG CO2 Laser Recovery Redness and swelling: 7–14 days Peeling and crusting Pinkness may last several weeks Erbium YAG Recovery Redness: 3–7 days Minimal crusting Faster return to daily activities Erbium YAG wins for shorter downtime, while CO2 laser requires more recovery time. Results Timeline and Longevity CO2 Laser vs Erbium YAG CO2 Laser Results Initial improvement: 2–3 weeks Continued collagen remodeling: up to 6 months Results can last several years Erbium YAG Results Faster visible improvement Gradual collagen stimulation May require maintenance treatments CO2 laser offers longer-lasting and more transformative results. Safety and Skin Type Considerations CO2 Laser vs Erbium YAG Skin type plays a crucial role when choosing between CO2 Laser vs Erbium YAG. CO2 Laser Safety Best suited for lighter skin tones (Fitzpatrick I–III) Higher risk of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) in darker skin Requires experienced practitioner Erbium YAG Safety Safer for a wider range of skin tones Lower risk of PIH Better option for sensitive skin Proper laser settings and aftercare are essential for both. Pain and Comfort Levels CO2 Laser: Moderate discomfort; often requires topical or local anesthesia Erbium YAG: Generally more comfortable; topical numbing is usually sufficient Comfort expectations should be discussed during consultation. Cost Comparison CO2 Laser vs Erbium YAG The cost of laser resurfacing treatments in Malaysia varies based on several factors, including the clinic’s reputation, doctor’s expertise, laser technology used, treatment area size, and depth of resurfacing required. While prices differ, understanding the general cost structure helps set realistic expectations. CO₂ Laser: Higher cost per sessionCO₂ laser treatments typically range at the higher end of the price spectrum due to their advanced technology and deeper skin penetration. Because results are more dramatic, many patients achieve their goals in fewer sessions, sometimes even a single treatment. This can make CO₂ laser more cost-effective in the long term for severe wrinkles or deep acne scars, despite the higher upfront cost. Erbium YAG: Lower cost per sessionErbium YAG treatments are usually more affordable per session, making them attractive for patients with mild to moderate skin concerns. However, multiple sessions may be required to achieve optimal results, especially for texture refinement and fine lines. When spread across several visits, the total cost may approach that of a single CO₂ laser treatment. Overall Value Consideration The true value is not based on price alone. It depends on: The severity of skin concerns The number of sessions needed Your downtime tolerance Desired speed and intensity of results Patients seeking dramatic, long-lasting improvement may find CO₂ laser offers better value despite higher costs, while those preferring gradual enhancement with minimal downtime may benefit more from Erbium YAG treatments. Who Is an Ideal Candidate for CO2 Laser? CO₂ laser resurfacing is a powerful treatment designed for individuals seeking significant skin rejuvenation and correction of advanced skin concerns. It is best suited for patients who are prepared for a more intensive procedure and recovery period. You may be an ideal candidate if you: Have deep wrinkles or scarsCO₂ laser is highly effective for treating deep acne scars, pronounced wrinkles, surgical scars, and severe sun damage. Its ability to penetrate deeper skin layers stimulates robust collagen remodeling and skin tightening. Want dramatic, long-lasting resultsCompared to milder laser treatments, CO₂ laser delivers more visible and longer-lasting improvements, often after a single session. Results continue to improve over several months as new collagen forms. Can tolerate downtime and recoveryCO₂ laser involves a longer healing period, including redness, swelling, crusting, and peeling. Downtime may range from one to two weeks, with residual redness lasting longer. This treatment is ideal for patients who can plan time off
The Ultimate Pico Laser Aftercare Guide
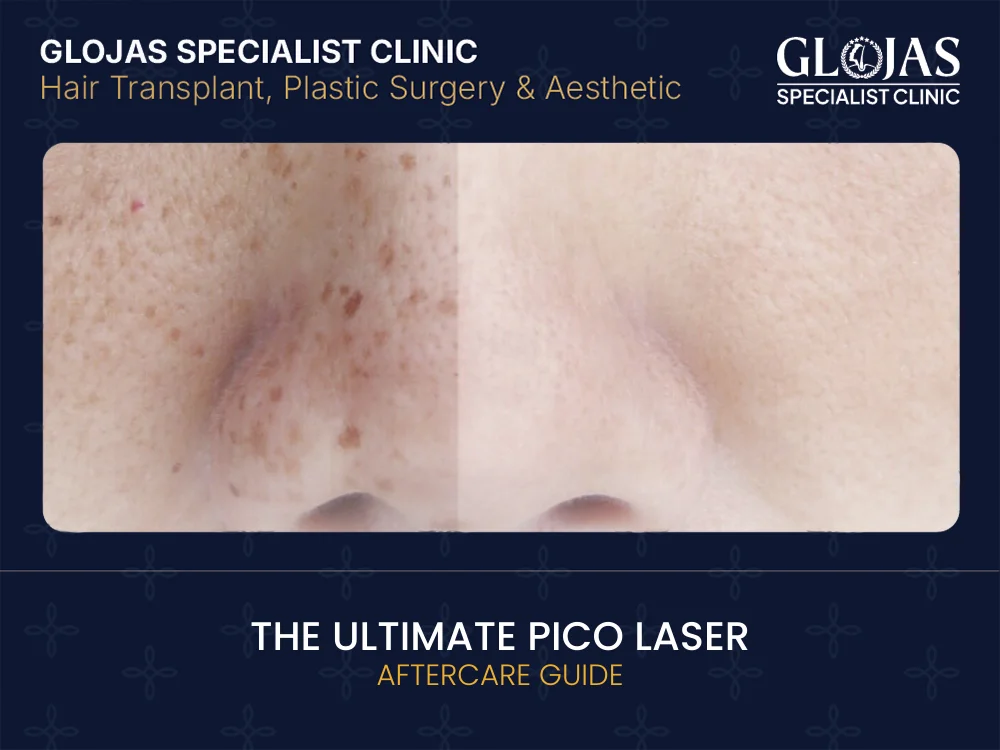
Pico laser is widely used for pigmentation, acne scars, and overall skin rejuvenation. While the technology is advanced and gentle, the treatment outcome does not depend on the laser alone. What you do after the procedure plays a major role in skin recovery and final results. This Ultimate Pico Laser Aftercare Guide explains what happens to your skin, what to do day by day, and how to protect your results for the long term. What Is Pico Laser Aftercare and Why Is It Important? Pico Laser Aftercare refers to the skincare steps and lifestyle adjustments needed after a pico laser treatment to support healing and prevent complications. Although pico laser uses ultra-short pulses that minimize heat damage, the skin still undergoes controlled inflammation. Proper Pico Laser aftercare helps calm the skin, reduce redness, prevent post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), and ensure smoother, longer-lasting results. How Pico Laser Affects the Skin Pico laser works by delivering energy in picoseconds, creating a photoacoustic effect that breaks pigment into tiny particles. These particles are then cleared naturally by the body. After treatment, the skin may experience: Temporary redness Mild swelling Warm or tight sensation Darkening of pigment before it fades These reactions are normal and part of the healing process. The First 24 Hours After Pico Laser The first day is the most critical phase of recovery. What You Should Do Keep the treated area clean and dry Wash gently using a mild, non-foaming cleanser Apply soothing products recommended by your provider Use broad-spectrum sunscreen if exposed to daylight What You Should Avoid Touching, rubbing, or scratching the skin Makeup unless approved Hot showers, saunas, or steam rooms Protecting the skin barrier during this phase helps prevent irritation. Days 2–7: Early Healing Phase During this period, the skin begins stabilizing. Common Skin Changes Redness gradually subsides Pigmented spots may look darker before lightening Mild dryness or flaking may appear Recommended Care Continue gentle cleansing twice daily Use fragrance-free moisturizers Apply mineral sunscreen daily Avoid exfoliation and active ingredients This phase is essential for preventing pigmentation rebound. Skincare Ingredients That Support Healing Choosing the right ingredients can improve comfort and recovery. Recommended Ingredients Hyaluronic acid for hydration Ceramides to repair the skin barrier Panthenol (Vitamin B5) for soothing Centella asiatica for inflammation control Low-strength niacinamide for barrier support These ingredients help restore balance without irritating sensitive skin. Ingredients to Avoid After Pico Laser Certain skincare products can interfere with healing. Avoid Temporarily Retinoids and retinol Alpha hydroxy acids (AHA) Beta hydroxy acids (BHA) Vitamin C in the early phase Physical scrubs or cleansing brushes Most active ingredients can be slowly reintroduced after full recovery. Sun Protection: The Most Important Pico Laser Aftercare Step Sun exposure is the leading cause of complications after laser treatments. Best Sun Protection Practices Use SPF 30 or higher every day Reapply sunscreen every 2–3 hours Wear wide-brim hats when outdoors Avoid direct sun during peak hours Consistent sun protection significantly lowers the risk of PIH. Can You Wear Makeup After Pico Laser? Whether you can wear makeup after pico laser treatment depends on your skin’s sensitivity, the treatment intensity, and how your skin responds during the first 24–48 hours. While pico laser has minimal downtime, giving your skin time to recover is important for optimal results. General Guidelines for Makeup Use After Pico Laser Light makeup after 24 hoursIn most cases, light makeup can be applied about 24 hours after treatment, once redness and warmth have subsided. Tinted sunscreen or mineral-based powder is often preferred during the early healing phase. Choose gentle, skin-friendly productsUse non-comedogenic, fragrance-free, and hypoallergenic makeup to reduce the risk of irritation or clogged pores. Mineral makeup is usually better tolerated, especially for sensitive or post-laser skin. Avoid heavy foundation initiallyHeavy or full-coverage foundation should be avoided for the first few days, as it can trap heat, block pores, and interfere with skin healing. Allow the skin to breathe and recover naturally. Additional Tips for Safe Makeup Use Apply makeup with clean brushes or sponges Remove makeup gently without rubbing Avoid products with active ingredients such as retinoids, acids, or alcohol Always apply broad-spectrum sunscreen before makeup during the day Exercise, Heat, and Lifestyle Considerations Heat and sweat can increase inflammation. Avoid for 48–72 Hours Intense workouts Swimming pools Hot yoga or saunas Steam rooms Light walking is usually safe, but heavy exercise should wait. How Long Does Pico Laser Recovery Take? Pico laser recovery time is generally short, especially when compared to traditional laser treatments. Healing varies based on factors such as skin type, treatment intensity, targeted concern (pigmentation, acne scars, or skin rejuvenation), and how well Pico Laser aftercare instructions are followed. Typical Pico Laser Recovery Timeline Redness (1–3 days)Immediately after treatment, mild redness and warmth are common. This usually feels similar to a light sunburn and settles within a few hours to a few days. Sensitive skin types may experience slightly longer redness. Pigment Darkening (3–7 days)For pigmentation treatments, dark spots may temporarily appear darker before they fade. This is a normal part of the skin’s healing process, as pigmented cells rise to the surface and shed naturally. Avoid picking or exfoliating during this phase. Skin Normalization (1–2 weeks)As the skin heals, tone and texture gradually even out. Any dryness, roughness, or flaking resolves, revealing clearer and brighter skin. Most patients can return to normal skincare routines within this period. Ongoing Skin Improvement Although the surface recovery is quick, pico laser continues to work beneath the skin. Collagen and elastin remodeling occur over several weeks, leading to progressive improvements in skin texture, fine lines, acne scars, and overall skin quality. Factors That Affect Recovery Time Individual skin sensitivity Treatment depth and energy settings Size of the treated area Sun exposure and post-treatment care Use of gentle, hydrating skincare products With proper Pico Laser aftercare and sun protection, most patients experience minimal downtime and noticeable results within weeks, making pico laser a popular option for those seeking effective skin improvement with a fast recovery. Warning
How Fractional CO2 Laser Actually Works
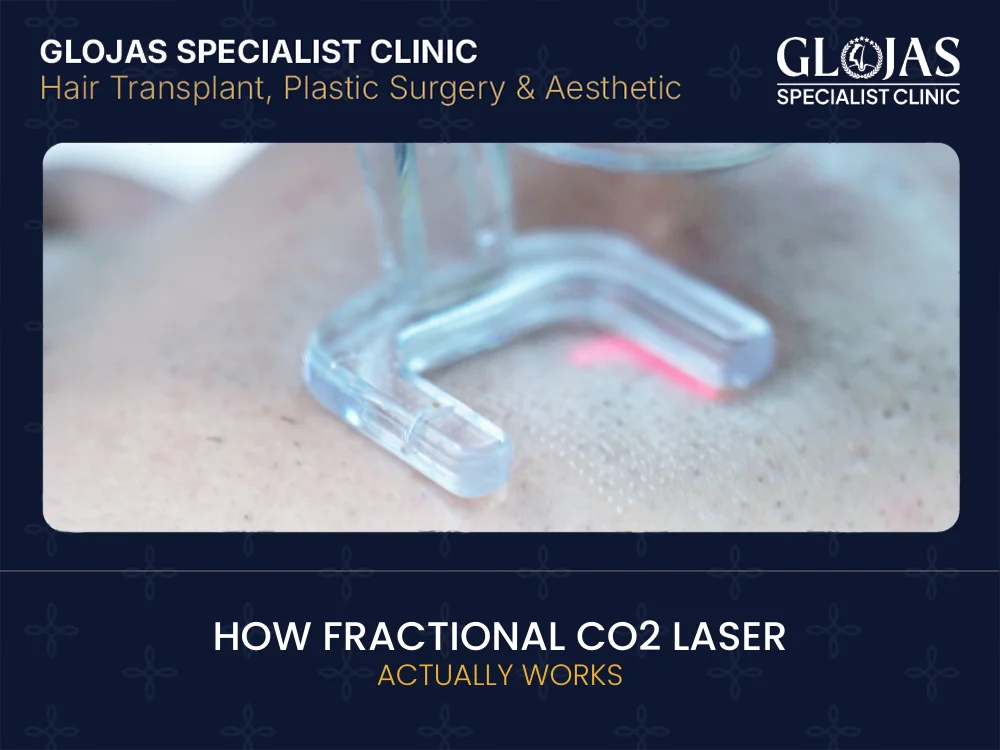
Fractional CO2 laser is one of the most powerful skin resurfacing treatments available today. It is widely used to improve acne scars, wrinkles, enlarged pores, and uneven skin texture. But many people still ask the same question: how fractional CO2 laser works actually and why it delivers such noticeable results. This guide explains the science, process, benefits, risks, and realistic expectations—without hype or medical jargon. If you are considering laser resurfacing, this article will help you make an informed decision. How Fractional CO2 Laser Works: A Simple Explanation How fractional CO2 laser works is based on controlled skin injury and natural healing. The laser delivers microscopic columns of thermal energy into the skin while leaving the surrounding tissue intact. These micro-injuries stimulate collagen production and skin renewal from within. Unlike older lasers that treated the entire surface, fractional technology treats only a fraction of the skin at a time. This improves safety, healing speed, and outcomes. In short: · The laser creates tiny treatment zones · Old, damaged skin is replaced · New collagen forms · Skin becomes smoother and firmer This balance between effectiveness and recovery is what makes fractional CO2 laser works so popular. What Is a Fractional CO2 Laser? Fractional CO2 laser is an ablative laser that uses carbon dioxide (CO2) wavelength at 10,600 nm. This wavelength is strongly absorbed by water in the skin, allowing precise vaporization of damaged tissue. Key characteristics: · Ablative (removes micro-layers of skin) · Fractional (treats skin in tiny columns) · Deep collagen stimulation · Medical-grade resurfacing technology Common devices include: · Fraxel Repair · Lumenis UltraPulse · DEKA SmartXide · eCO2 Laser Systems The Science Behind Fractional CO2 Laser Works Technology To truly understand how fractional CO2 laser works, it helps to know what happens at the cellular level. 1. Creation of Microthermal Treatment Zones (MTZs) The laser creates thousands of microscopic channels in the skin. These are called microthermal zones. Each zone: · Penetrates deep into the dermis · Triggers controlled thermal damage · Leaves surrounding skin untouched 2. Collagen Remodeling The body responds by activating fibroblasts, which produce: · New collagen · New elastin · Healthier skin structure This process continues for several months after treatment. 3. Skin Renewal Old skin cells are replaced with new ones. Texture improves, scars soften, and wrinkles become less visible. What Skin Concerns Can Fractional CO2 Laser Works Treat? Fractional CO2 laser works is used for moderate to severe skin concerns, including: · Acne scars (ice pick, boxcar, rolling) · Surgical or traumatic scars · Fine lines and deep wrinkles · Sun damage and photoaging · Enlarged pores · Uneven skin texture · Skin laxity · Stretch marks (selected cases) Because it penetrates deeper than non-ablative lasers, results are often more dramatic. What Happens During a Fractional CO2 Laser Works Treatment? Before Treatment · Medical consultation and skin assessment · Pre-treatment skincare (sometimes retinoids or bleaching agents) · Antiviral medication if needed During Treatment · Topical or local anesthesia is applied · Laser passes over the treatment area · Sensation: heat, pressure, mild stinging Session duration: · 20–60 minutes depending on area and intensity After Treatment · Redness and swelling · Warm or sunburn-like feeling · Tiny grid marks may appear temporarily Fractional CO2 Laser Downtime and Healing Timeline Downtime depends on treatment intensity. Typical recovery: · Day 1–3: Redness, swelling, oozing · Day 4–7: Crusting and peeling · Day 7–10: Skin re-epithelialization · Week 2–4: Pinkness fades · Month 3–6: Continued collagen improvement This is why fractional CO2 laser is considered a medium-to-high downtime procedure. Benefits of Fractional CO2 Laser Works Treatment Fractional CO2 laser treatment is widely regarded as one of the most powerful skin resurfacing technologies in aesthetic dermatology, especially for patients with advanced skin concerns. Below is an expanded explanation of its key benefits: Significant collagen stimulationFractional CO₂ lasers deliver controlled thermal energy deep into the dermis, triggering the skin’s natural wound-healing response. This process stimulates the production of new collagen and elastin, leading to firmer, thicker, and more youthful-looking skin over time. The collagen remodeling continues for several months after treatment, which is why results keep improving gradually. Long-lasting resultsUnlike superficial treatments that offer temporary improvement, fractional CO₂ laser provides long-term skin remodeling. Once new collagen is formed, improvements in skin texture, scarring, and wrinkles can last for years, especially when combined with good skincare and sun protection. Highly effective for deep scars and wrinklesThis treatment is particularly effective for deep acne scars, surgical scars, enlarged pores, and pronounced wrinkles. The laser penetrates deeper than non-ablative devices, breaking down scar tissue and encouraging smoother, more even skin regeneration—making it a preferred option for severe or long-standing scarring. Improves both skin texture and toneFractional CO₂ laser resurfacing not only smooths uneven texture but also improves overall skin tone. Patients often notice brighter skin, reduced roughness, refined pores, and a more even complexion as damaged surface layers are replaced with healthier skin. Customizable treatment depth and intensityOne of the major advantages of fractional CO₂ laser technology is its high level of customization. Treatment depth, energy levels, and coverage can be adjusted based on skin type, concern severity, and downtime tolerance. This allows clinicians to tailor treatments for acne scars, wrinkles, pigmentation irregularities, or skin laxity with precision. For patients with severe acne scarring or advanced skin aging, fractional CO₂ laser treatment remains a gold-standard solution due to its ability to deliver dramatic, clinically proven results that many other modalities cannot achieve. Risks and Side Effects You Should Know While effective, fractional CO2 laser is not risk-free. Possible side effects: · Prolonged redness · Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) · Infection (rare with proper care) · Scarring (very rare) · Temporary acne flare-ups Risk is higher in darker skin tones if not properly managed. This is why doctor-led treatment and proper settings are critical. Who Is a Good Candidate for Fractional CO2 Laser Works? Fractional CO₂ laser treatment is a powerful resurfacing procedure, but it is not suitable for everyone. Careful
Is Pico Laser Safe for Dark Skin?

Laser skin treatments were once considered risky for darker skin tones. Many people with melanin-rich skin were warned about burns, scars, and unwanted pigmentation. Today, technology has changed that perception. One question still dominates search results: Is pico laser safe for dark skin? This article explains the science, safety, benefits, and limitations of pico laser treatments so you can make an informed decision with confidence. What Does Pico Laser Safe Really Mean? The term pico laser safe refers to laser technology that uses ultra-short picosecond pulses to treat the skin with minimal heat. Instead of burning pigment, the laser shatters it into microscopic particles using a photoacoustic effect. This approach significantly reduces the risk of overheating melanin-rich skin, making pico laser treatments safer for darker skin tones when performed by trained medical professionals. Why Pico Laser Safe Matters More for Dark Skin Dark skin contains higher concentrations of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. Melanin absorbs light energy easily. With older laser systems, this often led to complications such as: ·Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) ·Burns or blisters ·Uneven skin tone ·Prolonged healing time Because of these risks, not all laser devices are suitable for Fitzpatrick skin types IV, V, and VI. Safety depends on pulse duration, wavelength, and operator expertise. How Pico Laser Safe Technology Works Pico lasers deliver energy in trillionths of a second. This ultra-fast pulse changes how the skin responds to laser treatment. Key Mechanisms ·Uses photoacoustic energy instead of thermal heat ·Breaks pigment into tiny fragments ·Minimizes damage to surrounding tissue ·Triggers natural pigment clearance by the body This makes pico lasers fundamentally different from traditional laser systems. Why Pico Laser Safe Is Considered for Dark Skin Several features contribute to its improved safety profile: ·Short pulse duration limits heat buildup ·Selective pigment targeting avoids surrounding melanin ·Lower risk of PIH compared to older lasers ·Controlled energy delivery tailored to skin type These characteristics explain why pico laser has become a preferred option for treating darker skin tones in aesthetic dermatology. Skin Concerns Pico Laser Safe Can Treat in Dark Skin Pico laser treatments are commonly used for: Hyperpigmentation Safely breaks down excess pigment without damaging healthy skin. Melasma Used carefully as part of a controlled treatment plan. Acne Scars Improves texture and stimulates collagen remodeling. Uneven Skin Tone Gradually enhances clarity and brightness. Tattoo Removal Effective for stubborn pigment with lower scarring risk. Clinical Evidence and Dermatology Experience Pico laser technology is well established in modern dermatology and aesthetic medicine, with widespread global use for pigmentation disorders, acne scars, tattoo removal, and overall skin rejuvenation. Its effectiveness is supported by clinical studies and years of real-world dermatology experience. Research and long-term clinical practice show that pico laser treatments have low complication rates when performed by trained medical professionals using appropriate parameters. The ultra-short pulse duration allows targeted pigment and tissue disruption while minimizing heat damage to surrounding skin, which contributes to its strong safety profile—particularly for darker skin tones. Most reported side effects are mild and temporary, such as short-lived redness, swelling, or sensitivity. These effects typically resolve within a few days and are significantly reduced when patients follow proper pre- and post-treatment care, including sun protection and gentle skincare routines. Equally important is careful patient selection and individualized treatment planning. A medical consultation ensures the laser settings are adjusted based on skin type, condition, and treatment goals, further improving outcomes and safety. When these principles are followed, pico laser remains a reliable, evidence-based option with consistently high patient satisfaction. Possible Side Effects and How They Are Managed Even safe technologies require proper handling. Temporary effects may include: ·Redness ·Mild swelling ·Short-term darkening before lightening How Risks Are Reduced ·Accurate skin assessment ·Conservative laser parameters ·Strict sun avoidance ·Medical-grade skincare support Choosing an experienced provider plays a major role in safety. Who Is a Good Candidate for Pico Laser? Pico laser treatments are designed to be versatile and safe, but they are especially beneficial for individuals with specific skin concerns and lifestyle preferences. You may be a good candidate if you meet one or more of the following criteria: Have darker skin tones (Fitzpatrick III–VI)Pico laser technology uses ultra-short pulses that reduce heat buildup, making it safer for darker skin tones with a lower risk of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH). Experience pigmentation issues or acne scarsConditions such as melasma, sunspots, post-acne marks, and uneven skin tone respond well to pico laser due to its ability to break down pigment particles precisely. Want a non-invasive treatment optionPico laser is non-surgical and does not damage surrounding skin tissue, making it ideal for patients seeking effective results without needles or incisions. Prefer minimal downtimeMost patients experience only mild redness or swelling that subsides within a short period, allowing a quick return to daily activities. Are free from active skin infections or severe inflammationHealthy skin at the time of treatment helps ensure optimal results and reduces the risk of complications. Ultimately, a medical consultation is essential to assess your skin type, concerns, and goals. A qualified practitioner can tailor the treatment parameters to your needs, ensuring both safety and effective outcomes. What to Expect During and After Treatment During Treatment Pico laser sessions are generally quick and well tolerated. You may feel mild tingling, warmth, or a snapping sensation, similar to a light rubber band flicking the skin. The intensity varies depending on the treatment area and settings used.To enhance comfort, a topical numbing cream may be applied before the procedure, especially for sensitive areas. Each session usually lasts 15–30 minutes, depending on the size of the area being treated. After Treatment Recovery is usually minimal, making pico laser a popular option for patients with busy schedules: Redness and mild swelling are common and typically subside within 24–48 hours The skin may feel slightly warm or sensitive, similar to mild sun exposure Gradual skin improvement occurs as pigmentation fades and collagen production increases over time Daily activities can be resumed quickly, often on the same day, with basic aftercare