Dutasteride is a prescription medication that has gained significant attention for its effectiveness in treating male pattern baldness (androgenetic alopecia) and conditions related to the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Originally developed for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), Dutasteride works by reducing DHT levels in the body, which can slow hair loss and promote regrowth.
In this guide, we explore everything you need to know about Dutasteride—its mechanism of action, medical uses, benefits, risks, dosage, comparison with Finasteride, and expert FAQs.
What is Dutasteride?
Dutasteride is a 5-alpha-reductase inhibitor that blocks the conversion of testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone linked to both prostate enlargement and male pattern baldness.
Generic Name: Dutasteride
Brand Names: Avodart, Avolve, and generic alternatives
Drug Class: 5-alpha-reductase inhibitor
Approved Use: Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
Off-label Use: Hair loss treatment in men
How Dutasteride Works for Hair Loss
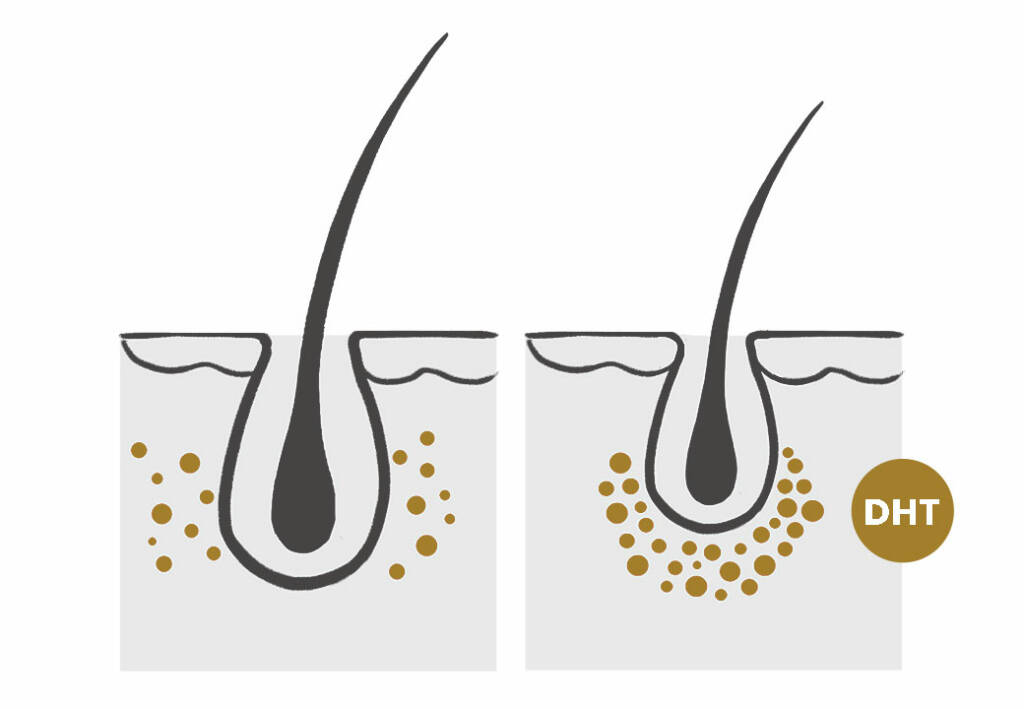
Hair loss caused by genetics is often linked to high DHT sensitivity in hair follicles. DHT miniaturizes hair follicles over time, leading to thinning and eventual balding.
Dutasteride reduces DHT levels by over 90%, compared to Finasteride which lowers it by about 60–70%. This makes Dutasteride a more powerful option for:
Slowing progression of male pattern baldness
Increasing hair thickness and density
Maintaining long-term hair growth results
Medical Uses of Dutasteride
1. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Relieves urinary symptoms caused by an enlarged prostate
Prevents complications like urinary retention
Reduces the need for prostate surgery
2. Male Pattern Baldness (Androgenetic Alopecia)
Prescribed off-label for men experiencing significant hair thinning
Often considered for those who did not respond well to Finasteride
3. Other Investigational Uses
Studied for female hair loss (with limited evidence)
Potential in managing certain hormonal disorders (still under research)
Dutasteride vs. Finasteride: Which is Better?
| Feature | Dutasteride | Finasteride |
|---|---|---|
| FDA Approval for Hair Loss | ❌ (off-label) | ✅ |
| DHT Suppression | ~90% | ~60–70% |
| Half-life | 4–5 weeks | 5–6 hours |
| Effectiveness | Stronger, more consistent | Effective but moderate |
| Side Effects | Slightly higher risk | Lower risk |
👉 If maximum DHT reduction is the goal, Dutasteride is more effective. However, Finasteride is officially approved for hair loss and may be a safer first step.
Dosage and Administration
Typical Dose for BPH: 0.5 mg daily
Hair Loss (Off-label): 0.5 mg daily (some studies suggest 3x per week may still be effective)
Duration: At least 6–12 months for visible results
Consistency: Important to take regularly for sustained benefits
Side Effects of Dutasteride
Like any medication, Dutasteride has potential side effects, though not everyone experiences them.
Common Side Effects:
Reduced libido
Erectile dysfunction
Decreased semen volume
Less Common Side Effects:
Gynecomastia (breast tenderness in men)
Depression or mood changes
Allergic reactions (rash, swelling)
Long-Term Considerations:
DHT plays a role in male sexual health—long-term suppression may cause persistent effects in rare cases.
Always consult a board-certified doctor before starting Dutasteride.
Who Should Avoid Dutasteride?
Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding (can cause birth defects in male fetuses)
Children and adolescents
Men with liver disease without medical supervision
Those allergic to Dutasteride or similar drugs
Dutasteride and Hair Transplant Combination
For men undergoing hair transplant surgery, Dutasteride is sometimes prescribed post-procedure to preserve non-transplanted hair and enhance results. Studies suggest that combining surgical and medical approaches leads to superior long-term density.
Dutasteride in Malaysia and Asia
Dutasteride is increasingly popular in Malaysia, Singapore, South Korea, and Japan as part of advanced hair restoration programs. Although used off-label, many specialists prescribe it under close monitoring.
Natural Alternatives to Dutasteride
For individuals concerned about side effects, some natural DHT-blockers are available:
Saw Palmetto
Pumpkin Seed Oil
Green Tea Extract
Zinc
⚠️ While these may support scalp health, they are not as effective as prescription medications like Dutasteride.
Conclusion
Dutasteride is a powerful treatment option for hair loss and prostate enlargement, offering stronger DHT suppression than Finasteride. However, it comes with higher risks and should only be used under medical supervision. For men struggling with advanced hair loss, Dutasteride can be a game-changer—especially when combined with other therapies.
FAQs About Dutasteride
1. Is Dutasteride safe for long-term use?
Yes, but it should be monitored by a doctor, as long-term DHT suppression can cause persistent side effects in rare cases.
2. How long does it take for Dutasteride to show results for hair loss?
Most patients notice improvements after 6–12 months of consistent use.
3. Can women use Dutasteride for hair loss?
It is not recommended for women, especially during pregnancy, due to risk of birth defects.
4. Is Dutasteride better than Finasteride for hair loss?
Yes, Dutasteride suppresses more DHT and is often more effective, but Finasteride is safer as a first-line treatment.
5. Do I need a prescription for Dutasteride?
Yes. It is a prescription-only medication and should be taken under a doctor’s supervision.
