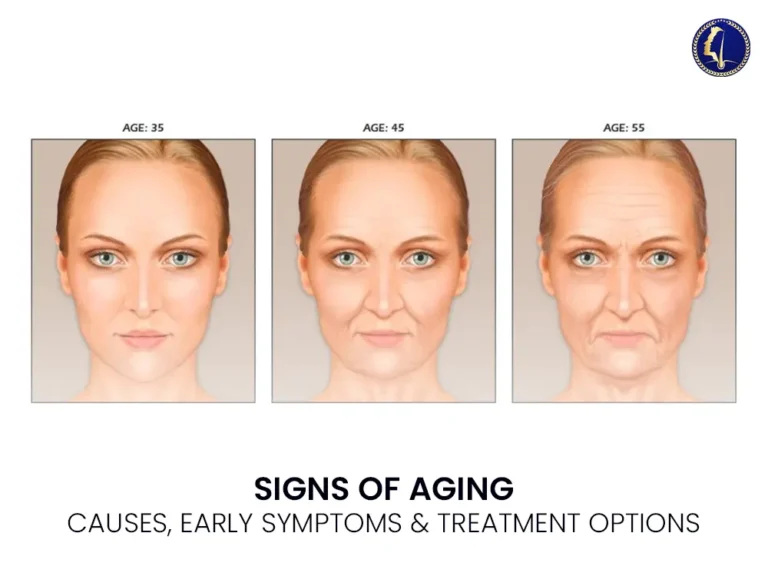
Signs of Aging
Introduction
Aging is a complex biological process influenced by both intrinsic and extrinsic factors. While it is a natural part of life, the visible signs of aging can affect an individual’s appearance, self-esteem, and overall skin health. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the most common signs of aging, their clinical causes, and evidence-based treatment options—guided by medical understanding and dermatological science.
What Are the Common Signs of Aging?
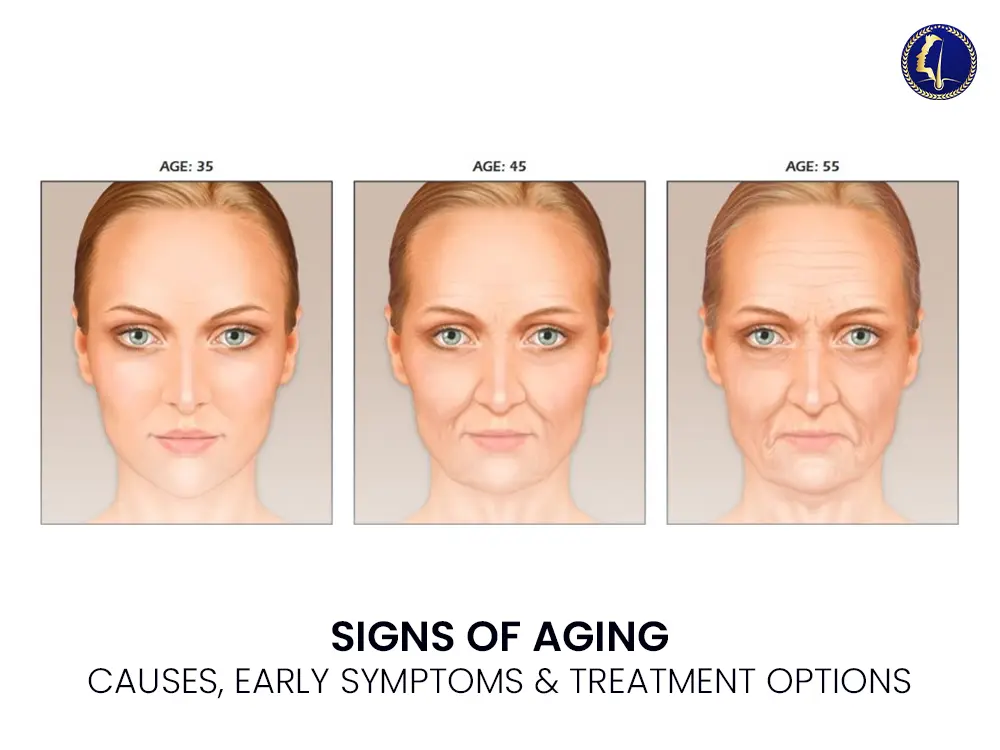
The signs of aging manifest differently for each individual, influenced by genetics, lifestyle, environment, and underlying health conditions. Below are the most clinically recognized dermatological signs:
1. Fine Lines and Wrinkles
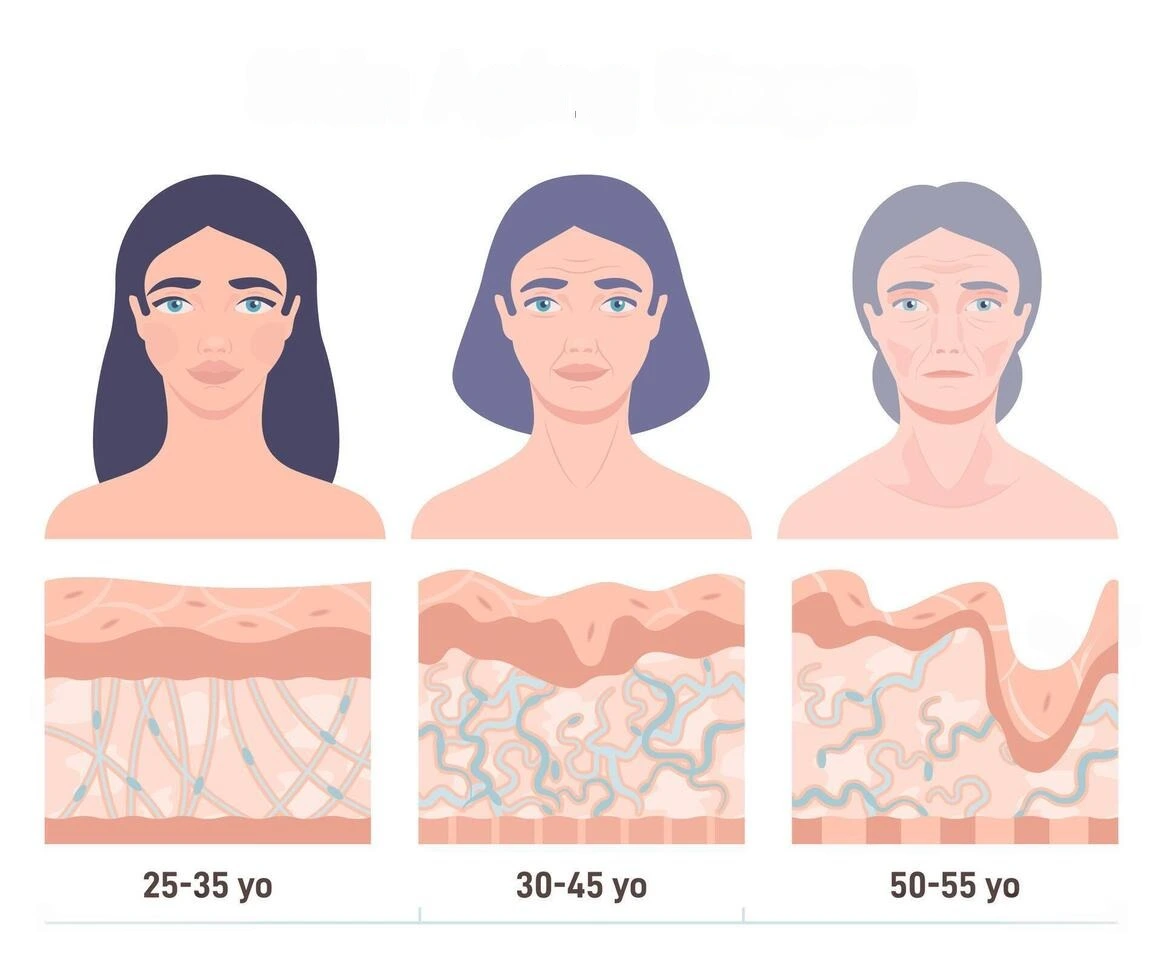
These are among the earliest and most noticeable signs. Wrinkles typically appear due to the breakdown of collagen and elastin—key proteins that support skin firmness and elasticity.
Dynamic wrinkles (e.g., crow’s feet) result from repeated facial expressions.
Static wrinkles form over time due to volume loss and skin laxity.
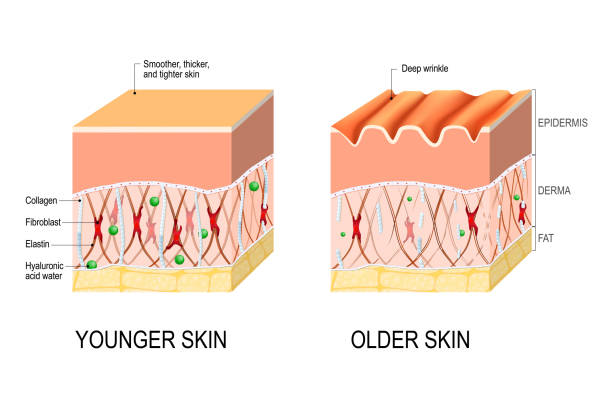
2. Loss of Skin Elasticity and Sagging
As skin ages, it loses structural support due to the degradation of collagen and hyaluronic acid. This results in sagging skin, especially around the cheeks, jawline, and neck.
3. Age Spots and Hyperpigmentation
Also known as solar lentigines, age spots are flat, brown lesions caused by prolonged UV exposure. They indicate photoaging, a condition that accelerates skin aging.
4. Thinning Skin
The epidermal and dermal layers gradually become thinner, making the skin appear translucent and more susceptible to bruising and damage.
5. Dryness and Texture Changes
Sebum production decreases with age, leading to drier skin. Textural changes such as roughness or scaliness are common, especially in postmenopausal women.
6. Volume Loss (Fat and Muscle)
Facial volume diminishes with age due to the reduction in subcutaneous fat, bone resorption, and muscle atrophy. This contributes to a hollow appearance around the eyes and cheeks.
7. Visible Blood Vessels and Redness
Aging skin may exhibit telangiectasia (broken capillaries) and increased facial redness due to cumulative sun exposure and thinning skin.
Causes of Aging: Intrinsic vs. Extrinsic Factors

🔬 Intrinsic Aging (Chronological Aging)
Genetically programmed biological changes.
Typically starts in the late 20s to early 30s.
Slower skin cell turnover, reduced collagen synthesis, and hormonal shifts.
🌞 Extrinsic Aging (Environmental Factors)
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is the most significant external contributor (responsible for up to 90% of visible aging).
Pollution, smoking, alcohol, stress, and diet also accelerate skin aging through oxidative stress and inflammation.
Medical & Dermatological Treatment Options
A range of treatments can help mitigate or reverse visible signs of aging, depending on the severity and type of concern.
1. Topical Treatments
Retinoids (Tretinoin, Retinol): Stimulate collagen and improve cell turnover.
Antioxidants (Vitamin C, E): Combat oxidative stress and brighten skin.
Peptides: Help repair skin structure and signal cellular regeneration.
Sunscreens: Essential for preventing further UV damage.
2. Non-Invasive Procedures
Microneedling: Enhances collagen production via controlled skin injury.
Chemical Peels: Exfoliate damaged skin layers and improve tone/texture.
Laser Therapy (e.g., Fraxel): Targets pigmentation and wrinkles.
Radiofrequency and Ultrasound: Tighten skin by stimulating deeper dermal layers.
3. Injectables
Botulinum Toxin (Botox): Reduces dynamic wrinkles.
Dermal Fillers (Hyaluronic Acid, Sculptra): Restore volume and smooth folds.
4. Lifestyle Modifications
Hydration, a nutrient-rich diet, avoiding smoking, and managing stress support overall skin health and slow the aging process.
Preventive Care & Patient Education
Educating patients on preventive measures is key to managing aging effectively:
Daily broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 30+)
Gentle skincare routines avoiding harsh scrubs
Regular dermatological check-ups
Avoidance of tanning beds and excessive sun exposure
Antioxidant-rich diet and hydration
Dermatologists and medical professionals should personalize treatment plans based on skin type, Fitzpatrick classification, and individual aging patterns.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What age do signs of aging usually appear?
Most people begin to notice early signs like fine lines in their late 20s to early 30s, although genetics and lifestyle can accelerate or delay this process.
2. Can aging be reversed?
While aging can’t be completely reversed, medical treatments such as retinoids, microneedling, and laser therapy can significantly reduce the appearance of aging signs.
3. Are over-the-counter anti-aging creams effective?
Some OTC products with ingredients like retinol, peptides, and vitamin C can improve mild signs of aging, though clinical-grade treatments often yield more dramatic results.
4. How does sun exposure affect skin aging?
UV radiation is a primary cause of extrinsic aging, leading to pigmentation, collagen breakdown, and increased skin laxity.
5. Is microneedling safe for aging skin?
Yes, when performed by a qualified medical professional, microneedling is safe and effective for stimulating collagen and improving skin texture in aging individuals.
Conclusion
Understanding the signs of aging from a medical and dermatological perspective empowers both patients and providers to take proactive steps. Whether you’re in your 30s or 60s, there’s a range of safe, evidence-based interventions to maintain skin health and confidence. Consult a board-certified dermatologist to develop a tailored plan aligned with your skin’s unique needs and aging profile.
The signs of aging can appear earlier than expected if proper skincare is not maintained. Common signs of aging include fine lines, wrinkles, sagging skin, and age spots. Recognizing the signs of aging early allows individuals to address these signs of aging with appropriate treatments. Dermatologists often assess the signs of aging to determine the best anti-aging strategy. Whether it’s lifestyle changes or clinical interventions, understanding the signs of aging is key to managing the visible signs of aging over time.