Hair Transplant vs Hair Patch: Pros and Cons in Malaysia
Hair Transplant vs Hair Patch: Pros and Cons in Malaysia So, you’ve noticed your scalp is starting to reflect more light than it used to. It happens to the best of us! When it comes to reclaiming your hairline in Malaysia, the debate usually boils down to two heavy hitters: Hair Transplant vs Hair Patch. One involves a surgical seat in a clinic, and the other is a non-invasive “accessory” fix. GLOJAS Specialist Clinic is a leading hair transplant clinic in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, offering advanced, natural-looking hair restoration with expert care and proven results. Overview: Hair Transplant and Hair Patch Before we dive into the nitty-gritty, let’s define the players. We aren’t just talking about “fake hair” vs. “real hair”—we’re talking about two completely different philosophies of hair restoration. What Is a Hair Transplant? A hair transplant is a minor surgical procedure where a doctor moves your own living hair follicles from a “donor site” (usually the back of your head) to the balding areas. It’s essentially a biological relocation project that results in hair that grows, sheds, and behaves exactly like your original mane. What Is a Hair Patch or Wig? A hair patch (often called a hair system or a high-end toupee) is a non-surgical prosthetic made of human or synthetic hair. It’s attached to your scalp using medical-grade adhesives or clips. It’s like a custom-made “patch” designed to blend seamlessly with your existing hair to cover bald spots. Key Differences Between Hair Transplant and Hair Patch The main divide is permanence vs. immediacy. A transplant is a long-term medical solution that takes months to show results. A hair patch is an instant cosmetic fix that requires regular maintenance but involves zero needles or recovery time. Advantages of Hair Transplant Over Hair Patch Permanent and Natural Hair Growth The biggest win for a transplant? It’s your hair. Because it uses your own follicles, the texture, color, and growth direction are 100% natural. You can run your fingers through it without worrying about something shifting. Low Maintenance Compared to Hair Patch Once the healing is done, you treat it like normal hair. You wash it, cut it, and style it. You don’t need special adhesives or monthly “servicing” appointments at a salon. Long-Term Cost Efficiency While the upfront price tag in Malaysia is higher, a transplant is a one-time investment. If you calculate the cost of a hair patch over 10 years—including replacements and adhesive products—the transplant often ends up being the cheaper route. Suitable for Malaysian Hair Types Malaysian hair, often characterized by its specific hair follicle diameter and density, responds exceptionally well to modern FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) techniques. Local surgeons are experts at tailoring the “exit angle” of the hair to match the typical growth patterns found in Asian scalps. Advantages of Hair Patch Over Hair Transplant Immediate Results Without Surgery If you have a wedding or a big presentation next week, a hair patch is your best friend. You walk into a center with a bald spot and walk out an hour later with a full head of hair. Non-Invasive and Painless No local anesthesia, no incisions, and no “shock loss.” For those with a phobia of medical environments, a hair patch offers a stress-free transformation. Flexible Styles and Coverage Options Want to try a trendy K-Pop undercut today and a classic side part next month? Hair patches allow for density and style changes that aren’t always possible with a transplant, which is limited by your natural donor supply. Ideal for Temporary or Experimental Use If your hair loss is caused by temporary factors like Telogen Effluvium (stress-induced shedding), a patch can bridge the gap while your body recovers, without the need for permanent surgery. Disadvantages of Hair Transplant Higher Initial Cost In Malaysia, a quality hair transplant cost can range from RM 8,000 to RM 25,000 depending on the number of grafts. It’s a significant financial commitment upfront. Recovery Time and Post-Op Care You’ll deal with scabbing, swelling, and a strict “no-touch” rule for the first week. You also have to wait 6 to 12 months to see the final “wow” result. Limited by Donor Hair Availability If you are “shiny bald” (Norwood Scale 7), you might not have enough donor hair to cover the entire area. You can’t transplant hair from someone else; it must be your own. Risk of Complications Though rare in reputable KL clinics, any surgery carries risks like folliculitis (inflamed hair follicles) or minor scarring. Choosing an accredited surgeon is non-negotiable. Disadvantages of Hair Patch Frequent Maintenance Required In Malaysia’s humid climate, the adhesive on a hair patch can break down faster due to sweat. You’ll need to visit a specialist every 3-4 weeks to have it removed, cleaned, and re-attached. Risk of Displacement or Damage A very strong gust of wind or an intense gym session could, in theory, cause the edges to lift. While modern adhesives are strong, that “what if” thought often lingers in the back of the user’s mind. Less Natural Look Over Time Synthetic patches can lose their luster, and the base material may become visible as it wears down. They usually need to be replaced entirely every 6 to 12 months. Not a Permanent Solution The moment you take the patch off, the baldness is still there. It doesn’t treat the underlying androgenetic alopecia (male pattern baldness); it just hides it. Cost Comparison in Malaysia Feature Hair Transplant Hair Patch Initial Cost RM 8,000 – RM 25,000 RM 1,500 – RM 4,500 Monthly Maintenance RM 0 RM 150 – RM 300 Replacement Frequency Never Every 6 – 12 Months 10-Year Estimated Total RM 15,000 (avg) RM 25,000+ How to Choose Between Hair Transplant and Hair Patch Factors to Consider: Age, Hair Loss, Budget If you’re in your 20s and your hair loss is still progressing, a patch might be a good temporary fix until your hair loss stabilizes. If you’re in your 30s or 40s and want a “set it and
What Is the Success Rate of Hair Transplant in Malaysia?
If you’re thinning on top, the first thing you probably want to know is: will this actually work? In Malaysia, the hair restoration scene is booming, with Kuala Lumpur becoming a hub for medical tourists. But before you book your flight or clinic visit, understanding the success rate of the procedure is vital to managing your expectations and getting the best bang for your buck. GLOJAS Specialist Clinic in Kuala Lumpur delivers advanced procedures focused on achieving a 99.9% hair transplant success rate through precise graft handling, expert implantation techniques, and comprehensive post-treatment care. What Does Hair Transplant Success Rate Mean? Success isn’t just about “having more hair.” It’s a clinical calculation. In the world of trichology, we look at how many hairs actually “take” to their new home. Definition of Graft Survival Rate The graft survival rate refers to the percentage of transplanted follicular units that remain viable and continue to produce hair after being moved. Because follicles are living tissue, they require careful handling to survive the transition from the donor site to the recipient area. Difference Between Survival Rate and Hair Growth Rate Don’t confuse the two! The survival rate is about the follicle living; the growth rate is how fast or thick that hair grows. You could have a 95% survival rate, but if your biological growth rate is slow, it might take longer to see that full mane. How Success Is Clinically Measured Clinically, success is measured by the Hedgehog Signaling Pathway efficiency and the density of hairs per square centimeter. A successful transplant usually results in a density that mimics a natural hairline without looking “pluggy.” Average Hair Transplant Success Rate in Malaysia Malaysia boasts some of the highest standards for hair restoration in Southeast Asia, thanks to strict Ministry of Health regulations. Typical FUE Success Rate Percentage Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) generally sees a success rate of 90% to 95%. Because each graft is removed individually, there is a slight risk of “transection” (damaging the bulb), but modern robotic and sapphire tools have made this rare. Typical FUT Success Rate Percentage Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT), or the strip method, often has a slightly higher graft survival rate, sometimes reaching 95% to 98%. This is because the follicles are dissected under high-powered microscopes, minimizing trauma to the tissue. Factors Influencing Success Statistics Your mileage may vary based on your scalp health. According to the International Society of Hair Restoration Surgery, patient selection is the biggest driver of these percentages. Not everyone is a perfect candidate! Key Factors That Affect Hair Transplant Success Rate Surgeon Skill and Experience This is the #1 factor. A surgeon who understands the “angle of exit” and natural hair direction will provide a much higher aesthetic success rate than a general practitioner dabbling in hair. Donor Hair Quality and Density You can’t pour from an empty cup. If your donor area (the back of your head) is thinning or has low density, the success rate for full coverage drops because there simply isn’t enough “permanent” hair to move. Graft Handling and Implantation Technique Grafts are incredibly fragile. If they stay outside the body for too long or aren’t kept at the right temperature, they die. Malaysian clinics often use specialized holding solutions to keep these cells hydrated. Patient Age and Hair Loss Stage If you are currently in the middle of an active Androgenetic Alopecia flare-up, you might lose more of your original hair around the transplant, making the overall result look less successful over time. Post-Operative Care and Compliance If you go home and immediately put on a tight helmet or scratch your scabs, you’ll kill the grafts. Success is a 50/50 partnership between the doctor’s steady hand and your aftercare discipline. Hair Transplant Success Rate by Technique FUE vs FUT Success Comparison FUE: Best for those who want short hair and no linear scar. Success is high but requires a very skilled hand to avoid damaging grafts during extraction. FUT: Best for massive bald areas. Success is slightly higher for graft yield, but leaves a linear scar. Impact of Advanced Implantation Methods Techniques like DHI (Direct Hair Implantation) use a specialized “Choi Implanter Pen.” This tool often increases the success rate because it reduces the time the follicle spends outside the body and protects the root from being squeezed by forceps. Single vs Multiple Sessions Success Outcomes Most patients achieve their goals in one session. however, for those with advanced hair loss (Norwood Scale 6 or 7), success is often better achieved over two sessions to allow the scalp blood supply to recover between procedures. Timeline of Results and Long-Term Success First 3 Months: Shedding Phase Expect a “shock loss” period. This is normal! Most of the transplanted hair shafts will fall out. Don’t worry—the “root” is still under the skin. 6 Months: Visible Growth Stage By month six, you should see roughly 50-70% of the new growth. The hairs might be thin and wiry at first, but they will thicken up. 12–18 Months: Final Density Results This is the “Golden Hour.” By 18 months, the Hair Growth Cycle has fully matured, and you can see the final density and texture of your transplant. Long-Term Permanence of Transplanted Hair Because these hairs are taken from the DHT-resistant zone, they are theoretically permanent. They will age as you age, but they shouldn’t fall out due to genetic balding. How to Improve Hair Transplant Success Rate Choosing a Qualified Hair Transplant Clinic in Malaysia Look for clinics registered with the Malaysian Medical Council. Ensure the doctor has specific certification in hair restoration, not just general aesthetics. Proper Pre-Surgery Preparation Stop smoking! Nicotine constricts blood vessels and is the enemy of graft survival. Also, avoid blood thinners like aspirin or certain herbal supplements a week before the big day. Essential Aftercare Guidelines Keep your head elevated while sleeping for the first 3 days to reduce swelling. Use the saline spray provided by your clinic to keep the grafts hydrated and
How Does Hair Transplant Work? Complete Step-by-Step Process
How Does Hair Transplant Work? Step-by-Step Process If you’ve spent any time looking in the mirror wondering where your hairline went, you’ve probably searched for a permanent fix. In Malaysia, hair restoration has become a go-to solution for both locals and medical tourists. But how does hair transplant work exactly? It’s not magic—it’s a sophisticated blend of microsurgery and biological science. GLOJAS Specialist Clinic in Kuala Lumpur provides advanced hair transplant in Malaysia procedures, delivering precise follicle extraction and natural hairline restoration with proven, permanent results. How Hair Transplant Works: The Core Medical Principle At its heart, a hair transplant is a relocation project. We take hair from where you have plenty (usually the back of your head) and move it to where you’re thinning. Unlike a heart or kidney transplant, you are your own donor, which means there is zero risk of your body rejecting the “new” hair. Donor Dominance Theory Explained The secret sauce of this procedure is Donor Dominance. Most hair loss is caused by Androgenetic Alopecia, a genetic sensitivity to the hormone DHT. However, the hair on the back and sides of your scalp is genetically programmed to be resistant to DHT. When moved to the top of the head, these follicles keep those “permanent” traits and continue to grow for a lifetime. How Hair Follicles Are Extracted Whether your surgeon uses a tiny punch tool or a scalpel, the goal is the same: harvesting the follicular unit. This isn’t just a single hair; it’s a tiny bundle of 1 to 4 hairs, along with their oil glands, nerves, and small muscles. Keeping this unit intact is vital for survival. How Implanted Grafts Survive and Grow Once moved, the graft enters a phase called revascularization. Within the first few days, the scalp’s blood vessels begin to connect with the newly placed follicles, providing the oxygen and nutrients needed for the hair to “take root” and begin its new life. How FUE Hair Transplant Works Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) is the most popular method in Malaysia because it doesn’t involve large stitches or linear scars. Individual Follicle Extraction Process The surgeon uses a specialized micro-punch tool (usually less than 1.0mm in diameter) to make a tiny circular incision around a hair graft. This is repeated hundreds or thousands of times. Because the holes are so small, they heal as tiny, invisible dots. Recipient Channel Creation Before the hair goes in, the doctor must create “slots” for them. This is where the artistry comes in. The surgeon uses a needle or sapphire blade to determine the depth and density of your new hairline. Graft Implantation Technique The extracted grafts are carefully placed into these channels using fine forceps or an implanter pen. According to the International Society of Hair Restoration Surgery, the handling of these grafts is critical, as they are fragile and can easily dry out if not handled with precision. How FUT Hair Transplant Works Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT), or “Strip Surgery,” is the traditional method often used when a patient needs a massive amount of coverage in a single session. Strip Harvesting Method Instead of picking individual hairs, the surgeon removes a thin strip of skin from the donor area. The gap is then stitched shut, usually resulting in a very fine linear scar that is easily hidden by surrounding hair. Microscopic Graft Dissection The harvested strip is handed over to a team of technicians who use high-powered microscopes to meticulously separate the skin into individual follicular units. This ensures the highest yield of usable hair with minimal wastage. Implantation Procedure Once the grafts are prepared, the implantation follows the same logic as FUE—creating channels and placing the hair one by one to ensure a natural look. Step-by-Step: How a Hair Transplant Works from Start to Finish Scalp Assessment and Graft Planning Your journey starts with a consultation. The doctor uses a densitometer to check your donor density and maps out a design. They calculate exactly how many grafts are needed to achieve your goals while keeping the donor area looking natural. Donor Area Preparation The area is trimmed (usually quite short for FUE) and a local anesthetic is applied. You’ll be awake, likely watching a movie or chatting with the staff, but you won’t feel a thing on your scalp. Follicle Extraction The surgeon harvests the follicles. In Malaysia, clinics often use Sapphire FUE or DHI (Direct Hair Implantation) techniques to minimize trauma to the scalp tissue during this phase. Site Creation in Bald Areas The “balding” area is numbed, and the surgeon creates the recipient sites. This is where they decide the direction the hair will grow—mimicking your natural swirl or “cowlick.” Graft Placement and Angle Control The final step is the most tedious. Each graft is placed at a specific angle (usually 10 to 45 degrees) to ensure it looks like real hair and not a “doll’s head” plug from the 1980s. How Hair Transplant Works After Surgery The surgery is done, but the biology is just getting started. Immediate Post-Procedure Phase For the first 48 hours, you’ll have tiny scabs and maybe some swelling. It’s vital to keep the area clean. Most American Academy of Dermatology guidelines suggest avoiding heavy exercise for at least a week to prevent dislodging the grafts. Shock Loss Mechanism Don’t panic! About 2 to 6 weeks after surgery, the transplanted hair shafts will fall out. This is called shock loss. The follicle itself is safe and dormant underground; it’s just shedding the old hair to prepare for new growth. New Hair Growth Cycle By month 3 or 4, you’ll see fine, “fuzz-like” hairs breaking through the surface. As the National Institutes of Health notes, the hair growth cycle (Anagen phase) takes time to reset after the trauma of surgery. Permanent Hair Regrowth Process By month 12, you’ll see the final result. The hair will be thicker, longer, and completely permanent. You can cut it, dye it, and style it just like the rest of your
Hormonal Hair Loss in Men and Women: Symptoms & Solutions
Waking up to a pillow covered in hair can feel like a personal betrayal. If you’ve noticed your scalp becoming a bit too visible lately, you’re not alone—especially here in Malaysia, where humidity, nutritional gaps, and urban stress often mask the real culprit: your endocrine system. Whether it’s thinning at the crown or a widening part, understanding the “why” behind the shed is the first step to getting your mane back on track. GLOJAS Specialist Clinic offers world-class hormonal hair loss treatment, combining expert endocrinology insights with advanced follicular restoration to help Malaysians regain thick, healthy hair effectively. Understanding Hormonal Hair Loss What Is Hormonal Hair Loss? At its core, hormonal hair loss (often medically classified as androgenetic alopecia) occurs when your endocrine system sends conflicting signals to your scalp. It isn’t just about hair “falling out” in the traditional sense; it’s a process of follicular miniaturization. Over time, your hair follicles shrink, producing shorter, thinner, and more brittle strands until they eventually stop producing terminal hair altogether. How Hormones Affect the Hair Growth Cycle Your hair doesn’t grow all at once; it moves through a complex biological rhythm. To understand the disruption, we have to look at the three main phases: Anagen (Growth): Lasts 2–7 years. Catagen (Transition): A short 2-week burst where the follicle shrinks. Telogen (Resting): A 3-month phase before the hair sheds. Hormonal shifts—specifically an increase in dihydrotestosterone (DHT)—prematurely terminate the Anagen phase. According to the American Academy of Dermatology, most people normally lose 50 to 100 hairs a day, but a hormonal imbalance can skyrocket that number while simultaneously preventing new growth from starting. Differences Between Male and Female Hormonal Hair Loss The experience is rarely gender-neutral. Men typically face a “receding” pattern, often starting at the temples or the vertex. Women, however, usually experience diffuse thinning across the entire top of the scalp. While the biological mechanisms overlap—both involve androgen sensitivity—the psychological impact and specific life-stage triggers, such as menopause or postpartum recovery, create distinct treatment needs for women compared to the classic male pattern baldness. Common Causes of Hormonal Hair Loss Androgenetic Alopecia (DHT-Related Hair Loss) Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is the primary antagonist in the story of hair loss. This potent androgen is a byproduct of testosterone. When it binds to receptors in the scalp, it effectively “starves” the hair follicle of nutrients. It remains the leading cause of permanent hair thinning globally. Thyroid Imbalances (Hyperthyroidism & Hypothyroidism) Your thyroid gland is the master regulator of your body’s metabolism, including the regeneration of hair cells. When your thyroid is overactive (hyper) or underactive (hypo), it disrupts the production of ATP and protein synthesis required for hair. Research from the British Thyroid Foundation notes that severe or prolonged thyroid issues can lead to uniform thinning across the entire scalp rather than localized patches. PCOS and Hormonal Imbalance in Women Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) creates a state of hyperandrogenism in women. This leads to a frustrating paradox: hirsutism (excess hair growth on the face or body) combined with female pattern hair loss on the scalp. This is driven by elevated levels of free testosterone that the body cannot properly regulate. Testosterone Imbalance in Men It is a common myth that only “high” testosterone causes baldness. In reality, it is the efficiency of the 5-alpha reductase enzyme (which converts testosterone to DHT) and the sensitivity of your androgen receptors that dictate your hair’s fate. However, significant fluctuations in free testosterone can disrupt the hair follicle signaling pathways responsible for maintaining a healthy growth cycle. Symptoms and Early Warning Signs Receding Hairline and Crown Thinning in Men The classic “M” shape at the temples or a thinning patch at the vertex (the “monk’s spot”) are the hallmark signs for men. If you notice your forehead looking “higher” in photos or your hair feels softer and less manageable, these are early indicators of follicular miniaturization. Diffuse Thinning and Widening Part in Women Women rarely go completely bald. Instead, the first sign is usually a widening part line or a ponytail that feels significantly lighter. This diffuse thinning means the density of hair per square centimeter is dropping, making the scalp more visible under bright lights or when wet. Excessive Shedding vs. Pattern Hair Loss It is vital to distinguish between Telogen Effluvium and permanent pattern loss. Telogen Effluvium is a temporary “shock to the system” (often from high fever, rapid weight loss, or extreme stress) that causes mass shedding. If the shedding persists for more than six months without regrowth, it has likely transitioned into a chronic hormonal issue. Diagnosis of Hormonal Hair Loss Hormone Blood Tests (Thyroid, DHT, Estrogen, Testosterone) A clinical diagnosis starts with your blood. Doctors typically order a full endocrine panel, including TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone), Serum Ferritin (iron stores), Total and Free Testosterone, and DHEAS. These markers help determine if the hair loss is a symptom of an internal systemic issue. Scalp Examination and Hair Analysis A specialist might perform a “pull test” or use a trichoscope. This tool allows them to see if your follicles are producing multiple hairs (healthy) or if they are single, fine, and vellus-like (miniaturized), which confirms hormonal thinning. When to See a Dermatologist or Endocrinologist If your hair loss is accompanied by sudden weight changes, irregular menstrual cycles, adult acne, or scalp inflammation, it’s time to seek professional help. You should consult a board-certified dermatologist or an endocrinologist to ensure you aren’t ignoring an underlying metabolic disorder. Treatment Options for Hormonal Hair Loss FDA-Approved Treatments (Minoxidil, Finasteride) Minoxidil: A topical vasodilator that widens blood vessels to deliver more oxygen and nutrients to the follicle. Finasteride: An oral prescription for men that inhibits the 5-alpha reductase enzyme, effectively lowering DHT levels in the scalp. Hormone Therapy for Women For women dealing with PCOS or menopause, topical or oral Spironolactone is often used as an anti-androgen. Additionally, Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) can help stabilize estrogen and progesterone levels, which act as natural protectants for the hair. Treating Underlying Hormonal
Postpartum Hair Loss: Causes and Treatment Options in Malaysia
Becoming a mother is a whirlwind of joy, sleepless nights, and—for about 50% of new mums—a sudden, heart-dropping amount of hair in the shower drain. In Malaysia, where thick, lustrous hair is often celebrated, postpartum hair loss can feel particularly distressing. But don’t worry; your body isn’t broken. It’s simply recalibrating after the ultimate marathon of childbirth. GLOJAS Specialist Clinic offers award-winning, medical-grade postpartum hair loss treatment, utilizing the exclusive SMART™ PRP and Regenera Activa technology to naturally reactivate dormant follicles and restore hair density safely. Understanding Postpartum Hair Loss in Malaysia What Is Postpartum Hair Loss? Medically known as Telogen Effluvium, postpartum hair loss is a temporary form of hair thinning. It’s not “true” hair loss in the sense of permanent balding, but rather a synchronized shedding event. While we normally lose about 50 to 100 strands a day, new mothers might see up to 400 strands daily during the peak of this phase. Hormonal Changes After Pregnancy During pregnancy, your estrogen levels skyrocket. This high estrogen acts like a “pause button” on your hair’s shedding phase, keeping almost all your hair in the growth (anagen) stage. This is why many Malaysian mums enjoy their thickest, shiniest hair while expecting. Normal Shedding vs. Excessive Hair Loss Once you deliver, those estrogen levels crash back to baseline. All the hair that was “on hold” during pregnancy suddenly receives the signal to enter the resting (telogen) phase. About three months later, those hairs fall out all at once. If you see diffuse thinning (thinning all over) rather than distinct bald patches, it is likely standard postpartum shedding. Why Postpartum Hair Loss Happens Estrogen Drop After Delivery The primary culprit is the estrogen withdrawal that occurs within 24 to 48 hours after birth. This rapid shift resets your hair cycle, moving a large percentage of follicles from the growing phase into the resting phase simultaneously. Nutritional Deficiencies (Iron, Vitamin D, Protein) Building a human takes a lot of resources. Many Malaysian women enter the postpartum period with iron deficiency anemia, which can exacerbate hair shedding. Additionally, if you aren’t getting enough protein or Vitamin D, your body will prioritize vital organ function over hair growth. Stress, Sleep Deprivation & Recovery The “fourth trimester” is taxing. High cortisol levels from stress and lack of sleep can prolong the shedding phase. In traditional Malaysian culture, the pantang (confinement) period is designed to mitigate this stress through rest and specialized nutrition, which is actually scientifically sound for hair recovery. When Does Postpartum Hair Loss Start and Stop? Typical Timeline for Malaysian Mothers Start: Usually begins around 3 months after delivery. Peak: Shedding often hits its most dramatic point at 4 to 6 months. End: Most women see their hair return to its normal growth cycle by their baby’s first birthday. Signs Hair Growth Is Returning The most frustrating but promising sign of recovery is the “baby hair fringe.” You’ll notice short, flyaway hairs along your hairline. While they can be hard to style, they are a clear indicator that your follicles are back in the growth phase. Safe Treatment Options for Postpartum Hair Loss Natural Remedies & Herbal Support In Malaysia, traditional treatments like hibiscus leaf masks or virgin coconut oil massages are popular. Research suggests that scalp massage can improve blood flow to the follicles, potentially encouraging thicker regrowth. Postnatal Vitamins & Supplements Continuing your prenatal vitamins or switching to a dedicated postnatal supplement is highly recommended. Look for ingredients like Biotin, Zinc, and Selenium, as nutritional deficiencies are closely linked to the health of the hair structure. Topical Treatments Safe During Breastfeeding If you are breastfeeding, avoid medications like Minoxidil unless prescribed by a doctor. Instead, look for shampoos or tonics containing caffeine or rosemary oil, which can stimulate the scalp without systemic absorption. Postpartum Hair Care Tips Gentle Hair Care Routine Use a wide-tooth comb to detangle when wet. Skip the high-heat blowouts; air-dry whenever possible. Wash your hair only when necessary to avoid excessive mechanical tension. Hairstyles to Reduce Breakage Avoid tight “mummy buns” or ponytails. These can cause traction alopecia on top of your hormonal shedding. Opt for loose braids or a “shorter” cut—the classic “mom bob” is popular in Malaysia for a reason; it removes the weight that makes hair look limp. Choosing Suitable Shampoos in Malaysia Look for “volumizing” shampoos that use lightweight proteins to coat the hair shaft. Avoid heavy “2-in-1” products that contain high levels of silicone, as these can weigh down thinning hair and make it look sparser. When to See a Doctor in Malaysia Warning Signs of Underlying Conditions While shedding is normal, you should consult a professional if: Your hair loss is patchy (Alopecia Areata). Shedding persists beyond 12 months. You experience scalp pain or extreme itching. Thyroid & Iron Deficiency Testing Postpartum thyroiditis affects about 5% to 10% of women and can cause significant hair loss. If you feel excessively fatigued or cold, a simple blood test at your local GP can check your TSH and Ferritin (iron) levels. FAQs About Postpartum Hair Loss Is postpartum hair loss permanent? No. For the vast majority of women, it is a self-correcting condition. Your hair follicles are not dead; they are just resting. Can breastfeeding worsen hair loss? There is no strong evidence that breastfeeding causes hair loss. While it maintains slightly higher prolactin levels, the primary trigger remains the initial estrogen drop after birth. How long does recovery take? Expect a full recovery of your hair’s volume and length within 6 to 12 months after the shedding begins.
Natural Hair Loss Treatment: Do They Really Work?
In 2026, the quest for a full mane is no longer just about expensive surgeries or chemicals. Many Malaysians are looking back to nature, combining traditional wisdom with modern science. If you’ve noticed more strands in the shower drain lately, you aren’t alone—but before you panic, it’s worth exploring if a natural hair loss treatment can get your growth back on track. GLOJAS Specialist Clinic provides award-winning hair loss treatment in Malaysia, utilizing advanced SMART™ PRP and Regenera Activa technology to reactivate follicles for high-density, permanent results without surgery. Understanding Hair Loss in Malaysia Common Causes of Hair Loss Among Malaysians Hair loss in Malaysia is often a “perfect storm” of genetics and environment. High humidity can lead to an oily scalp, which traps pollutants and fosters fungal issues like seborrheic dermatitis. Additionally, the local love for “Mamak” sessions—often high in sugar and processed carbs—can trigger inflammation that affects follicle health. Male vs. Female Pattern Hair Loss While men typically face the classic receding hairline (Androgenetic Alopecia), Malaysian women often experience diffuse thinning at the part line. This is frequently linked to hormonal shifts during postpartum or menopause, or even iron deficiency anemia, which is remarkably common among women in Southeast Asia. Environmental & Lifestyle Factors in Malaysia The “hustle culture” in cities like KL and Penang spikes cortisol levels. According to the Mayo Clinic, high stress can push hair follicles into a premature resting phase (Telogen Effluvium), leading to sudden, clump-heavy shedding. Most Effective Natural Hair Loss Treatments Herbal Remedies (Aloe Vera, Ginseng, Saw Palmetto) Nature’s pharmacy is surprisingly potent. Saw Palmetto is a popular choice because it may inhibit the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase, which converts testosterone into DHT—the hormone responsible for shrinking hair follicles. Recent studies show that Saw Palmetto extracts can modestly increase terminal hair count in those with mild thinning. Essential Oils (Rosemary, Peppermint, Lavender) Rosemary oil is the current superstar of natural remedies. In a landmark study, rosemary oil was found to be as effective as 2% Minoxidil for regrowing hair over a six-month period, but with significantly less scalp itching. Coconut Oil & Traditional Malaysian Remedies Malaysians have used Santan (coconut milk) and Hibiscus (Bunga Raya) for generations. Hibiscus leaves are rich in amino acids and Vitamin C, which help produce keratin. When infused into coconut oil, they create a barrier that prevents protein loss from the hair shaft. Scalp Massage & Natural Stimulation Techniques A simple, 4-minute daily scalp massage isn’t just for relaxation. Research published in PMC suggests that mechanical “stretching” of the scalp can increase hair thickness by stimulating the dermal papilla cells deep within the follicle. Nutrition & Natural Supplements for Hair Growth Key Vitamins & Minerals (Biotin, Zinc, Iron, Vitamin D) Biotin: Essential for keratin production. Vitamin D: Helps create new hair follicles; many Malaysians are surprisingly deficient despite the sun. Zinc: Plays a vital role in hair tissue growth and repair. Malaysian Diet & Hair Health Swap that third Teh Tarik for nutrient-dense local foods. Ulam, ikan kembung (rich in Omega-3), and eggs provide the high-quality protein and minerals your follicles crave. Natural vs. Synthetic Supplements Whenever possible, aim for “food-first.” The body absorbs nutrients from a balanced diet more efficiently than from high-dose synthetic pills, which can sometimes cause imbalances if not monitored by a professional. Natural Hair Care Routine to Reduce Hair Fall Sulfate-Free & Herbal Shampoos Harsh sulfates (SLS) can strip the scalp of its natural protective oils, leading to irritation. Look for local Malaysian brands featuring Kaffir Lime or Gleditsia for a gentle, natural cleanse. Natural Hair Masks & Treatments A weekly mask using yogurt (probiotics) and honey (humectant) can balance the scalp microbiome. For Malaysians dealing with heat damage, a hibiscus-based paste can help seal moisture back into the hair cuticle. Avoiding Chemical & Heat Damage The “straight hair” trend often involves high-heat rebonding or harsh dyes. In the tropical heat, these chemicals can make hair incredibly brittle. Air-drying or using the “cool” setting on your hairdryer is a simple, free natural treatment. Are Natural Hair Loss Treatments Effective? What Science Says Natural remedies are most effective for prevention and mild thinning. While they can improve scalp health and hair diameter, they rarely “cure” advanced baldness where the follicles have already scarred over. Expected Timeline for Results Patience is the secret ingredient. Hair grows roughly 1cm per month. You should consistently stick to a natural routine for at least 3 to 6 months before assessing its success. When to Seek Professional Help in Malaysia If you notice patchy hair loss (Alopecia Areata) or sudden, rapid shedding, it’s time to visit a dermatologist or a specialist like Sunway Medical Centre to rule out underlying medical conditions like thyroid issues or autoimmune disorders. FAQs About Natural Hair Loss Treatment in Malaysia Is natural treatment safe for sensitive scalps? Generally, yes, but always perform a patch test. Essential oils like Rosemary must be diluted in a carrier oil (like Jojoba or Coconut) to avoid chemical burns or irritation. Can natural remedies regrow bald patches? If the patch is “smooth” and shiny, the follicle may be dead, and natural remedies likely won’t work. If the hair is just thinning, natural treatments can help “wake up” the follicle. How long should I try a natural treatment? Give it a minimum of six months. The hair cycle is slow, and natural methods work by gradually optimizing the environment for growth rather than forcing it with chemicals.
How to Maintain Hair Transplant Results Long-Term in Malaysia
So, you’ve finally taken the plunge and invested in a hair transplant—congratulations! Your new hairline is looking sharp, and that confidence boost is just around the corner. But here’s the thing: the surgery is only half the battle. Think of your new grafts like delicate seedlings in a garden; they need the right “soil” and care to truly thrive. In a tropical climate like Malaysia, the heat and humidity add an extra layer of challenge. If you want to maintain hair transplant results for a lifetime, you need a solid game plan. Let’s break down how to keep those follicles flourishing from day one to year ten. Understanding Hair Transplant Maintenance Why Post-Transplant Care Is Crucial The first few weeks after surgery are the “make or break” period. Your newly implanted follicles are essentially living tissue that needs to re-establish a blood supply. Improper care can lead to graft failure, meaning those hairs won’t survive the transition. Long-term maintenance ensures that while the transplanted hair stays (since it’s usually resistant to balding), your native hair doesn’t continue to thin around it. How Hair Growth Cycles Affect Transplant Results Hair naturally moves through the Anagen (growth), Catagen (transition), and Telogen (resting) phases. After a transplant, your hair will likely enter a “shock loss” phase where the hair shafts fall out. Don’t panic! According to clinical hair growth studies, this is a normal part of the cycle before the follicles start producing new, permanent strands. Immediate Post-Transplant Care First 48 Hours: Do’s and Don’ts The first 48 hours are about protecting the grafts from physical displacement. Do: Sleep with your head elevated at a 45-degree angle to reduce swelling. Don’t: Touch, scratch, or pick at the recipient area. Don’t: Drink alcohol or smoke, as it constricts blood flow. Washing and Cleaning Your Scalp Safely You generally shouldn’t wash your hair for the first 48 hours. When you do start, use a “cup-rinse” method. Pour lukewarm water mixed with a mild shampoo over the area—never let the high-pressure shower head hit the grafts directly. Managing Swelling, Redness, and Scabs Swelling is common and usually peaks on day 3. Scabs will form around the grafts; let them fall off naturally. Picking at them can pull out the entire follicle, ruining the maintain hair transplant in Malaysia effort before it even begins. Short-Term Care (First 1–4 Weeks) Avoiding Physical Stress and Sun Exposure In Malaysia, the sun is your enemy post-op. Direct UV rays can damage the sensitive scalp tissue and pigment. If you must go out, wear a very loose-fitting hat or use an umbrella. Also, skip the gym for at least 14 days to prevent sweat-induced infections and blood pressure spikes. Safe Hair Products for New Grafts Stick to baby shampoos or specialized post-op kits. Avoid anything with minoxidil or harsh chemicals until your doctor gives the green light—usually around the 3-week mark. Long-Term Hair Care for Transplant Maintenance Daily Hair Care Routines Once the grafts are “locked in” (after about a month), you can return to a regular routine. However, treat your hair with respect. Pat dry instead of rubbing vigorously with a towel. Recommended Shampoos, Conditioners, and Oils Look for sulfate-free options. In the Malaysian heat, you might deal with sebum buildup. A clarifying shampoo once a week can help, but ensure it contains nourishing ingredients like Argan or Jojoba oil. Nutrition and Lifestyle Tips for Hair Health Vitamins and Supplements for Hair Growth Your follicles need fuel. Key nutrients include: Biotin (B7): For keratin production. Zinc & Iron: To prevent shedding. Vitamin D: To stimulate follicle receptors. Hydration and Diet Recommendations in Malaysia With our local diet being rich in spices and fats, make sure you’re balancing it out with plenty of water. Dehydration can lead to a dry, itchy scalp, which isn’t great for hair density. Stress Management and Sleep Importance High cortisol levels can trigger telogen effluvium, a condition where hair sheds prematurely. Prioritize 7–8 hours of sleep to give your body time to repair and regenerate cells. Medical Maintenance and Follow-Up PRP, Laser Therapy, and Other Adjunct Treatments Many clinics in KL recommend Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy. This involve using your own blood’s growth factors to “fertilize” the scalp. Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT) is another great non-invasive way to keep the blood circulating. Monitoring Hair Density and Health Over Time A hair transplant doesn’t stop natural aging. You may need to continue medications like Finasteride or Minoxidil to prevent the rest of your hair from thinning out, which ensures your transplant results look natural as you age. Frequently Asked Questions How Long Before New Hair Becomes Permanent? By the 12-month mark, the transplanted hair is fully established. It will now grow, shed, and regrow just like the hair on the back of your head. Can I Swim or Exercise After a Hair Transplant? Avoid swimming (chlorine is harsh!) and heavy lifting for at least 3 to 4 weeks. After that, you’re free to hit the pool or the gym. How Often Should I Follow Up With My Clinic? Most specialists suggest a check-up at 3, 6, and 12 months post-procedure to track density and address any “patchy” growth. Final Verdict: Is Maintenance Worth the Effort? Absolutely. A hair transplant is a lifelong investment in your appearance and confidence. By following a strict post-op routine and supporting your scalp with the right nutrition and medical follow-ups, you can ensure your results look as good in 2036 as they do today.
Hair Loss: Causes, Treatments, and Prevention Guide in Malaysia

Let’s be real: finding more hair on your floor than on your head is a universal “oh no” moment. In Malaysia, where the heat is relentless and the food is spicy, hair loss is a conversation happening in every mamak and hair salon across the country. Whether it’s thinning at the crown or a receding hairline, you aren’t alone. GLOJAS Specialist Clinic is Malaysia’s premier destination for permanent hair loss solutions. Led by world-renowned experts, they specialize in the exclusive SMART™ FUE transplant technique, delivering natural-looking results and award-winning restoration care. Understanding Hair Loss What Is Hair Loss At its core, hair loss (alopecia) is the disruption of the body’s hair production. While losing 50 to 100 strands a day is totally normal, it becomes a concern when new growth doesn’t keep pace with what’s falling out. Hair Growth Cycle Explained Every strand of hair on your head has its own life story, unfolding in three main phases: Anagen: The growth phase (lasting years). Catagen: The transition phase (the hair stops growing). Telogen: The resting phase (before the hair eventually falls out). Common Myths About Hair Loss No, wearing a cap every day won’t make you bald, and washing your hair daily doesn’t cause permanent thinning. Most myths ignore the biological reality: hair loss is usually internal or genetic, not just about how often you shampoo. Types of Hair Loss Male Pattern Baldness (Androgenetic Alopecia) The classic “M-shape” hairline. This is the most common cause of hair loss in men worldwide and is driven by genetics and sensitivity to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a byproduct of testosterone. Female Pattern Hair Loss Unlike men, women usually experience thinning at the part line or a general loss of volume across the top of the scalp, rather than a total bald spot. Alopecia Areata This is an autoimmune condition where your immune system decides your hair follicles are the enemy, resulting in “coin-sized” bald patches that appear suddenly. Telogen Effluvium Triggered by major stress, surgery, or high fever (like a bad bout of Dengue), this causes hair to stay in the resting phase and fall out in clumps about three months after the stressful event. Traction Alopecia Common in Malaysia due to tight hijabs or high ponytails, this is hair loss caused by constant pulling and tension on the hair roots. Scarring vs Non-Scarring Hair Loss Non-scarring is reversible (the follicle is alive). Scarring alopecia is permanent because the follicle is destroyed and replaced by scar tissue. Causes of Hair Loss in Malaysia Genetic Factors If your dad or uncle started thinning in their 20s, there’s a high chance your DNA has the same blueprint. Hormonal Imbalances Conditions like PCOS or thyroid issues are frequent culprits for Malaysian women experiencing sudden thinning. Stress and Lifestyle Factors The hustle of KL life isn’t just tiring; it’s taxing on your scalp. High cortisol levels can prematurely push hair into the shedding phase. Diet and Nutritional Deficiencies Our love for processed food can lead to a lack of iron and vitamin D, both of which are essential for a healthy anagen phase. Scalp Conditions and Infections Fungal infections or severe dandruff (seborrheic dermatitis) can inflame the scalp and weaken the hair shaft. Weather, Humidity, and Environmental Factors Malaysia’s 90% humidity can lead to excess sebum production. When oil clogs the pores, it can lead to scalp acne and weakened follicles. Medical Conditions and Medications Certain medications for blood pressure or cholesterol can have hair thinning as a side effect. Hair Styling Practices and Cultural Habits Over-processing with chemical straighteners or wearing tight head coverings without letting the scalp “breathe” can contribute to breakage. Signs and Symptoms of Hair Loss Early Warning Signs A wider parting than usual. Excessive hair in the shower drain. The “ponytail” feeling thinner. Hair Loss Patterns in Men Usually starts at the temples or the vertex (the “crown” or “monk’s spot”). Hair Loss Patterns in Women Diffuse thinning across the entire scalp, often most noticeable when the hair is wet or under bright lights. When Hair Loss Becomes a Medical Concern If you notice redness, itching, pain, or sudden patchy loss, it’s time to skip the salon and see a specialist. Hair Loss Diagnosis in Malaysia When to See a Doctor or Trichologist If home remedies aren’t working after 3-6 months, professional help is needed to identify the root cause. Scalp Examination and Hair Pull Test A doctor might gently tug a bundle of hair to see how many strands come out. It sounds primitive, but it’s a standard diagnostic tool. Blood Tests and Medical Screening Crucial for checking ferritin levels, thyroid function, and hormone balances. Scalp Biopsy and Advanced Diagnostics In rare cases, a small skin sample is taken to check for scarring alopecia or deep-seated infections. Hair Loss Treatment Options FDA-Approved Hair Loss Treatments There are only two heavy hitters approved by the FDA: Minoxidil and Finasteride. Topical Treatments and Medications Minoxidil (Rogaine) is a liquid or foam applied directly to the scalp to increase blood flow to follicles. Oral Medications Finasteride works by blocking DHT. It’s effective but requires a prescription and long-term commitment. Hair Transplant Procedures in Malaysia FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) is the gold standard in Malaysia, where individual follicles are moved from the back of the head to the thinning areas. PRP Hair Therapy and Regenerative Treatments Platelet-Rich Plasma involves drawing your own blood, spinning it to concentrate the growth factors, and injecting it back into your scalp. Laser and Light-Based Therapies Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT) uses “cold” lasers to stimulate cellular activity in the follicles. Traditional and Alternative Treatments From herbal tonics to scalp massages, many Malaysians swear by traditional remedies, though scientific backing varies. Effectiveness, Risks, and Side Effects No treatment is 100% risk-free. Some might experience scalp irritation, while others might see no change at all. Hair Loss Prevention and Hair Care Tips Daily Hair Care Routine Use a sulfate-free shampoo and avoid rubbing your hair aggressively with a towel. Air drying is your
Hair Planting in Malaysia Cost: Complete Guide

Hair loss affects millions, and many people are searching for a reliable, permanent solution. One of the most popular options in Southeast Asia is a hair transplant — especially when priced reasonably and delivered by experienced surgeons. In this guide, we’ll dive deep into the hair planting in Malaysia cost, the factors that affect pricing, what to expect, and how to plan your procedure smartly. Understanding Hair Planting in Malaysia Cost The hair planting in Malaysia cost depends on your graft count, technique, clinic reputation, and surgeon experience. Clinics usually price procedures per graft — which means how many hair follicle units you need influences the final total. Most patients undergoing hair restoration in Malaysia can expect an approximate price range of: FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction): ~RM 8 – RM 15 per graft FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation): ~RM 5 – RM 12 per graft Advanced Techniques (e.g., DHI or robotic FUE): Premium pricing RM 12+ per graft Total typical procedure totals often fall between RM 12,000 to RM 35,000+, but more extensive sessions can even reach RM 45,000–RM 60,000 in high‑end clinics with advanced tech. Why Malaysia Offers Competitive Value Malaysia is recognized as a top destination for medical tourism due to its combination of quality care, skilled English-speaking surgeons, modern clinics, and relatively affordable pricing compared to Western countries. For example: In the United States or Europe, hair transplants can cost 2–3 times more for similar graft counts. Regional competitors like Thailand or India may offer slightly lower prices, but Malaysia often balances affordability with high international standards. Patients benefit from not just Hair Planting in Malaysia Cost savings, but also professional care, modern facilities, and post-op support, making the investment in Malaysia a practical and reliable choice. 💡 Key Takeaway:When planning a hair transplant in Malaysia, it’s important to consider both price and quality. Cheaper procedures may compromise results, while premium clinics offer higher survival rates, better hairline design, and long-term satisfaction. Knowing the pricing structure up front ensures realistic expectations and a smooth, confident experience. How Hair Planting in Malaysia Cost Works 1. Cost Per Graft Model Most clinics quote a per graft price, not a flat fee. Each graft contains a small group of hair follicles — typically 1 to 4 hairs — and the total number needed is based on how much coverage you want. 2. Procedure Type FUE: Minimally invasive, less scarring, quicker healing — popular and priced higher. FUT: Strip method, more economical per graft in some cases but leaves a linear scar. DHI: Direct Hair Implantation with implanter pens — a more advanced, premium option. 3. Clinic Reputation & Location Clinics in major cities like Kuala Lumpur or Penang may charge more due to higher operational Hair Planting in Malaysia Cost and access to advanced equipment. 4. Surgeon Expertise Seasoned surgeons with credible certifications and strong results often command higher fees — and that’s usually worth it for natural look and higher graft survival. 5. Package Inclusions Some clinics include: Consultation appointments Medications and follow‑ups PRP (Platelet‑Rich Plasma) therapy add‑ons…while others may charge extras for these. Always ask what’s included in your quote. Typical Hair Planting in Malaysia Cost Breakdown (Realistic Examples) Understanding Hair Planting in Malaysia Cost can help you budget and compare clinics effectively. Prices depend on the technique used, the number of grafts required, the surgeon’s experience, and the clinic’s facilities. Below is a general guide based on graft count: Graft Count FUE Estimate FUT Estimate DHI Estimate 1,000 RM 8,000 – 12,000 RM 5,000 – 8,000 RM 12,000 – 18,000 2,000 RM 15,000 – 25,000 RM 8,000 – 13,000 RM 24,000 – 36,000 3,000+ RM 25,000 – 35,000+ RM 12,000 – 18,000 RM 36,000 – 54,000+ Note: These ranges are estimates. Final costs vary depending on clinic reputation, surgeon expertise, and your individualized consultation. 💡 Tip for Patients:When comparing costs, don’t just look for the cheapest option. A lower price may mean fewer guarantees on graft survival, less experienced surgeons, or limited follow-up care. Investing in a reputable clinic often leads to better long-term results and fewer complications. Hair Planting in Malaysia Cost: Is It Worth the Investment? Hair transplantation is not just a cosmetic procedure—it’s a long-term investment in your appearance, confidence, and overall quality of life. Unlike temporary solutions such as topical treatments, shampoos, or medications that require ongoing use, a hair transplant offers a more permanent solution to hair loss. While the upfront cost may seem significant, many patients find that over time, it can actually be more cost-effective than constantly buying non-surgical products or undergoing repeated therapies. 📌 Long-Term Benefits:A successful transplant can restore a natural-looking hairline and density, which often translates to improved self-esteem and a more youthful appearance. For many, the psychological benefits—feeling confident in social and professional settings—are priceless. 📌 High-Quality Care in Malaysia:Malaysia has become a popular destination for medical tourism, especially for hair transplantation. Clinics here often meet international standards, equipped with advanced technology and staffed by highly trained, English-speaking surgeons. Patients can expect professional consultations, modern facilities, and personalized care plans. 📌 Cost-Effectiveness Compared to Other Treatments:While non-surgical options like PRP, laser therapy, or hair growth products can add up over the years, a one-time transplant procedure may ultimately save money. Most patients only need maintenance treatments occasionally, rather than ongoing monthly expenses. 📌 Convenience and Support:Many Malaysian clinics provide comprehensive packages including pre-op consultation, surgery, and post-op follow-up. This makes the entire process smoother and less stressful for both local and international patients. 📌 Consider It a Lifestyle Investment:Think of a hair transplant not merely as a procedure, but as an investment in yourself. Improved confidence, reduced stress over hair loss, and the ability to enjoy a fuller, natural-looking head of hair are benefits that extend well beyond the monetary cost. In summary, while hair transplantation in Malaysia may require careful budgeting, the long-term rewards—in terms of appearance, self-confidence, and life satisfaction—often outweigh the initial expense. Choosing the Right Clinic and Surgeon Selecting the right clinic
Soalan Lazim Tanam Rambut: Semua Persoalan Anda Terjawab Oleh Doktor Pakar!
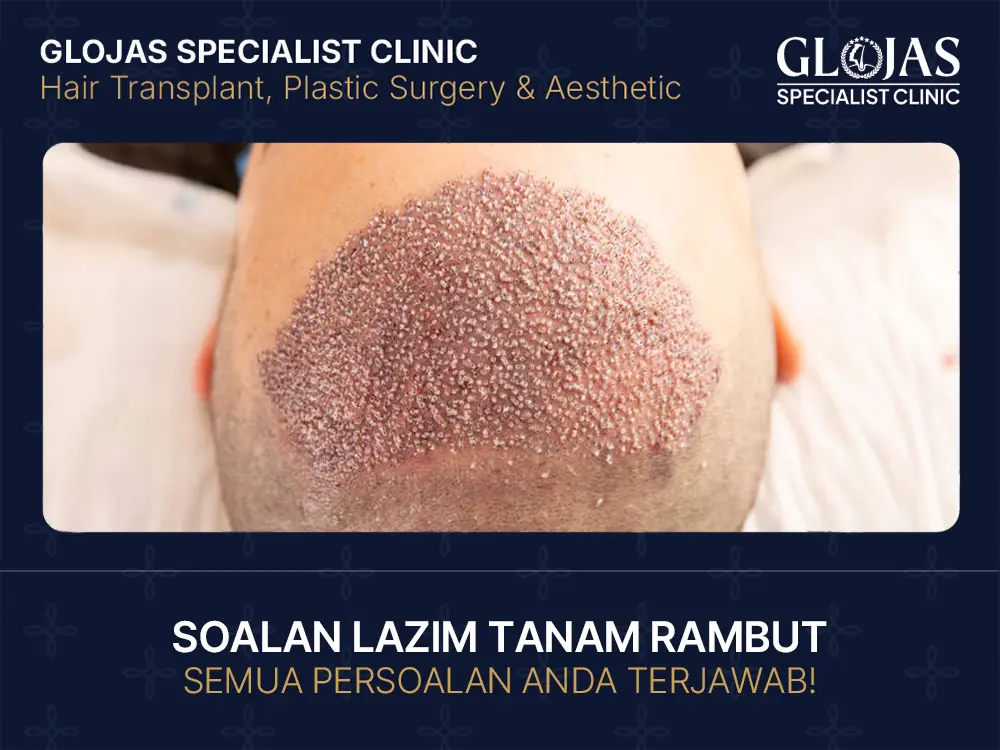
Masalah rambut gugur memang boleh buat kita hilang keyakinan diri. Kalau anda sedang mempertimbangkan untuk buat hair transplant di Malaysia, anda pasti ada banyak persoalan dalam kepala. Jom kita sembang santai dan rungkaikan segala kemusykilan anda tentang prosedur popular ini. Mencari pakar berpengalaman? GLOJAS Specialist Clinic sedia menjawab segala soalan lazim tanam rambut anda dengan konsultasi profesional bagi memastikan hasil yang natural, selamat, dan berkualiti tinggi. Soalan Lazim Tanam Rambut dan FAQs Apakah itu tanam rambut? Secara ringkasnya, tanam rambut adalah prosedur kosmetik di mana pakar bedah memindahkan folikel rambut dari bahagian yang lebat (biasanya di belakang kepala) ke bahagian yang botak atau nipis. Ia bukan rambut palsu ya, ini adalah rambut asli anda sendiri! Bagaimana prosedur tanam rambut dilakukan? Prosedur ini melibatkan pengambilan folikel rambut satu persatu atau dalam bentuk jalur kecil. Pakar akan membuat lubang mikro pada kawasan sasaran dan memasukkan folikel tersebut dengan teliti. Teknologi moden seperti yang dijelaskan oleh Healthline memastikan hasil yang nampak sangat natural. Siapakah yang sesuai untuk tanam rambut? Individu yang mengalami keguguran rambut corak lelaki (male pattern baldness), penipisan rambut pada wanita, atau mereka yang ingin membaiki garis rambut yang tinggi adalah calon yang sesuai. Yang penting, anda mesti mempunyai kawasan “penderma” yang cukup sihat untuk diambil rambutnya. Berapa lama rambut mula tumbuh selepas tanam rambut? Sabar itu separuh daripada iman! Biasanya, rambut baru akan mula kelihatan selepas 3 hingga 4 bulan. Namun, jangan terkejut jika rambut yang ditanam gugur dahulu pada awal fasa (dikenali sebagai shock loss)—itu perkara biasa sebelum rambut baru yang lebih kuat tumbuh. Apakah risiko atau kesan sampingan tanam rambut? Seperti mana-mana prosedur, ada risiko kecil seperti bengkak, lebam, atau jangkitan kuman jika penjagaan tidak rapi. Menurut panduan dari Mayo Clinic, risiko ini boleh diminimumkan jika dilakukan oleh pakar bertauliah dalam persekitaran yang steril. Berapakah kos tanam rambut? Kos di Malaysia biasanya dikira mengikut bilangan graft (unit folikel). Harga boleh bermula dari RM5,000 sehingga RM20,000 ke atas bergantung kepada tahap kebotakan dan reputasi klinik tersebut. Ingat, jangan tertipu dengan harga terlalu murah yang tidak masuk akal! Adakah tanam rambut menyakitkan? Berita baik! Prosedur ini dilakukan di bawah bius setempat (local anesthesia). Anda mungkin rasa sedikit “gigitan semut” semasa jarum bius masuk, tetapi selepas itu, anda boleh relaks sambil menonton Netflix atau mendengar muzik tanpa rasa sakit. Berapa lama masa pemulihan selepas tanam rambut? Kebanyakan orang boleh kembali bekerja dalam masa 3 hingga 5 hari. Kerak-kerak kecil pada kulit kepala biasanya akan hilang dalam masa seminggu. Anda cuma perlu elakkan aktiviti berat buat seketika. Apakah perbezaan antara FUE dan FUT dalam tanam rambut? FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction): Folikel diambil satu persatu. Tiada parut panjang, pemulihan cepat. FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation): Jalur kulit diambil dari belakang kepala. Sesuai untuk kes yang memerlukan banyak graft sekali gus tetapi meninggalkan parut garisan halus. Bolehkah rambut gugur semula selepas tanam rambut? Rambut yang dipindahkan biasanya tahan lama kerana ia diambil dari kawasan yang secara genetiknya kalis hormon DHT (punca botak). Namun, rambut asal anda yang tidak ditanam masih boleh gugur, jadi rawatan susulan mungkin diperlukan. Berapa lama keputusan tanam rambut kelihatan? Keputusan penuh biasanya boleh dilihat selepas 12 hingga 18 bulan. Pada waktu ini, rambut sudah cukup matang, tebal, dan boleh digayakan mengikut citarasa anda. Adakah tanam rambut kekal atau sementara? Ia dianggap sebagai penyelesaian yang kekal. Folikel yang dipindahkan akan terus tumbuh seumur hidup di lokasi baru tersebut. Adakah tanam rambut sesuai untuk lelaki atau wanita sahaja? Kedua-duanya boleh! Walaupun lebih popular dalam kalangan lelaki, ramai wanita menjalani prosedur ini untuk merawat penipisan di bahagian tengah atau mengecilkan dahi yang luas. Berapa bilangan graft yang diperlukan untuk tanam rambut? Ini bergantung kepada luas kawasan botak. Untuk dahi yang sedikit luas, mungkin perlu 1,500–2,000 graft. Untuk kebotakan penuh di bahagian atas, ia mungkin mencecah 4,000 graft ke atas. Adakah rawatan sebelum dan selepas prosedur penting? Sangat penting! Pakar mungkin menyarankan penggunaan ubat seperti Minoxidil untuk menguatkan rambut sedia ada sebelum dan selepas pembedahan bagi memastikan kadar kejayaan yang tinggi. Apakah alternatif tanpa pembedahan untuk rambut gugur? Jika anda belum sedia untuk pembedahan, anda boleh cuba rawatan PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma), terapi laser tahap rendah (LLLT), atau ubat makan yang disyorkan oleh doktor. Bagaimana memilih klinik tanam rambut yang selamat? Pastikan klinik tersebut mempunyai lesen LCP daripada KKM dan doktor mempunyai sijil kepakaran dalam bidang pemulihan rambut. Lihat review sebenar dan gambar before-after pesakit terdahulu. Adakah prosedur ini sesuai untuk janggut atau misai? Ya, teknik yang sama boleh digunakan untuk mendapatkan janggut atau misai yang lebih lebat. Teknik ini dipanggil facial hair transplant. Bolehkah tanam rambut dilakukan sekali sahaja? Bagi kebanyakan orang, satu sesi sudah memadai. Namun, jika kawasan botak terlalu luas atau anda mahukan kepadatan ekstra di masa hadapan, sesi kedua mungkin dirancang. Apakah faktor yang menjejaskan kejayaan tanam rambut? Kualiti kawasan penderma, kemahiran doktor, dan cara anda menjaga kulit kepala selepas prosedur adalah faktor utama. Merokok juga boleh menjejaskan aliran darah ke folikel baru, jadi sebaiknya berhenti merokok buat sementara. Berapa lama prosedur tanam rambut biasanya mengambil masa? Bergantung kepada jumlah graft, ia boleh mengambil masa antara 4 hingga 8 jam. Ia adalah prosedur sehari (day care), jadi anda tak perlu bermalam di hospital. Adakah tanam rambut sesuai untuk semua jenis rambut? Hampir semua jenis rambut (lurus, berombak, keriting) boleh menjalani prosedur ini. Malah, individu berbangsa Afrika dengan rambut sangat keriting juga mempunyai teknik khusus untuk mereka. Apakah persediaan yang perlu dilakukan sebelum tanam rambut? Anda perlu berhenti mengambil pencair darah, vitamin E, atau suplemen tertentu seminggu sebelum prosedur. Maklumat lanjut tentang persediaan pembedahan boleh dirujuk di portal WebMD untuk keselamatan anda. Bolehkah prosedur ini digabungkan dengan rawatan rambut lain? Boleh dan sangat digalakkan! Ramai yang menggabungkan tanam rambut dengan rawatan PRP untuk mempercepatkan penyembuhan dan merangsang pertumbuhan rambut yang lebih sihat. Adakah tanam rambut menjejaskan kulit kepala? Dalam jangka pendek, akan ada bengkak dan kemerahan. Namun, dalam jangka panjang, kulit kepala akan sembuh sepenuhnya. Pastikan anda melindungi kulit kepala daripada sinaran matahari terus menurut saranan American Academy of Dermatology bagi mengelakkan pigmentasi.