7 Surprising Facts About Melanin and How Fractional CO2 Laser Affects It
Melanin is a crucial component of our skin, playing a significant role in determining skin color and protecting us from the harmful effects of UV radiation. However, melanin is not just about skin tone; it also affects various aspects of our health and appearance. In recent years, cosmetic procedures like the Fractional CO2 Laser have […]
How Long Does an FUE Hair Transplant Last? Is It Permanent?
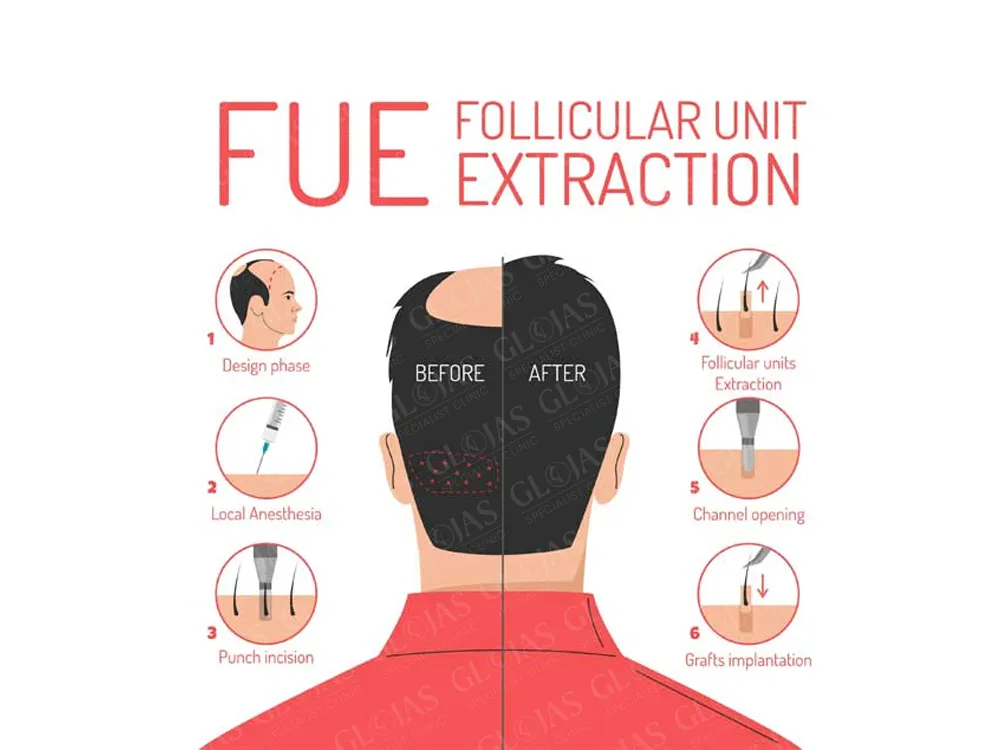
Hair loss can be a distressing experience for many individuals, impacting their confidence and self-esteem. As a solution, Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) hair transplants have gained popularity due to their minimally invasive nature and natural-looking results. However, one of the most pressing questions prospective patients have is, “How long does a FUE hair transplant last?” […]

